目录
- Bean的作用域
- 1.singleton(默认)
- 代码示例
- 2.prototype
- 代码示例
- 3.request
- 代码示例
- 4.session
- 代码示例
- 5.application
- 代码示例
- websocket
Bean的作用域
Spring支持6个作用域:singleton、prototype、request、session、application、websocket

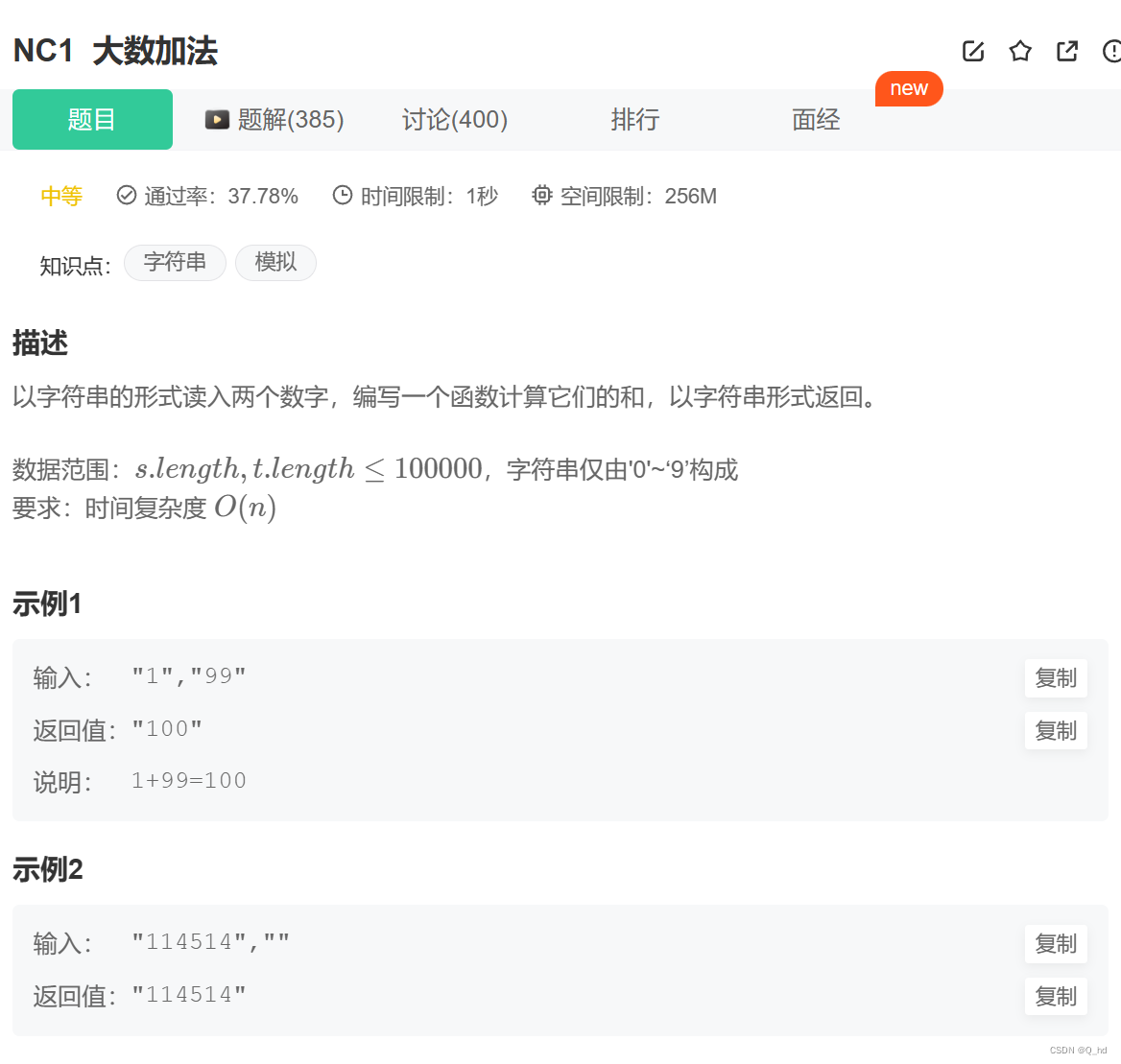
1.singleton(默认)
- singleton是scope属性的默认值,当我们把bean的scope属性设置为singleton时,代表将对该bean使用单例模式,单例想必大家都熟悉,也就是说每次使用该bean的id从容器中获取该bean的时候,都将会返回同一个bean实例。但这里的单例跟设计模式里的单例还有一些小区别。
- 设计模式中的单例是通过硬编码,给某个类仅创建一个静态对象,并且只暴露一个接口来获取这个对象实例,因此,设计模式中的单例是相对ClassLoader而言的,同一个类加载器下只会有一个实例
- 在Spring中,singleton单例指的是每次从同一个IOC容器中返回同一个bean对象,单例的有效范围是IOC容器,而不是ClassLoader。IOC容器会将这个bean实例缓存起来,以供后续使用
代码示例
@Controller
public class TestController {
ApplicationContext act = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
@RequestMapping("/test")
public String test(Model model){
model.addAttribute("service1",act.getBean("testService"));
model.addAttribute("service2",act.getBean("testService"));
model.addAttribute("service3",act.getBean("testService"));
return "scope";
}
}
service
public class TestService {
}
配置
<bean id="testService" class="cn.smbms.service.TestService" scope="singleton"/>
jsp
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>service1:${service1}</h1>
<h1>service2:${service2}</h1>
<h1>service3:${service3}</h1>
</body>
</html>
只要服务不重启,无论访问多次,每次都会从容器中获取三次testService

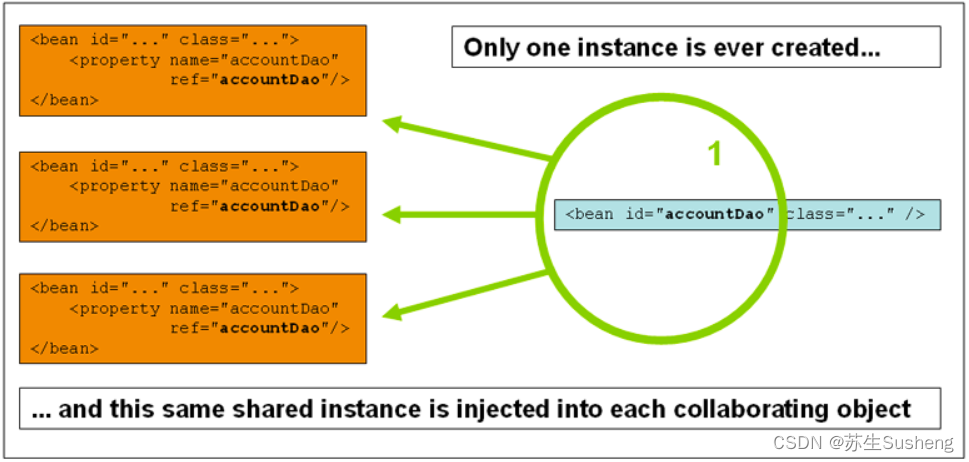
2.prototype
- 与singleton相反,设置为prototype的bean,每次调用容器的getBean方法或注入到另一个bean中时,都会返回一个新的实例
- 与其他的scope类型不同的是,Spring并不会管理设置为prototype的bean的整个生命周期,获取相关bean时,容器会实例化,或者装配相关的prototype-bean实例,然后返回给客户端,但不会保存prototype-bean的实例。
- 所以,尽管所有的bean对象都会调用配置的初始化方法,但是prototype-bean并不会调用其配置的destroy方法。所以清理工作必须由客户端进行。
- 所以,Spring容器对prototype-bean 的管理在一定程度上类似于 new 操作,对象创建后的事情将全部由客户端处理
代码示例
配置
<bean id="testService" class="cn.smbms.service.TestService" scope="prototype"/>
第一次访问
 第二次访问
第二次访问

3.request
- 只能在web环境下使用,如果使用 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 来加载使用了该属性的bean,那么就会抛出异常。
java.lang.IllegalStateException: No Scope registered for scope name 'request' - 如果将scope属性设置为 request 代表该bean的作用域为单个请求,请求结束,则bean将被销毁,第二次请求将会创建一个新的bean实例
代码示例
修改controller,从容器中获取两次bean
@RestController
public class TestController {
@Resource
private TestService testService1;
@Resource
private TestService testService2;
@RequestMapping("/test")
public String test(){
return testService1 + "----" + testService2;
}
}
修改service层,这次使用注解
@Service
@RequestScope
public class TestService {
}
第一次访问

第二次访问

4.session
- 首次http请求创建一个实例,作用域是浏览器首次访问直至浏览器关闭。
- 同一个HTTP Session共享一个Bean,不同Session使用不通的Bean,仅适用于WebApplicationContext环境。
代码示例
@Service
@SessionScope
public class TestService {
}
同一个Session多次请求,不变

换一个session(浏览器)
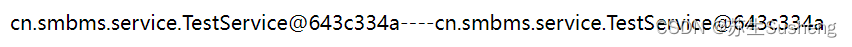
5.application
- application的作用域比session又要更广一些,session作用域是针对一个 Http Session,而application作用域,则是针对一个 ServletContext ,有点类似 singleton
- 但是singleton代表的是每个IOC容器中仅有一个实例,而同一个web应用中,是可能会有多个IOC容器的,但一个Web应用只会有一个 ServletContext,所以 application 才是web应用中货真价实的单例模式
代码示例
@Service
@ApplicationScope
public class TestService {
}
不重启项目,多次访问
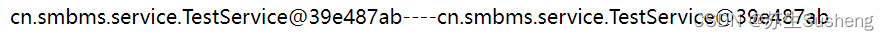 重启项目在访问
重启项目在访问
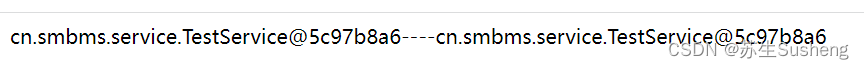
websocket
- websocket 的作用范围是 WebSocket ,即在整个 WebSocket 中有效。







![[数字人]唇形驱动,不生成头部动作算法总结](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/ae77ad70a10c45bda8d71267e1298843.png)