1.简写单词
题目链接:简写单词_牛客题霸_牛客网

思路:利用scanf读取特性,因为scanf是以空格,换行或者文件末尾为结束标志。
代码:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char str[100] = {0};
while (scanf("%s", str) != EOF)
{
if (str[0] >= 'a' && str[0] <= 'z') str[0] -= 32;
printf("%c", str[0]);
}
return 0;
}
利用c++cin的特性也可以
// #include <iostream>
// using namespace std;
// int main()
// {
// string str;
// while (cin >> str)
// {
// if (str[0] >= 'a' && str[0] <= 'z') str[0] -= 32;
// printf("%c", str[0]);
// }
// return 0;
// }2.爱框框
题目链接: 登录—专业IT笔试面试备考平台_牛客网
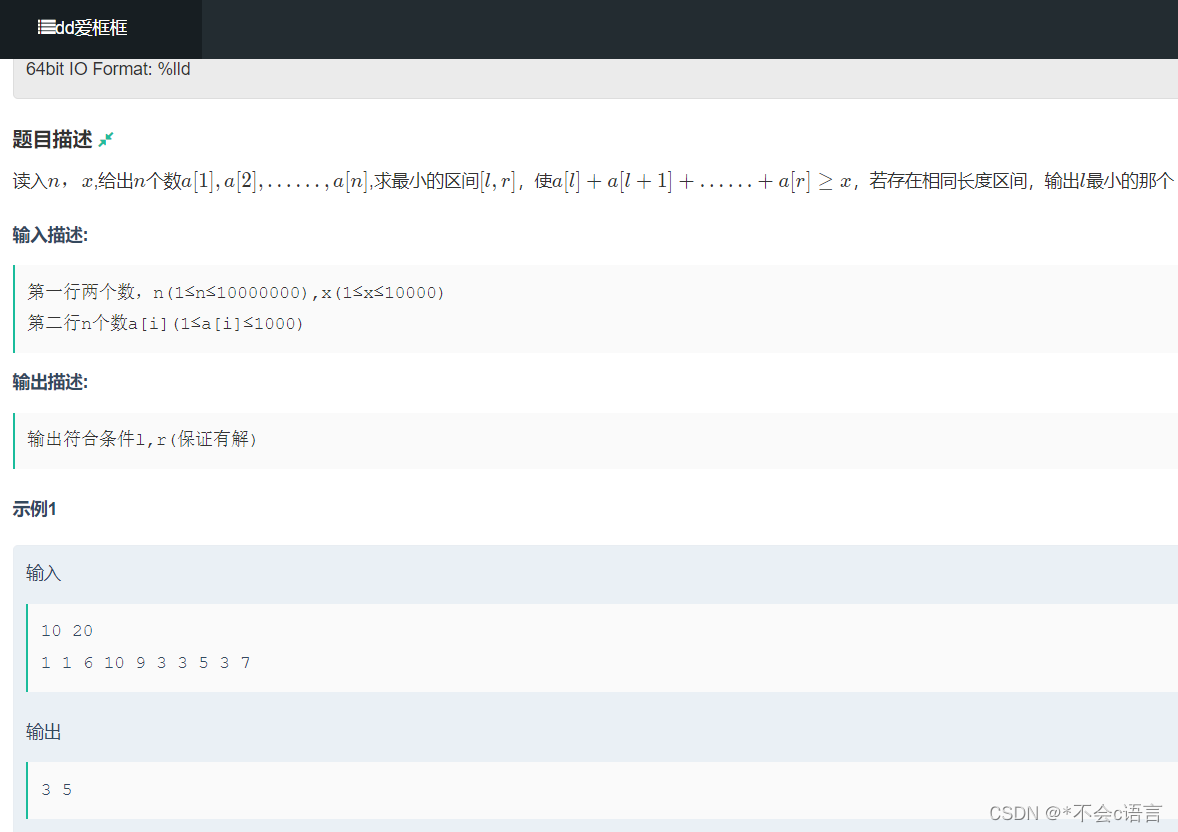
思路:可以先用暴力的思想,固定左端点和右端点,发现时间复杂度是O(N^2),但这道题的数据量是10^7,所以要优化成O(N),接着看题目给出的要求,a[i]是大于0的,所以用滑动窗口来优化暴力解法。
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;//别忘记写
int n, x;
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d", &n, &x);
int l = 1, r = 1, ret1 = -1, ret2 = -1, leng = 0x3f3f3f3f, sum = 0;
vector<int> arr(n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
cin >> arr[i];
while (r <= n)
{
sum += arr[r];
while (sum >= x && l <= r)//当l==r==n且sum >= x时,l++可能有越界的风险
{
if (r - l < leng)
{
leng = r -l;
ret1 = l;
ret2 = r;
}
sum -= arr[l];
l++;
}
r++;
}
cout << ret1 << ' ' << ret2;
return 0;
}经典的滑动窗口问题的一般解法:1.进窗口,2.判断,3./4.出窗口,4./3.更新结果。
3.除2!
题目链接:登录—专业IT笔试面试备考平台_牛客网
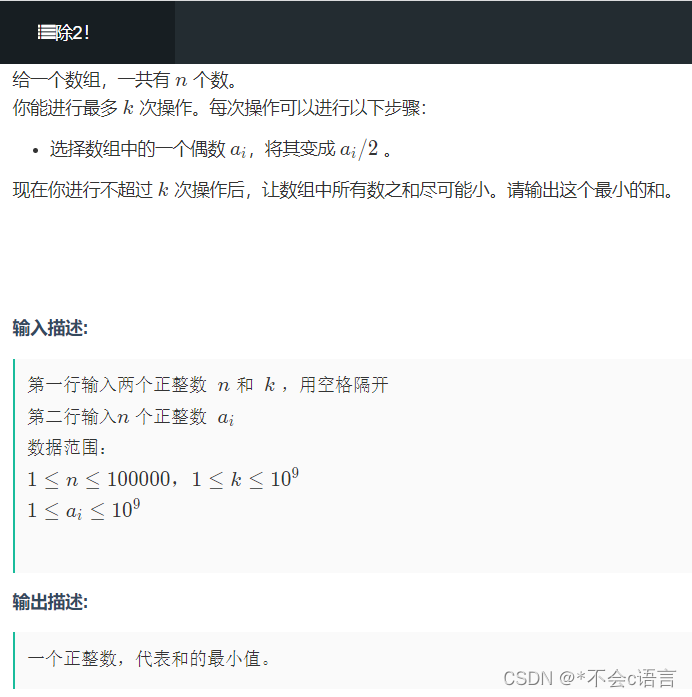
思路:那必然是操作最大的偶数/2,所以我们要用到堆。
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
int n, k;
const int N = 1e5 + 1;
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d", &n, &k);
priority_queue<int> heap;
long long sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
int x;
cin >> x;
sum += x;
if (x % 2 == 0) heap.push(x);
}
while (heap.size() != 0 && k--)
{
int t = heap.top() / 2;
heap.pop();
sum -= t;
if (t % 2 == 0) heap.push(t);
}
cout << sum;
return 0;
}