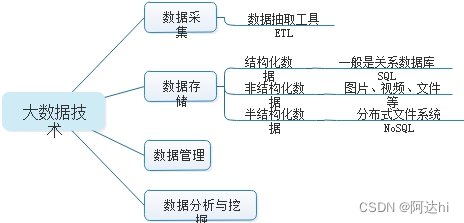
目录
一、基本类型原子类
二、数组类型原子类
三、引用类型原子类
四、对象的属性修改类型原子类
五、原子操作增强类
5.1、高性能热点商品应用
5.2、LongAdder架构图
5.3、源码分析
一、基本类型原子类
public class AtomicTest1 {
public static final int SIZE = 50;
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
MyAtomic myAtomic = new MyAtomic();
CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(SIZE);
for (int i = 1; i <= SIZE ; i++) {
new Thread(()->{
try {
for (int j = 1; j <= 1000 ; j++) {
myAtomic.add();
}
} finally {
countDownLatch.countDown();
}
},String.valueOf(i)).start();
}
//等待五十个线程全部计算完,获取结果
countDownLatch.await();
System.out.println("计算结果为:"+myAtomic.atomicInteger.get());
}
}
class MyAtomic{
AtomicInteger atomicInteger = new AtomicInteger();
public void add(){
atomicInteger.getAndIncrement();
}
}二、数组类型原子类
public class AtomicTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AtomicIntegerArray array = new AtomicIntegerArray(new int[]{1, 2, 3, 4});
for (int i = 0; i <array.length() ; i++) {
System.out.println(array.get(i));
}
}
}
三、引用类型原子类
public class AtomicTest3 {
static AtomicMarkableReference markableReference = new AtomicMarkableReference(100,false);
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(()->{
boolean marked = markableReference.isMarked();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + marked);
try {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
markableReference.weakCompareAndSet(100, 101, marked, !marked);
},"A").start();
new Thread(()->{
boolean marked = markableReference.isMarked();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + marked);
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
boolean b = markableReference.weakCompareAndSet(100, 102, marked, !marked);
System.out.println(b+"\t"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t"+markableReference.isMarked());
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t"+markableReference.getReference());
},"B").start();
}
}四、对象的属性修改类型原子类
1、使用目的:以一种线程安全的方式操作非线程安全对象内的某些字段
2、使用对象:①、更新对象属性必须使用public volatile修饰符。②、因为对象的属性修改类型原子类都是抽象类,所以每次使用都必须使用静态方法newUpdater()创建一个更新器,并且需要设置想要更新的类和属性。
public class AtomicTest4 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Bank bank = new Bank();
CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(10);
for (int i = 1; i <=10 ; i++) {
new Thread(()->{
try {
for (int j = 1; j <=1000 ; j++) {
bank.add(bank);
}
} finally {
countDownLatch.countDown();
}
},String.valueOf(i)).start();
}
countDownLatch.await();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() +"\t"+ bank.money);
}
}
class Bank{
String bankName = "NTM";
public volatile int money = 0;
AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater fieldUpdater = AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater.newUpdater(Bank.class,"money");
public void add(Bank bank){
fieldUpdater.getAndIncrement(bank);
}
}五、原子操作增强类
public class volatiles1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LongAdder longAdder = new LongAdder();
longAdder.increment();
longAdder.increment();
longAdder.increment();
System.out.println(longAdder.sum());//4
LongAccumulator longAccumulator = new LongAccumulator((x,y) -> x + y,0);
longAccumulator.accumulate(1);//1
longAccumulator.accumulate(3);//4
System.out.println(longAccumulator.get());
}
}
LongAdder只能用来计算加法,且从零开始计算
LongAccumulato提供了自定义的函数操作。
5.1、高性能热点商品应用
public class volatiles2 {
public static final int threadNum = 50;
public static final int W = 10000;
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
long startTime;
long endTime;
Num num = new Num();
CountDownLatch countDownLatch1 = new CountDownLatch(threadNum);
CountDownLatch countDownLatch2 = new CountDownLatch(threadNum);
CountDownLatch countDownLatch3 = new CountDownLatch(threadNum);
CountDownLatch countDownLatch4 = new CountDownLatch(threadNum);
startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 1; i <=threadNum ; i++) {
new Thread(()->{
try {
for (int j = 1; j <= 100 * W ; j++) {
num.getSynchronizedSum();
}
} finally {
countDownLatch1.countDown();
}
},String.valueOf(i)).start();
}
countDownLatch1.await();
endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("共花费:" + (endTime - startTime) + "毫秒\t" + num.num);
startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 1; i <=threadNum ; i++) {
new Thread(()->{
try {
for (int j = 1; j <= 100 * W ; j++) {
num.getAtomicLongSum();
}
} finally {
countDownLatch2.countDown();
}
},String.valueOf(i)).start();
}
countDownLatch2.await();
endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("共花费:" + (endTime - startTime) + "毫秒\t" + num.getAtomicLong());
startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 1; i <=threadNum ; i++) {
new Thread(()->{
try {
for (int j = 1; j <= 100 * W ; j++) {
num.getLongAdderSum();
}
} finally {
countDownLatch3.countDown();
}
},String.valueOf(i)).start();
}
countDownLatch3.await();
endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("共花费:" + (endTime - startTime) + "毫秒\t" + num.getLongAdder());
startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 1; i <=threadNum ; i++) {
new Thread(()->{
try {
for (int j = 1; j <= 100 * W ; j++) {
num.getLongAccumulatorSum();
}
} finally {
countDownLatch4.countDown();
}
},String.valueOf(i)).start();
}
countDownLatch4.await();
endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("共花费:" + (endTime - startTime) + "毫秒\t" + num.getLongAccumulator());
}
}
class Num{
int num = 0;
public synchronized void getSynchronizedSum(){
num++;
}
AtomicLong atomicLong = new AtomicLong(0);
public void getAtomicLongSum(){
atomicLong.getAndIncrement();
}
public long getAtomicLong(){
return atomicLong.get();
}
LongAdder longAdder = new LongAdder();
public void getLongAdderSum(){
longAdder.increment();
}
public long getLongAdder(){
return longAdder.sum();
}
LongAccumulator longAccumulator = new LongAccumulator((x,y)->x+y,0);
public void getLongAccumulatorSum(){
longAccumulator.accumulate(1);
}
public long getLongAccumulator(){
return longAccumulator.get();
}
}
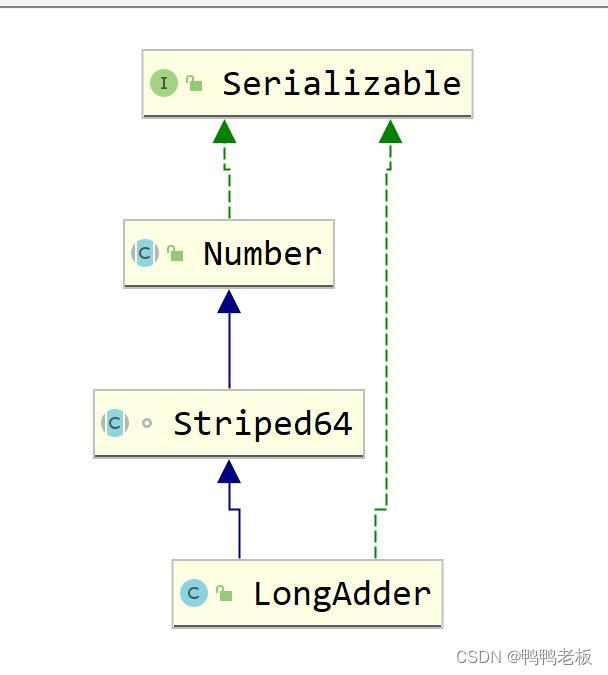
5.2、LongAdder架构图
原理:Striped64中一些变量及方法
base:类似于AtomicLong中全局的value值。在没有竞争情况下数据直接累加到base上,或者calls扩容时,也需要将数据写入到base上
collide:表示扩容意向,false一定不会扩容,true可能会扩容。
cellsBusy:初始化cells或者扩容cells需要获取锁,0表示无锁状态,1:表示其他线程已经持有了锁。
casCellsBusy():通过CAS操作修改cellsBusy的值,CAS成功代表获取锁,返回true
NCPU:当前计算机CPU数量,Cell数组扩容时会使用到
getProbe();获取当前线程的hash值
advanceProbe():重置当前线程的hash值。
LongAdder的基本思路就是分散热点,将value值分散到到一个Call数组中,不同线程会命中到数组的不同槽中,各个线程只对自己槽中的那个值进行CAS操作,这样热点就被分散了,冲突的概率就小很多。如果要获取真正的long值,只要将各个槽中的变量值累加返回。
sum()会将所有Cell数组中的value和base累加作为返回值,核心的思想就是将之前AtomicLong一个value的更新压力分散到多个value中去,从而降低更新热点。
5.3、源码分析

as:表示cells引用
b:表示获取的base值
v:表示cells数组的长度
m:表示cells数组的长度
a:表示当前线程命中的cell单元格
public void add(long x) {
Cell[] as; long b, v; int m; Cell a;
//首次首线程(as = cells != null)一定是false,此时走casBase方法,以CAS的方式更新base值,
且只有当cas失败时,才会走到if中
//条件1:cells不为空
//条件2:cas操作base失败,说明其它线程先一步修改了base正在出现竞争
if ((as = cells) != null || !casBase(b = base, b + x)) {
//true无竞争 false表示竞争激烈,多个线程hash到同一个cell,可能要扩容
boolean uncontended = true;
//条件1:cells为空
//条件2:应该不会出现
//条件3:当前线程所在的cell为空,说明当前线程还没有更新过cell,应该初始化一个cell
//条件4:更新当前线程所在的cell失败,说明现在竞争很激烈,多个线程hash到了同一个cell,
应扩容
if (as == null || (m = as.length - 1) < 0 ||
//getProbe()方法返回线程的threadlocalRandomProbe字段
//它是通过随机数生成的一个值,对于一个确定的线程这个值是固定的
(a = as[getProbe() & m]) == null ||
!(uncontended = a.cas(v = a.value, v + x)))
longAccumulate(x, null, uncontended);//调用Striped64中的方法处理。
}
}1、最初无竞争时只更新base
2、如果更新base失败后,首次新建一个Cell[]数组
3、当多个线程竞争同一个Cell比较激烈时,可能就要对Cell[]扩容。
longAccumulate(long x, LongBinaryOperator fn, boolean wasUncontended)x:需要增加的值,一般默认都是1
fn:默认传递的是null
wasUncontended:竞争标识,如果是false则代表有竞争,只有cells初始化之后,并且当前线程CAS竞争修改失败,才会是false
final void longAccumulate(long x, LongBinaryOperator fn,
boolean wasUncontended) {
//存储线程的probe值
int h;
//如果getProbe()返回0,说明随机数未初始化
if ((h = getProbe()) == 0) {
//使用ThreadLocalRandom为当前线程重新计算一个hash值,强制初始化
ThreadLocalRandom.current(); // force initialization
//重新获取prode值,hash值被重置就好比一个全新的线程一样,所以设置了wasUncontended竞争状态为true
h = getProbe();
//重新计算了当前线程的hash后认为此次不算是一次竞争,都未初始化,肯定还不存在竞争激烈wasUncontended竞争状态为true
wasUncontended = true;
}
//如果hash取模映射得到的Cell单元不是null,则为true,此值也可以看作是扩容意向
boolean collide = false; // True if last slot nonempty
for (;;) {
Cell[] as; Cell a; int n; long v;
//cells已经被初始化了
if ((as = cells) != null && (n = as.length) > 0) {
if ((a = as[(n - 1) & h]) == null) {
if (cellsBusy == 0) { // Try to attach new Cell
Cell r = new Cell(x); // Optimistically create
if (cellsBusy == 0 && casCellsBusy()) {
boolean created = false;
try { // Recheck under lock
Cell[] rs; int m, j;
if ((rs = cells) != null &&
(m = rs.length) > 0 &&
rs[j = (m - 1) & h] == null) {
rs[j] = r;
created = true;
}
} finally {
cellsBusy = 0;
}
if (created)
break;
continue; // Slot is now non-empty
}
}
collide = false;
}
else if (!wasUncontended) // CAS already known to fail
wasUncontended = true; // Continue after rehash
else if (a.cas(v = a.value, ((fn == null) ? v + x :
fn.applyAsLong(v, x))))
break;
else if (n >= NCPU || cells != as)
collide = false; // At max size or stale
else if (!collide)
collide = true;
else if (cellsBusy == 0 && casCellsBusy()) {
try {
if (cells == as) { // Expand table unless stale
Cell[] rs = new Cell[n << 1];
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
rs[i] = as[i];
cells = rs;
}
} finally {
cellsBusy = 0;
}
collide = false;
continue; // Retry with expanded table
}
h = advanceProbe(h);
}
//cells没有加锁且没有初始化,则尝试对它进行加锁,并初始化cells数组
else if (cellsBusy == 0 && cells == as && casCellsBusy()) {
boolean init = false;
try { // Initialize table
if (cells == as) {
Cell[] rs = new Cell[2];
rs[h & 1] = new Cell(x);
cells = rs;
init = true;
}
} finally {
cellsBusy = 0;
}
if (init)
break;
}
//cells正在进行初始化,则尝试直接在基数base上进行累加操作
else if (casBase(v = base, ((fn == null) ? v + x :
fn.applyAsLong(v, x))))
break; // Fall back on using base
}
}
public long sum() {
Cell[] as = cells; Cell a;
long sum = base;
if (as != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < as.length; ++i) {
if ((a = as[i]) != null)
sum += a.value;
}
}
return sum;
}
sum方法将所有Cell数组中的value和base累加作为返回值
核心思想就是将之前AtomicLong一个value的更新压力分散到多个value中去,从而降级更新热点。