最简单的办法就是使用多个 application.yml 配置文件 。一个叫 application-test.yml 测试用;另一个是正式使用的 application-prod.yml 。win环境下大部分是开发测试时候使用的,服务正式上线需要部署在Linux服务器上又换成了Linux。但开发初期或者项目不是很正式,也可以不这样写,就单独写一个application.yml 里面写好两个路径,再写一个文件配置类,在这里面写好方法就行。
application.yml
file:
path:
windows: D:\qr_code_duct\qr_code_back\ddinguia\server\files\
linux: /app/files/文件配置类 FileProperties
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "file")
public class FileProperties {
private PathConfig path;
public PathConfig getPath() {
return path;}
public void setPath(PathConfig path) {
this.path = path;}
public static class PathConfig {
private String windows;
private String linux;
public String getWindows() {
return windows;}
public void setWindows(String windows) {
this.windows = windows;}
public String getLinux() {
return linux;}
public void setLinux(String linux) {
this.linux = linux;}
}
public String getSavePath() {
String os = System.getProperty("os.name").toLowerCase();
if (os.contains("win")) {
return path.getWindows();
} else if (os.contains("nix") || os.contains("nux") || os.contains("aix")) {
return path.getLinux();
} else {
throw new IllegalStateException("Unsupported operating system: " + os);
}
}
}具体在代码中使用,就像正常调用参数一样就行,比如先在Service层里面引入
@Resource
private FileProperties fileProperties;然后直接使用即可:
File directory = new File(fileProperties.getSavePath() + File.separator + fileType + "s");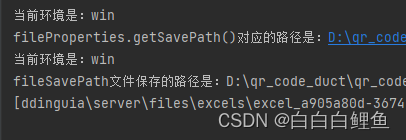





![buuctf——[CISCN2019 华北赛区 Day2 Web1]Hack World](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/524e8c15b49744208d8cda058ae1b43f.png)