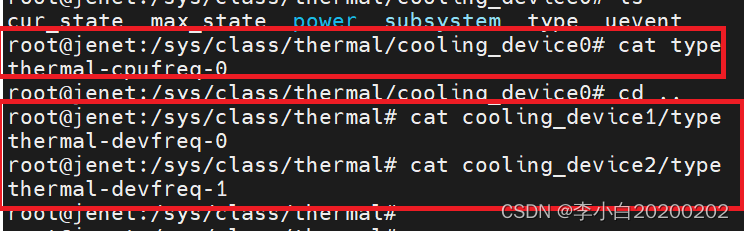
RK3568温控
cat /sys/class/thermal/thermal_zone0/temp
cat /sys/class/thermal/thermal_zone1/temp
cat /sys/class/thermal/cooling_device0/cur_state
cat /sys/class/thermal/cooling_device1/cur_state
cat /sys/class/thermal/cooling_device2/cur_state
thermal_zone0:是soc的温度;
thermal_zone1: 是gpu的温度。

冷却设备有三个:
功能介绍
Linux的Thermal机制是基于Zone为单位的热管理机制,核心包括三个部分:获取区域温度的设备thermal_zone_device、区域降温的设备thermal_cooling_device、温控策略thermal_governor。thermal_governor从thermal_zone_device获取区域温度,然后根据当前温度,决定调用哪个降温设备来为该区域降温。
(1)Thermal sensor driver:SoC内部CPU和GPU的旁边通常会有用于获取它们温度的传感器,比如 tsadc(Temperature Sensor ADC)。
注:
ADC,即Analog-to-Digital Converter(模拟数字转换器)
-
ADC的作用:将连续变化的模拟信号转换离散的数字信号的器件
-
常见的模拟信号:温度、压力、声音
-
AD转换步骤:采样、量化、编码
(2)Thermal cooling device:降温设备,比如风扇。这里有点特殊的是,CPU和GPU不仅是发热设备(即需要实施温控策略的设备),也可以是降温设备。当我们降低CPU/GPU的运行频率的时候,它们就在充当降温设备(降低产热量即是在降温)。
(3)Thermal governer:温控策略,Linux内核中的温控策略要比上面的空调控制精细得多,而且也提供了多种策略。
(4)Thermal core:组织并管理上面三个组件,并通过sysfs和用户空间交互。
归纳一下:核心为thermal_core;可以获取温度的设备抽象为thermal_zone_device,如Temp Sensor、NTC(板上的热敏电阻)等;控制温度的设备抽象为thermal_cooling_device,如风扇、CPU、DDR、GPU等;温控策略抽象为thermal_governor,如step_wise、bang_bang等。
linux thermal框架
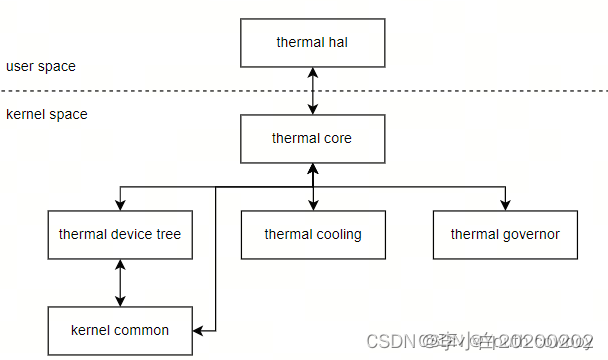
Linux Thermal框架可以分为Thermal Core、Thermal Governor、Thermal Cooling、Thermal Driver以及Thermal Device Tree五大部分。
Thermal Core:用于和user space、Thermal Governor、Thermal Driver交互。
Thermal Governor:主要包括gov_bang_bang、gov_fair_share、gov_power_allocator、gov_step_wise、gov_user_space等,最常用的为gov_power_allocator.
Thermal Cooling:主要包括cpufreq_cooling、cpuidle_cooling、devfreq_cooling等。
thermal core
内核将采集区域温度的设备抽象为结构体struct thermal_zone_device,主要成员包括char type[]设备名称;int temperature当前温度;int last_temperature上次采集问题;struct thermal_governer *governor对应governor; int polling_delay温度采集时间间隔等等。其中struct thermal_zone_device_ops *ops是采集区域温度设备的操作抽象,包括绑定降温设备,获取设备温度等。
kernel/linux/thermal.h中定义了thernal_zone_device & thermal_zone_device_ops、thermal_governor、thermal_cooling_device & thermal_cooling_device_ops结构体。
struct thermal_zone_device {
int id; // 设备的唯一标识符
char type[THERMAL_NAME_LENGTH]; // 设备名称
struct device device; // 设备相关联的struct device结构体
struct thermal_attr *trip_temp_attrs; // 温度触发器(trip)的温度属性链表
struct thermal_attr *trip_type_attrs; // 温度触发器的触发类型属性链表
struct thermal_attr *trip_hyst_attrs; // 温度触发器的滞后属性链表
void *devdata;
int trips;
unsigned long trips_disabled; /* bitmap for disabled trips */
int passive_delay;
int polling_delay; // 采集温度的时间间隔
int temperature; // 当前采集的温度
int last_temperature; // 上次采集的温度
int emul_temperature;
int passive;
unsigned int forced_passive; // 强制进入被动散热模式的标志
atomic_t need_update;
struct thermal_zone_device_ops *ops; // 区域温度设备的操作
struct thermal_zone_params *tzp; // 记录一些信息,如governor name
struct thermal_governor *governor; // 温控策略
void *governor_data;
struct list_head thermal_instances; // 降温设备
struct idr idr; // 管理热区设备实例的ID
struct mutex lock;
struct list_head node; // 热区设备的链表节点
struct delayed_work poll_queue; // 用于轮询区域温度
};
struct thermal_zone_params {
char governor_name[THERMAL_NAME_LENGTH];
/*
* a boolean to indicate if the thermal to hwmon sysfs interface
* is required. when no_hwmon == false, a hwmon sysfs interface
* will be created. when no_hwmon == true, nothing will be done
*/
bool no_hwmon;
int num_tbps; /* Number of tbp entries */
struct thermal_bind_params *tbp;
/*
* Sustainable power (heat) that this thermal zone can dissipate in
* mW
*/
u32 sustainable_power;
/*
* Proportional parameter of the PID controller when
* overshooting (i.e., when temperature is below the target)
*/
s32 k_po;
/*
* Proportional parameter of the PID controller when
* undershooting
*/
s32 k_pu;
/* Integral parameter of the PID controller */
s32 k_i;
/* Derivative parameter of the PID controller */
s32 k_d;
/* threshold below which the error is no longer accumulated */
s32 integral_cutoff;
/*
* @slope: slope of a linear temperature adjustment curve.
* Used by thermal zone drivers.
*/
int slope;
/*
* @offset: offset of a linear temperature adjustment curve.
* Used by thermal zone drivers (default 0).
*/
int offset;
};
struct thermal_zone_device_ops {
// 绑定一个降温设备到该热区设备
int (*bind) (struct thermal_zone_device *,
struct thermal_cooling_device *);
// 解绑一个降温设备从该热区设备
int (*unbind) (struct thermal_zone_device *,
struct thermal_cooling_device *);
// 获取当前热区设备的温度
int (*get_temp) (struct thermal_zone_device *, int *);
// 获取当前热区设备的工作模式
int (*get_mode) (struct thermal_zone_device *,
enum thermal_device_mode *);
// 设置当前热区设备的工作模式
int (*set_mode) (struct thermal_zone_device *,
enum thermal_device_mode);
// 获取指定温度触发器的触发类型
int (*get_trip_type) (struct thermal_zone_device *, int,
enum thermal_trip_type *);
// 获取触发等级对应的温度
int (*get_trip_temp) (struct thermal_zone_device *, int, int *);
// 设置触发等级对应的温度
int (*set_trip_temp) (struct thermal_zone_device *, int, int);
int (*get_trip_hyst) (struct thermal_zone_device *, int, int *);
int (*set_trip_hyst) (struct thermal_zone_device *, int, int);
int (*get_crit_temp) (struct thermal_zone_device *, int *);
int (*set_emul_temp) (struct thermal_zone_device *, int);
// 获取温度的变化趋势
int (*get_trend) (struct thermal_zone_device *, int,
enum thermal_trend *);
int (*notify) (struct thermal_zone_device *, int,
enum thermal_trip_type);
};
// 内核将温控策略抽象为结构体struct thermal_governor,
//主要成员包括:char name[THERMAL_NAME_LENGTH]策略名称;int (*throttle)()温控决策等等。
struct thermal_governor {
char name[THERMAL_NAME_LENGTH];
int (*bind_to_tz)(struct thermal_zone_device *tz);
void (*unbind_from_tz)(struct thermal_zone_device *tz);
int (*throttle)(struct thermal_zone_device *tz, int trip);
struct list_head governor_list;
};
// 执行温控策略的设备成为区域降温设备,
//内核抽象为结构体struct thermal_cooling_device,struct thermal_cooling_device_ops是区域降温设备的操作集合。
struct thermal_cooling_device {
int id; //每个thermal_cooling_device有独立的id
char type[THERMAL_NAME_LENGTH]; // 名称
struct device device;
struct device_node *np;
void *devdata;
const struct thermal_cooling_device_ops *ops;
bool updated; /* true if the cooling device does not need update */
struct mutex lock; /* protect thermal_instances list */
struct list_head thermal_instances;
struct list_head node;
};
struct thermal_cooling_device_ops {
//获取总的状态数,相当于降温等级
int (*get_max_state) (struct thermal_cooling_device *, unsigned long *);
//获取当前状态
int (*get_cur_state) (struct thermal_cooling_device *, unsigned long *);
//设置状态
int (*set_cur_state) (struct thermal_cooling_device *, unsigned long);
// 获取所请求的功率
int (*get_requested_power)(struct thermal_cooling_device *,
struct thermal_zone_device *, u32 *);
// 将指定状态(降温等级)转换为对应的功率
int (*state2power)(struct thermal_cooling_device *,
struct thermal_zone_device *, unsigned long, u32 *);
// 将指定功率转换为对应的状态(降温等级)
int (*power2state)(struct thermal_cooling_device *,
struct thermal_zone_device *, u32, unsigned long *);
};初始化
thermal_governor注册
以step_wise governor为例:
int thermal_gov_step_wise_register(void)
{
// 调用thermal_core.c中的方法
return thermal_register_governor(&thermal_gov_step_wise);
}static int __init thermal_init(void)
{
int result;
// 注册所有的governors
result = thermal_register_governors();
if (result)
goto error;
result = class_register(&thermal_class);
if (result)
goto unregister_governors;
result = genetlink_init();
if (result)
goto unregister_class;
result = of_parse_thermal_zones();
if (result)
goto exit_netlink;
result = register_pm_notifier(&thermal_pm_nb);
if (result)
pr_warn("Thermal: Can not register suspend notifier, return %d\n",
result);
return 0;
exit_netlink:
genetlink_exit();
unregister_class:
class_unregister(&thermal_class);
unregister_governors:
thermal_unregister_governors();
error:
idr_destroy(&thermal_tz_idr);
idr_destroy(&thermal_cdev_idr);
mutex_destroy(&thermal_idr_lock);
mutex_destroy(&thermal_list_lock);
mutex_destroy(&thermal_governor_lock);
return result;
}
static int __init thermal_register_governors(void)
{
int result;
// 调用step_wise governor中的方法,为系统默认的gov
result = thermal_gov_step_wise_register();
if (result)
return result;
result = thermal_gov_fair_share_register();
if (result)
return result;
result = thermal_gov_bang_bang_register();
if (result)
return result;
result = thermal_gov_user_space_register();
if (result)
return result;
// 注册IPA governor
return thermal_gov_power_allocator_register();
}
// 将第一个注册的governor设置为系统默认governor,即step_wise governor
int thermal_register_governor(struct thermal_governor *governor)
{
int err;
const char *name;
struct thermal_zone_device *pos;
if (!governor)
return -EINVAL;
mutex_lock(&thermal_governor_lock);
err = -EBUSY;
if (__find_governor(governor->name) == NULL) {
err = 0;
//链接到thermal_governor_list
list_add(&governor->governor_list, &thermal_governor_list);
if (!def_governor && !strncmp(governor->name,
DEFAULT_THERMAL_GOVERNOR, THERMAL_NAME_LENGTH))
def_governor = governor; //第一个设置为def_governor
}
.......
}thermal_zone_device注册
struct thermal_zone_device *thermal_zone_device_register(const char *type,
int trips, int mask, void *devdata,
struct thermal_zone_device_ops *ops,
struct thermal_zone_params *tzp,
int passive_delay, int polling_delay)
{
struct thermal_zone_device *tz;
enum thermal_trip_type trip_type;
int trip_temp;
int result;
int count;
int passive = 0;
struct thermal_governor *governor;
.........................................................................
//分配内存
tz = kzalloc(sizeof(struct thermal_zone_device), GFP_KERNEL);
.........................................................................
//初始化idr,并获取id
idr_init(&tz->idr);
mutex_init(&tz->lock);
result = get_idr(&thermal_tz_idr, &thermal_idr_lock, &tz->id);
..........................................................................
strlcpy(tz->type, type ? : "", sizeof(tz->type)); //设置名称
tz->ops = ops; //操作集合
tz->tzp = tzp; //参数
tz->device.class = &thermal_class;
tz->devdata = devdata;
tz->trips = trips;
tz->passive_delay = passive_delay;
tz->polling_delay = polling_delay; //采集时间间隔
/* A new thermal zone needs to be updated anyway. */
atomic_set(&tz->need_update, 1);
........................................................................
//根据governor name,设置降温策略
if (tz->tzp)
governor = __find_governor(tz->tzp->governor_name);
else
governor = def_governor;
.........
//链接到thermal_tz_list
mutex_lock(&thermal_list_lock);
list_add_tail(&tz->node, &thermal_tz_list);
mutex_unlock(&thermal_list_lock);
/* 尝试绑定已注册的降温设备 */
bind_tz(tz);
thermal_zone_device_reset(tz);
/* Update the new thermal zone and mark it as already updated. */
if (atomic_cmpxchg(&tz->need_update, 1, 0))
thermal_zone_device_update(tz, THERMAL_EVENT_UNSPECIFIED);
return tz;
..........
}thermal_cooling_device注册
struct thermal_cooling_device *
thermal_cooling_device_register(char *type, void *devdata,
const struct thermal_cooling_device_ops *ops)
{
return __thermal_cooling_device_register(NULL, type, devdata, ops);
}
static struct thermal_cooling_device *
__thermal_cooling_device_register(struct device_node *np,
char *type, void *devdata,
const struct thermal_cooling_device_ops *ops)
{
struct thermal_cooling_device *cdev;
struct thermal_zone_device *pos = NULL;
int result;
if (type && strlen(type) >= THERMAL_NAME_LENGTH)
return ERR_PTR(-EINVAL);
if (!ops || !ops->get_max_state || !ops->get_cur_state ||
!ops->set_cur_state)
return ERR_PTR(-EINVAL);
// 分配内存
cdev = kzalloc(sizeof(struct thermal_cooling_device), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!cdev)
return ERR_PTR(-ENOMEM);
result = get_idr(&thermal_cdev_idr, &thermal_idr_lock, &cdev->id);
if (result) {
kfree(cdev);
return ERR_PTR(result);
}
strlcpy(cdev->type, type ? : "", sizeof(cdev->type));
mutex_init(&cdev->lock);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&cdev->thermal_instances);
// 初始化成员,将mtk的ops和devdata赋值给thermal_cooling_device
cdev->np = np;
cdev->ops = ops;
cdev->updated = false;
cdev->device.class = &thermal_class;
cdev->device.groups = cooling_device_attr_groups;
cdev->devdata = devdata;
dev_set_name(&cdev->device, "cooling_device%d", cdev->id);
// 注册device
result = device_register(&cdev->device);
if (result) {
release_idr(&thermal_cdev_idr, &thermal_idr_lock, cdev->id);
kfree(cdev);
return ERR_PTR(result);
}
/* Add 'this' new cdev to the global cdev list */
// 新的thermal_cooling_device加入到thermal_cdev_list链表
mutex_lock(&thermal_list_lock);
list_add(&cdev->node, &thermal_cdev_list);
mutex_unlock(&thermal_list_lock);
/* Update binding information for 'this' new cdev */
// 尝试绑定到已注册的温度采集设备thermal_zone_device
bind_cdev(cdev);
mutex_lock(&thermal_list_lock);
list_for_each_entry(pos, &thermal_tz_list, node)
if (atomic_cmpxchg(&pos->need_update, 1, 0))
thermal_zone_device_update(pos);
mutex_unlock(&thermal_list_lock);
return cdev;
}
static void bind_cdev(struct thermal_cooling_device *cdev)
{
int i, ret;
const struct thermal_zone_params *tzp;
struct thermal_zone_device *pos = NULL;
mutex_lock(&thermal_list_lock);
// 遍历thermal_zone_device list,逐个绑定thermal_cooling_device
list_for_each_entry(pos, &thermal_tz_list, node) {
if (!pos->tzp && !pos->ops->bind)
continue;
if (pos->ops->bind) {
// 调用 thermal_zone_device中thermal_zone_device_ops成员中的bind方法
ret = pos->ops->bind(pos, cdev);
if (ret)
print_bind_err_msg(pos, cdev, ret);
continue;
}
tzp = pos->tzp;
if (!tzp || !tzp->tbp)
continue;
for (i = 0; i < tzp->num_tbps; i++) {
if (tzp->tbp[i].cdev || !tzp->tbp[i].match)
continue;
if (tzp->tbp[i].match(pos, cdev))
continue;
tzp->tbp[i].cdev = cdev;
__bind(pos, tzp->tbp[i].trip_mask, cdev,
tzp->tbp[i].binding_limits,
tzp->tbp[i].weight);
}
}
mutex_unlock(&thermal_list_lock);
}温度采集设备与降温设备的联系
同一个温度采集设备可以对应多个降温设备,结构体struct thermal_instance用于连接温度采集设备与降温设备,成员struct thermal_zone_device *tz是对应的温度采集设备,struct thermal_cooling_device *cdev是对应的降温设备,int trip触发登记(对应一个温度),当温度采集设备采集的温度达到一定值时,调用对应trip登记的降温设备。
struct thermal_instance {
.................................................................
struct thermal_zone_device *tz; //对应温度采集设备
struct thermal_cooling_device *cdev; //对应降温设备
int trip; //触发等级
struct list_head tz_node; //链接到温度采集设备
struct list_head cdev_node; //链接到降温设备
.................................................................
};以温度采集设备绑定降温设备为例,当温度采集设备注册时会尝试绑定所有已经注册的降温设备。以CPU为例,bind接口对应的是tscpu_bind(),从代码中可以看出如果降温设备的名称为g_bind0--g_bind9中的一个将会绑定CPU温度采集设备和降温设备。tscpu_bind()接口中也定义了各种名称降温设备对应的触发等级。
static void bind_tz(struct thermal_zone_device *tz)
{
int i, ret;
struct thermal_cooling_device *pos = NULL;
const struct thermal_zone_params *tzp = tz->tzp;
if (!tzp && !tz->ops->bind)
return;
mutex_lock(&thermal_list_lock);
if (tz->ops->bind) {
//尝试绑定所有的已经注册的降温设备
list_for_each_entry(pos, &thermal_cdev_list, node) {
ret = tz->ops->bind(tz, pos);
if (ret)
print_bind_err_msg(tz, pos, ret);
}
goto exit;
}
...........................................................
}
static int tscpu_bind(struct thermal_zone_device *thermal, struct thermal_cooling_device *cdev)
{
int table_val = 0;
if (!strcmp(cdev->type, g_bind0)) {
table_val = 0;
tscpu_config_all_tc_hw_protect(trip_temp[0], tc_mid_trip);
} else if (!strcmp(cdev->type, g_bind1)) {
table_val = 1;
tc_mid_trip = trip_temp[1];
tscpu_config_all_tc_hw_protect(trip_temp[0], tc_mid_trip);
} else if (!strcmp(cdev->type, g_bind2)) {
table_val = 2;
} else if (!strcmp(cdev->type, g_bind3)) {
table_val = 3;
} else if (!strcmp(cdev->type, g_bind4)) {
.....................................................
} else {
return 0;
}
//以table_val为触发等级绑定发热设备和降温设备
if (mtk_thermal_zone_bind_cooling_device(thermal, table_val, cdev)) {
tscpu_warn("tscpu_bind error binding cooling dev\n");
return -EINVAL;
}
tscpu_printk("tscpu_bind binding OK, %d\n", table_val);
return 0;
}温度采集设备知道了触发等级和降温温度,还需要知道触发等级对应的温度。thermal_zone_device_ops的get_trip_temp()用于查询触发等级对应的温度,以mtkcpu为例,所有降温设备的触发温度保存在数据中,触发等级就是该数组的下标。
static int tscpu_get_trip_temp
(struct thermal_zone_device *thermal, int trip, int *temp)
{
*temp = trip_temp[trip];
return 0;
}cooling device
以cpu coolig为例:
cpufreq_state2power:根据cpu cooling state换算cpu power。
static int cpufreq_state2power(struct thermal_cooling_device *cdev,
struct thermal_zone_device *tz,
unsigned long state, u32 *power)
{
unsigned int freq, num_cpus;
cpumask_t cpumask;
u32 static_power, dynamic_power;
int ret;
struct cpufreq_cooling_device *cpufreq_device = cdev->devdata;
cpumask_and(&cpumask, &cpufreq_device->allowed_cpus, cpu_online_mask);
// 根据cpumask得到在线cpu核数
num_cpus = cpumask_weight(&cpumask);
/* None of our cpus are online, so no power */
if (num_cpus == 0) {
*power = 0;
return 0;
}
// 根据cpu state得到当前的频率
freq = cpufreq_device->freq_table[state];
if (!freq)
return -EINVAL;
// 计算当前频率下的cpu动态功耗
dynamic_power = cpu_freq_to_power(cpufreq_device, freq) * num_cpus;
// 计算当前频率下的cpu静态功耗
ret = get_static_power(cpufreq_device, tz, freq, &static_power);
if (ret)
return ret;
// 计算当前频率下的cpu总的功耗
*power = static_power + dynamic_power;
return 0;
}cpufreq_power2state:根据cpu power换算cpu cooling state.
static int cpufreq_power2state(struct thermal_cooling_device *cdev,
struct thermal_zone_device *tz, u32 power,
unsigned long *state)
{
unsigned int cpu, cur_freq, target_freq;
int ret;
s32 dyn_power;
u32 last_load, normalised_power, static_power;
struct cpufreq_cooling_device *cpufreq_device = cdev->devdata;
cpu = cpumask_any_and(&cpufreq_device->allowed_cpus, cpu_online_mask);
/* None of our cpus are online */
if (cpu >= nr_cpu_ids)
return -ENODEV;
// 计算当前cpu频率
cur_freq = cpufreq_quick_get(cpu);
// 计算当前频率下的静态功耗
ret = get_static_power(cpufreq_device, tz, cur_freq, &static_power);
if (ret)
return ret;
// 计算当前频率下的动态功耗
dyn_power = power - static_power;
dyn_power = dyn_power > 0 ? dyn_power : 0;
last_load = cpufreq_device->last_load ?: 1;
// 计算归一化功耗
normalised_power = (dyn_power * 100) / last_load;
// 根据归一化功耗计算出目标频率
target_freq = cpu_power_to_freq(cpufreq_device, normalised_power);
// 根据目标频率得到cpu state
*state = cpufreq_cooling_get_level(cpu, target_freq);
if (*state == THERMAL_CSTATE_INVALID) {
dev_warn_ratelimited(&cdev->device,
"Failed to convert %dKHz for cpu %d into a cdev state\n",
target_freq, cpu);
return -EINVAL;
}
trace_thermal_power_cpu_limit(&cpufreq_device->allowed_cpus,
target_freq, *state, power);
return 0;
}
static u32 cpu_freq_to_power(struct cpufreq_cooling_device *cpufreq_cdev,
u32 freq)
{
int i;
for (i = cpufreq_cdev->max_level - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
if (freq > cpufreq_cdev->em->table[i].frequency)
break;
}
// 查表获取
return cpufreq_cdev->em->table[i + 1].power;
}遍历了一下cpufrep_cdev里的em->table,这个table蕴含了freq和power的对应关系,这个table是跟芯片密切相关的,往往在出厂的时候就已经预制好了。
Linux Thermal框架-CSDN博客
模拟量转数字量原理
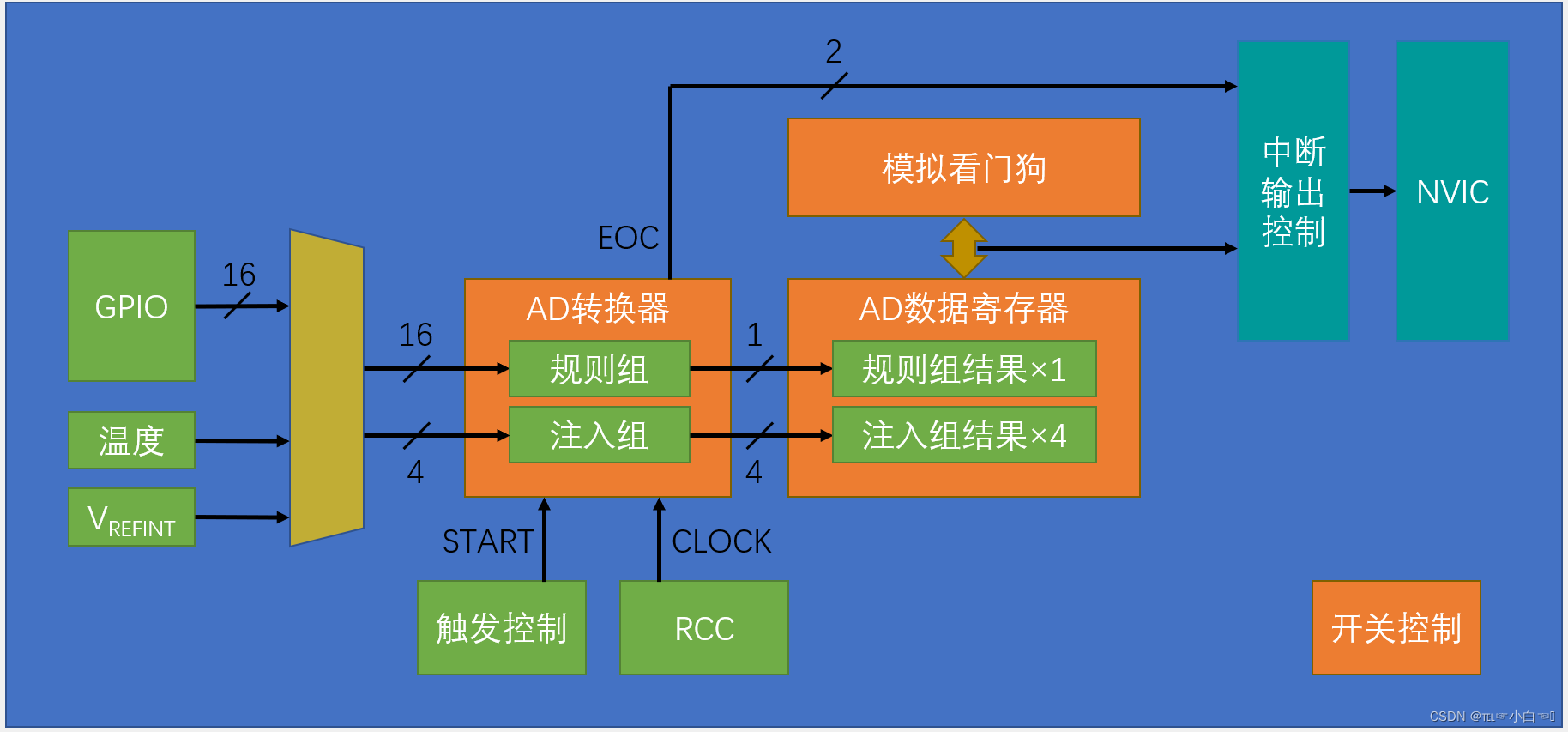
模拟量转数字量的过程通常涉及一下几个关键步骤:
采样:该步骤将连续的模拟信号转换为时间上离散变化的信号。
保持:该步骤存储采样结果,直到下一次采样。
量化:该步骤将采样电平转换为与之最接近的离散数字电平;
编码:该步骤将量化后的结果便是为特定的数制形式。
模拟信号转化为数字信号的过程中,会使用到模数转换器(ADC),这种转换通常需要一个参考模拟量作为转换的标准,常见的参考标准为ADC芯片最大的可转换信号大小。
ADC的分辨率用于标识模拟输入信号的位数,提高分辨率可以更准确低复现模拟信号并降低量化误差,但这也可能增加成本。例如一个8位的ADC可以将5V的模拟量分为256等分,从而得出相应的数字量。
此外,还有间接比较型的模数转换,该转换中输入模拟量不是直接参考电压比较,而是将二者变为中间的某种物理量再进行比较,然后将比较所得的结果进行数字编码。