CompletableFuture 是 Java 8 引入的一种新的 Future,设计目的是为了编写非阻塞的异步代码。
传统异步编程方式
传统异步编程方式获得异步任务值,首先我们得通过future task ,然后创建一个实现callable内部类,或者通过lambda的表达式,然后再结合thread,或者线程池的方式去执行它,具体代码如下。
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class CompletableFutureTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
FutureTask<String> futureTask = new FutureTask<>(new Callable<String>() {
@Override
public String call() throws Exception {
Thread.sleep(2000);
return "futureTask 执行完成";
}
});
new Thread(futureTask).start();
//get()方法作用:以阻塞的方式获取任务执行结果
System.out.println("new Thread的方式获取结果:" + futureTask.get());
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
executorService.submit(futureTask);
//get()方法作用:以阻塞的方式获取任务执行结果
System.out.println("线程池的方式获取结果:" + futureTask.get());
executorService.shutdown(); // 关闭线程池
System.out.println("TODO...");
}
}
运行结果:

可以看出整个实现过程比较麻烦,想要获得返回值会调用它的get()方法,会阻塞后面的代码,如果后面的代码并不依赖future task的返回值的话,其实我们更希望以并行的方式去执行,性能肯定是更高的,那么我们结合CompletableFuture来进行改造。
CompletableFuture实现异步编程方式
1.异步执行
supplyAsync
supplyAsync是创建带有返回值的异步任务。它有如下两个方法,一个是使用默认线程池(ForkJoinPool.commonPool())的方法,一个是带有自定义线程池的重载方法。
// 带返回值异步请求,默认线程池
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier)
// 带返回值的异步请求,可以自定义线程池
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier, Executor executor)
具体代码:
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class CompletableFutureTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<String> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
return "默认线程池执行有返回值的任务";
});
System.out.println(completableFuture.get());//get()方法抛出ExecutionException, InterruptedException检查时异常,程序必须做处理
// 自定义线程池
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
CompletableFuture<String> completableFutureWithThreadExecutor = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
return "自定义线程池执行有返回值的任务";
},executorService);
System.out.println(completableFutureWithThreadExecutor.join());//join()方法只抛出运行时异常,程序可不做处理
}
}
运行结果:

runAsync
runAsync是创建没有返回值的异步任务。它有如下两个方法,一个是使用默认线程池(ForkJoinPool.commonPool())的方法,一个是带有自定义线程池的重载方法,具体代码如下。
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class CompletableFutureTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<Void> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("默认线程池执行没有返回值的任务");
});
System.out.println("result:" + completableFuture.get());
// 自定义线程池
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
CompletableFuture<Void> completableFutureWithThreadExecutor = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("自定义线程池执行没有返回值的任务");
},executorService);
System.out.println("result:" + completableFutureWithThreadExecutor.get());
}
}
运行结果:

2.获取任务结果的方法
// 如果完成则返回结果,否则就抛出具体的异常
public T get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException
// 最大时间等待返回结果,否则就抛出具体异常
public T get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException
// 完成时返回结果值,否则抛出unchecked异常。为了更好地符合通用函数形式的使用,如果完成此 CompletableFuture所涉及的计算引发异常,则此方法将引发unchecked异常并将底层异常作为其原因
public T join()
// 如果完成则返回结果值(或抛出任何遇到的异常),否则返回给定的 valueIfAbsent。
public T getNow(T valueIfAbsent)
// 如果任务没有完成,返回的值设置为给定值
public boolean complete(T value)
// 如果任务没有完成,就抛出给定异常
public boolean completeExceptionally(Throwable ex)
3.多任务组合处理
allOf / anyOf
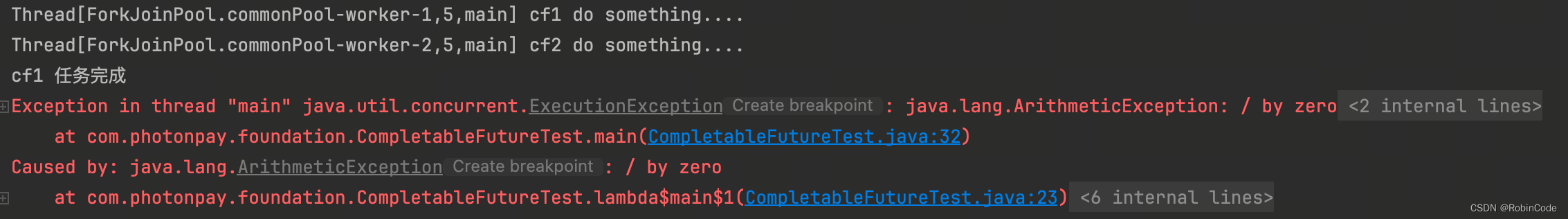
allOf:CompletableFuture是多个任务都执行完成后才会执行,只有有一个任务执行异常,则返回的CompletableFuture执行get方法时会抛出异常,如果都是正常执行,则get返回null,具体代码如下。
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class CompletableFutureTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<String> cf1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf1 do something....");
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("cf1 任务完成");
return "cf1 任务完成";
});
CompletableFuture<String> cf2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf2 do something....");
int a = 1/0;
Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("cf2 任务完成");
return "cf2 任务完成";
});
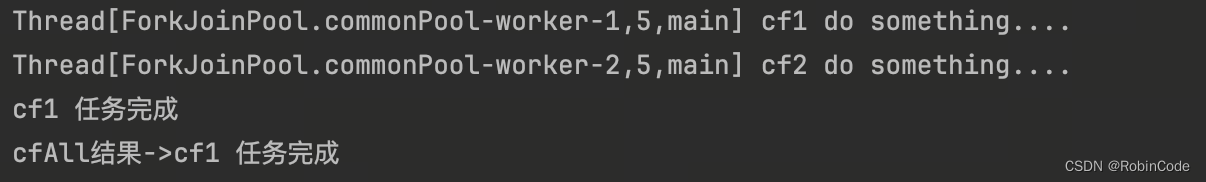
CompletableFuture<Void> cfAll = CompletableFuture.allOf(cf1, cf2);
System.out.println("cfAll结果->" + cfAll.get());
}
}
运行结果:
anyOf :CompletableFuture是多个任务只要有一个任务执行完成,则返回的CompletableFuture执行get方法时会抛出异常,如果都是正常执行,则get返回执行完成任务的结果,具体代码如下。
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class CompletableFutureTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<String> cf1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf1 do something....");
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("cf1 任务完成");
return "cf1 任务完成";
});
CompletableFuture<String> cf2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf2 do something....");
Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("cf2 任务完成");
return "cf2 任务完成";
});
CompletableFuture<Object> cfAll = CompletableFuture.anyOf(cf1, cf2);
System.out.println("cfAll结果->" + cfAll.get());
}
}
运行结果:
4.异步回调处理
thenRun和thenRunAsync
thenRun表示某个任务执行完成后执行的动作,即回调方法,无入参,无返回值,具体代码如下。
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class CompletableFutureTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<Integer> cf1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf1 do something....");
return 1;
});
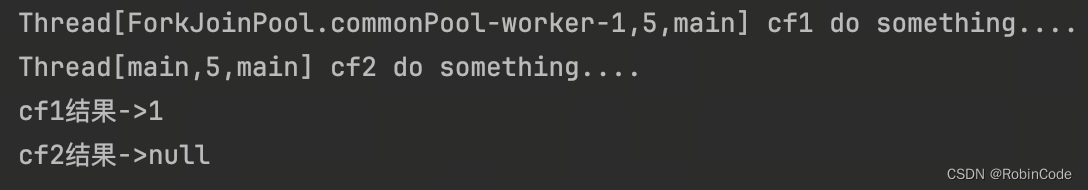
CompletableFuture<Void> cf2 = cf1.thenRun(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf2 do something....");
});
//等待任务1执行完成
System.out.println("cf1结果->" + cf1.get());
//等待任务2执行完成
System.out.println("cf2结果->" + cf2.get());
}
}
运行结果:
thenRunAsync具体代码如下。
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class CompletableFutureTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<Integer> cf1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf1 do something....");
return 1;
});
CompletableFuture<Void> cf2 = cf1.thenRunAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf2 do something....");
});
//等待任务1执行完成
System.out.println("cf1结果->" + cf1.get());
//等待任务2执行完成
System.out.println("cf2结果->" + cf2.get());
}
}
运行结果:
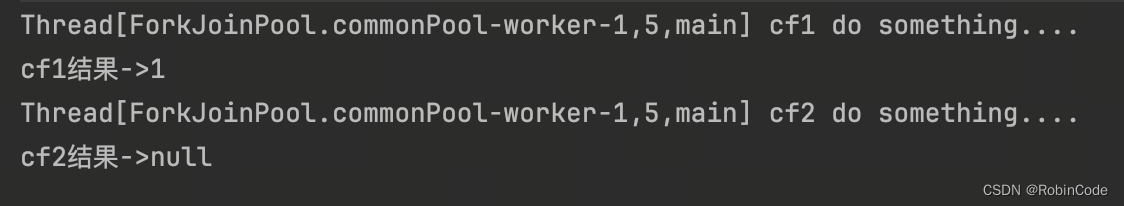
从上面代码和测试结果我们发现thenRun和thenRunAsync区别在于,使用thenRun方法时子任务与父任务使用的是同一个线程,而thenRunAsync在子任务中可能是另起一个线程执行任务,并且thenRunAsync可以自定义线程池,默认的使用ForkJoinPool.commonPool()线程池。
thenAccept和thenAcceptAsync
thenAccep表示某个任务执行完成后执行的动作,即回调方法,会将该任务的执行结果即方法返回值作为入参传递到回调方法中,无返回值,具体代码如下。
public class CompletableFutureTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<Integer> cf1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf1 do something....");
return 1;
});
CompletableFuture<Void> cf2 = cf1.thenAccept((result) -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf2 do something....,入参:" + result);
});
//等待任务1执行完成
System.out.println("cf1结果->" + cf1.get());
//等待任务2执行完成
System.out.println("cf2结果->" + cf2.get());
}
}
运行结果:
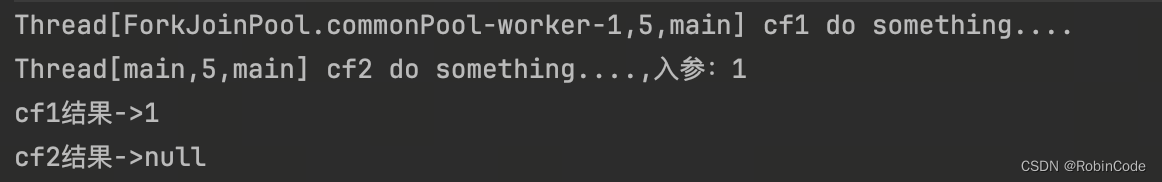
测试结果我们发现thenAccep和thenAccepAsync区别在于,使用thenAccep方法时子任务与父任务使用的是同一个线程,而thenAccepAsync在子任务中可能是另起一个线程执行任务,并且thenAccepAsync可以自定义线程池,默认的使用ForkJoinPool.commonPool()线程池。
thenApply和thenApplyAsync
thenApply 表示某个任务执行完成后执行的动作,即回调方法,会将该任务的执行结果即方法返回值作为入参传递到回调方法中,带有返回值,具体代码如下。
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class CompletableFutureTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<Integer> cf1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf1 do something....");
return 1;
});
CompletableFuture<Integer> cf2 = cf1.thenApplyAsync((result) -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf2 do something....");
result += 2;
return result;
});
//等待任务1执行完成
System.out.println("cf1结果->" + cf1.get());
//等待任务2执行完成
System.out.println("cf2结果->" + cf2.get());
}
}
运行结果:
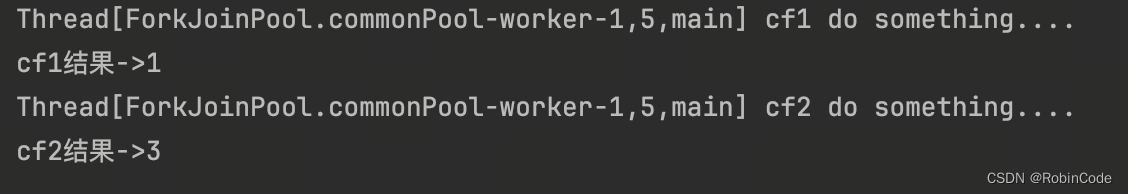
从上面代码和测试结果我们发现thenApply和thenApplyAsync区别在于,使用thenApply方法时子任务与父任务使用的是同一个线程,而thenApplyAsync在子任务中是另起一个线程执行任务,并且thenApplyAsync可以自定义线程池,默认的使用ForkJoinPool.commonPool()线程池。
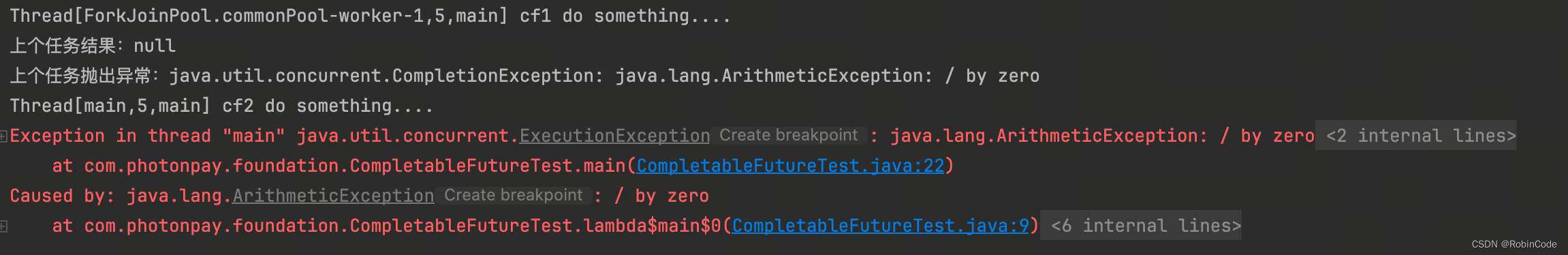
whenComplete和whenCompleteAsync
whenComplete是当某个任务执行完成后执行的回调方法,会将执行结果或者执行期间抛出的异常传递给回调方法,如果是正常执行则异常为null,回调方法对应的CompletableFuture的result和该任务一致,如果该任务正常执行,则get方法返回执行结果,如果是执行异常,则get方法抛出异常,具体代码如下。
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class CompletableFutureTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<Integer> cf1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf1 do something....");
int a = 1/0;
return 1;
});
CompletableFuture<Integer> cf2 = cf1.whenComplete((result, e) -> {
System.out.println("上个任务结果:" + result);
System.out.println("上个任务抛出异常:" + e);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf2 do something....");
});
// //等待任务1执行完成
// System.out.println("cf1结果->" + cf1.get());
// //等待任务2执行完成
System.out.println("cf2结果->" + cf2.get());
}
}
运行结果:
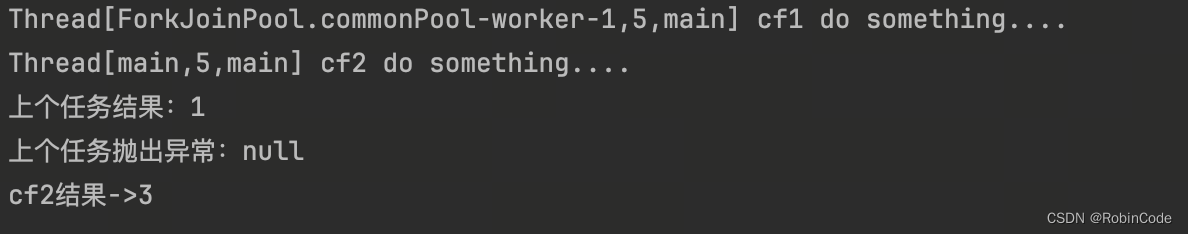
handle和handleAsync
跟whenComplete基本一致,区别在于handle的回调方法有返回值,具体代码如下。
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class CompletableFutureTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<Integer> cf1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf1 do something....");
//int a = 1/0;
return 1;
});
CompletableFuture<Integer> cf2 = cf1.handle((result, e) -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf2 do something....");
System.out.println("上个任务结果:" + result);
System.out.println("上个任务抛出异常:" + e);
return result+2;
});
//等待任务2执行完成
System.out.println("cf2结果->" + cf2.get());
}
}
运行结果:
总结
以上例子展示了 CompletableFuture 的基本使用方法,包括创建异步任务、结果处理、异常处理和结果组合。在实际开发中,你可以根据需要组合使用这些方法来实现复杂的异步逻辑。