最邻近插值
在图像分割任务中:原图的缩放一般采用双线性插值,用于上采样或下采样;而标注图像的缩放有特定的规则,需使用最临近插值,不用于上采样或下采样。
自定义函数
这个是通过输入原始图像和一个缩放因子来对图像进行邻近插值:
def nearest_neighbor_interpolation1(image, scale_factor):
"""
最邻近插值算法
:paraninput_array
:输入图像数组:param output_shape
:输出图像的 shape:return
:输出图像数组"""
# 输入图像的宽高
height, width = image.shape[:2]
# 计算输出图像的宽高
out_height = int(height * scale_factor)
out_width = int(width * scale_factor)
# 创建输出图像
output_image = np.zeros((out_height, out_width, 3), dtype = np.uint8)
# 遍历输出图像的每个像素,分别计算其在输入图像中最近的像素坐标,并将其像素值赋值给当前像素
for out_y in range(out_height):
for out_x in range(out_width):
# 计算当前像素在输入图像中的坐标
input_x = int(round(out_x / scale_factor))
input_y = int(round(out_y / scale_factor))
# 判断计算出来的输入像素坐标是否越界,如果越界则赋值为边界像素
input_x = min(input_x, width - 1)
input_y = min(input_y, height - 1)
# 将输入像素的像素值赋值给输出像素
output_image[out_y, out_x] = image[input_y, input_x]
return output_image这个是通过输入原始图像和目标图像的高和宽来对图像进行邻近插值:
def nearest_neighbor_interpolation2(image, target_height, target_width):
"""
Nearest neighbor interpolation algorithm
:param image: Input image array
:param target_height: Target height of the output image
:param target_width: Target width of the output image
:return: Output image array
"""
# Input image dimensions
height, width = image.shape[:2]
# Create output image
output_image = np.zeros((target_height, target_width, 3), dtype=np.uint8)
# Calculate scaling factors
scale_x = target_width / width
scale_y = target_height / height
# Traverse each pixel in the output image, calculate the nearest pixel coordinates in the input image,
# and assign its pixel value to the current pixel
for out_y in range(target_height):
for out_x in range(target_width):
# Calculate the nearest pixel coordinates in the input image
input_x = int(round(out_x / scale_x))
input_y = int(round(out_y / scale_y))
# Ensure that the calculated input pixel coordinates are within the bounds of the input image
input_x = min(input_x, width - 1)
input_y = min(input_y, height - 1)
# Assign the pixel value of the input pixel to the output pixel
output_image[out_y, out_x] = image[input_y, input_x]
return output_image使用第二个函数将图像进行可视化:
# 读取图像
image_path = "D:\\My Data\\Figure\\下载.jpg"
image = np.array(Image.open(image_path))
# 目标图像大小
target_height, target_width = 512, 512
# 使用自定义线性插值对图像进行缩放
output_image = nearest_neighbor_interpolation2(image, target_height, target_width)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 可视化处理后的图像
plt.imshow(output_image)
plt.axis('off') # 关闭坐标轴
plt.show()torch官方定义的函数
F.interpolate(image_tensor, size=(target_height, target_width), mode='nearest')
from PIL import Image
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 读取图像
image_path = "D:\\My Data\\Figure\\下载.jpg"
image = Image.open(image_path)
# 将图像转换为 PyTorch 张量,并添加批量维度
image_tensor = torch.tensor(np.array(image), dtype=torch.float32).permute(2, 0, 1).unsqueeze(0)
# 目标图像大小
target_height, target_width = 512, 512
# 使用最近邻插值对图像进行缩放
output_nearest = F.interpolate(image_tensor, size=(target_height, target_width), mode='nearest')
# 将张量转换回 numpy 数组
output_nearest_array = output_nearest.squeeze().permute(1, 2, 0).numpy().astype(np.uint8)
将图像进行可视化
# 可视化处理后的图像
plt.imshow(output_nearest_array)
plt.axis('off') # 关闭坐标轴
plt.show()双线性插值
自定义函数
corner_align=False为不使用角对齐为边对齐,True为使用角对齐,这个是处理灰度图像的双线性插值
import numpy as np
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
def bilinear_interpolation(image, out_height, out_width, corner_align=False):
# 获取输入图像的宽高
height, width = image.shape[:2]
# 创建输出图像
output_image =np.zeros((out_height, out_width), dtype=np.float32)
# 计算x、y轴缩放因子
scale_x_corner = float(width - 1) / (out_width - 1) # (3-1)/(5-1)=0.5
scale_y_corner = float(height - 1) / (out_height - 1) # (3-1)/(5-1)=0.5
scale_x = float(width) / out_width # 3/5=0.6
scale_y = float(height) / out_height
# 遍历输出图像的每个像素,分别计算其在输入图像中最近的四个像素的坐标,然后按照加权值计算当前像素的像素值
for out_y in range(out_height):
for out_x in range(out_width):
if corner_align == True:
# 计算当前像素在输入图像中的位置
x = out_x * scale_x_corner
y = out_y * scale_y_corner
else:
x = (out_x + 0.5) * scale_x - 0.5
y = (out_y + 0.5) * scale_y - 0.5
x = np.clip(x, 0, width - 1)
y = np.clip(y, 0, height - 1)
# 获取当前像素在输入图像中最近的四个像素的坐标
x0, y0 = int(x), int(y)
x1, y1 = x0 + 1, y0 + 1
#对原图像边缘进行特殊处理
if x0 == width - 1:
xθ = width - 2
x1 = width - 1
if y0 == height - 1:
yθ = height - 2
y1 = height - 1
xd = x - x0
yd = y - y0
p00 = image[y0, x0]
p01 = image[y0, x1]
p10 = image[y1, x0]
p11 = image[y1, x1]
x0y = p01 * xd + (1 - xd) * p00
x1y = p11 * xd + (1 - xd) * p10
output_image[out_y, out_x] = x1y * yd + (1 - yd) * x0y
return output_image
def bilinear_interpolation(image,out_height, out_width, corner_align=False):
# 获取输入图像的宽高
height, width = image.shape[:2]
# 创建输出图像
output_image =np.zeros((out_height, out_width),dtype=np.float32)
# 计算x、y轴缩放因子
scale_x_corner = float(width - 1) / (out_width - 1) # (3-1)/(5-1)=0.5
scale_y_corner = float(height - 1) / (out_height - 1) # (3-1)/(5-1)=0.5
scale_x = float(width) / out_width # 3/5=0.6
scale_y = float(height) / out_height
# 遍历输出图像的每个像素,分别计算其在输入图像中最近的四个像素的坐标,然后按照加权值计算当前像素的像素值
for out_y in range(out_height):
for out_x in range(out_width):
if corner_align == True:
# 计算当前像素在输入图像中的位置
x = out_x * scale_x_corner
y = out_y * scale_y_corner
else:
x =(out_x + 0.5)* scale_x - 0.5
y =(out_y + 0.5)* scale_y - 0.5
x = np.clip(x, 0 , width - 1)
y = np.clip(y, 0 , height - 1)
# 获取当前像素在输入图像中最近的四个像素的坐标
x0, y0 = int(x), int(y)
x1, y1 = x0 + 1, y0 + 1
#对原图像边缘进行特殊处理
if x0 == width -1:
xθ = width - 2
x1 = width - 1
if y0 == height -1:
yθ = height - 2
y1 = height - 1
xd = x - x0
yd = y - y0
p00 = image[y0, x0]
p01 = image[y0, x1]
p10 = image[y1, x0]
p11 = image[y1, x1]
x0y = p01 * xd +(1 - xd) * p00
x1y = p11 * xd +(1 - xd) * p10
output_image[out_y, out_x] = x1y * yd +(1 - yd) * x0y
return output_image我们随机生成一张3×3的图像,与torch中的代码进行比较,查看输出结果:
image_array = np.random.rand(3,3)
image = torch.as_tensor(image_array, dtype=torch.float32).unsqueeze(0).unsqueeze(0)
result = F.interpolate(image, size = (5, 5), mode='bilinear', align_corners=False)
result1 = F.interpolate(image, size = (5, 5), mode='bilinear', align_corners=True)
image = bilinear_interpolation(image_array, 5, 5, corner_align=False)
image1 = bilinear_interpolation(image_array, 5, 5, corner_align=True)
print('image:', image)
print('result:', result)
print('image1:', image1)
print('result1:', result1)
输出结果对比
image: [[0.8258898 0.82657003 0.8275904 0.6760163 0.5749669 ]
[0.6941199 0.68340033 0.667321 0.5252699 0.4305692 ]
[0.49646503 0.46864578 0.42691696 0.29915038 0.21397266]
[0.4779709 0.5350506 0.62067014 0.63449866 0.64371765]
[0.46564147 0.57932043 0.74983895 0.8580642 0.9302143 ]]
result: tensor([[[[0.8259, 0.8266, 0.8276, 0.6760, 0.5750],
[0.6941, 0.6834, 0.6673, 0.5253, 0.4306],
[0.4965, 0.4686, 0.4269, 0.2992, 0.2140],
[0.4780, 0.5351, 0.6207, 0.6345, 0.6437],
[0.4656, 0.5793, 0.7498, 0.8581, 0.9302]]]])
image1: [[0.8258898 0.8267401 0.8275904 0.7012786 0.5749669 ]
[0.6611774 0.6442155 0.62725365 0.5108617 0.39446977]
[0.49646503 0.461691 0.42691696 0.3204448 0.21397266]
[0.48105323 0.5347156 0.58837795 0.5802357 0.5720935 ]
[0.46564147 0.6077402 0.74983895 0.8400266 0.9302143 ]]
result1: tensor([[[[0.8259, 0.8267, 0.8276, 0.7013, 0.5750],
[0.6612, 0.6442, 0.6273, 0.5109, 0.3945],
[0.4965, 0.4617, 0.4269, 0.3204, 0.2140],
[0.4811, 0.5347, 0.5884, 0.5802, 0.5721],
[0.4656, 0.6077, 0.7498, 0.8400, 0.9302]]]])进程已结束,退出代码0
这个是处理彩色图像3通道的双线性插值:不一样的地方为output_image = np.zeros((out_height, out_width, 3), dtype=np.uint8)。
def bilinear_interpolation(image, out_height, out_width, corner_align=False):
height, width = image.shape[:2]
output_image = np.zeros((out_height, out_width, 3), dtype=np.uint8)
scale_x_corner = float(width - 1) / (out_width - 1)
scale_y_corner = float(height - 1) / (out_height - 1)
scale_x = float(width) / out_width
scale_y = float(height) / out_height
for out_y in range(out_height):
for out_x in range(out_width):
if corner_align:
x = out_x * scale_x_corner
y = out_y * scale_y_corner
else:
x = (out_x + 0.5) * scale_x - 0.5
y = (out_y + 0.5) * scale_y - 0.5
x = np.clip(x, 0, width - 1)
y = np.clip(y, 0, height - 1)
x0, y0 = int(x), int(y)
x1, y1 = x0 + 1, y0 + 1
if x0 == width - 1:
x1 = width - 1
if y0 == height - 1:
y1 = height - 1
xd = x - x0
yd = y - y0
p00 = image[y0, x0]
p01 = image[y0, x1]
p10 = image[y1, x0]
p11 = image[y1, x1]
x0y = p01 * xd + (1 - xd) * p00
x1y = p11 * xd + (1 - xd) * p10
output_image[out_y, out_x] = x1y * yd + (1 - yd) * x0y
return output_image
torch官方定义的函数
from PIL import Image
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 读取图像
image_path = "D:\\My Data\\Figure\\下载.jpg"
image = Image.open(image_path)
# 将图像转换为 PyTorch 张量,并添加批量维度
image_tensor = torch.tensor(np.array(image), dtype=torch.float32).permute(2, 0, 1).unsqueeze(0)
# 目标图像大小
target_height, target_width = 512, 512
# 使用双线性插值角对齐对图像进行缩放
output_bilinear_corners_True = F.interpolate(image_tensor, size=(target_height, target_width), mode='bilinear', align_corners=True)
# 将张量转换回 numpy 数组
output_bilinear_corners_True_array = output_bilinear_corners_True.squeeze().permute(1, 2, 0).numpy().astype(np.uint8)
# 使用双线性插值边对齐对图像进行缩放
output_bilinear_corners_False = F.interpolate(image_tensor, size=(target_height, target_width), mode='bilinear', align_corners=False)
# 将张量转换回 numpy 数组
output_bilinear_corners_False_array = output_bilinear_corners_False.squeeze().permute(1, 2, 0).numpy().astype(np.uint8)将其进行可视化
# 可视化处理后的图像
plt.imshow(output_bilinear_corners_True_array)
plt.axis('off') # 关闭坐标轴
plt.show()例子
自定义函数图像处理
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
def bilinear_interpolation(image, out_height, out_width, corner_align=False):
height, width = image.shape[:2]
output_image = np.zeros((out_height, out_width, 3), dtype=np.uint8)
scale_x_corner = float(width - 1) / (out_width - 1)
scale_y_corner = float(height - 1) / (out_height - 1)
scale_x = float(width) / out_width
scale_y = float(height) / out_height
for out_y in range(out_height):
for out_x in range(out_width):
if corner_align:
x = out_x * scale_x_corner
y = out_y * scale_y_corner
else:
x = (out_x + 0.5) * scale_x - 0.5
y = (out_y + 0.5) * scale_y - 0.5
x = np.clip(x, 0, width - 1)
y = np.clip(y, 0, height - 1)
x0, y0 = int(x), int(y)
x1, y1 = x0 + 1, y0 + 1
if x0 == width - 1:
x1 = width - 1
if y0 == height - 1:
y1 = height - 1
xd = x - x0
yd = y - y0
p00 = image[y0, x0]
p01 = image[y0, x1]
p10 = image[y1, x0]
p11 = image[y1, x1]
x0y = p01 * xd + (1 - xd) * p00
x1y = p11 * xd + (1 - xd) * p10
output_image[out_y, out_x] = x1y * yd + (1 - yd) * x0y
return output_image
def nearest_neighbor_interpolation(image, scale_factor):
"""
最邻近插值算法
:paraninput_array
:输入图像数组:param output_shape
:输出图像的 shape:return
:输出图像数组"""
# 输入图像的宽高
height, width = image.shape[:2]
# 计算输出图像的宽高
out_height = int(height * scale_factor)
out_width = int(width * scale_factor)
# 创建输出图像
output_image = np.zeros((out_height, out_width, 3), dtype = np.uint8)
# 遍历输出图像的每个像素,分别计算其在输入图像中最近的像素坐标,并将其像素值赋值给当前像素
for out_y in range(out_height):
for out_x in range(out_width):
# 计算当前像素在输入图像中的坐标
input_x = int(round(out_x / scale_factor))
input_y = int(round(out_y / scale_factor))
# 判断计算出来的输入像素坐标是否越界,如果越界则赋值为边界像素
input_x = min(input_x, width - 1)
input_y = min(input_y, height - 1)
# 将输入像素的像素值赋值给输出像素
output_image[out_y, out_x] = image[input_y, input_x]
return output_image
#读取原始图像
input_image = Image.open("D:\My Data\Figure\下载.jpg")
image_array = np.array(input_image)
image_tensor = torch.as_tensor(image_array, dtype=torch.float32)
# 添加批量维度,并将通道维度放在第二个位置
image_tensor = image_tensor.permute(2, 0, 1).unsqueeze(0) # 转换为 (3, 288, 200) 的张量
#最近邻插值输出缩放后的图像
output_array = nearest_neighbor_interpolation(image_array,1.5)
output_nearest_neighbor_interpolation = Image.fromarray(output_array)
#双线性插值输出缩放后的图像,使用角对齐
output_bilinear_corner_True = bilinear_interpolation(image_array, 512, 512, corner_align=True)
# output_bilinear_corner_True = Image.fromarray(output_bilinear_corner_True)
# output_bilinear_corner_True = F.interpolate(image_tensor, size = (512, 512), mode='bilinear', align_corners=True)
# output_bilinear_corner_True =output_bilinear_corner_True.squeeze().permute(1, 2, 0).numpy().astype(np.uint8)
#双线性插值输出缩放后的图像,使用边对齐
output_bilinear_corner_False = bilinear_interpolation(image_array, 512, 512, corner_align=False)
# output_bilinear_corner_False = Image.fromarray(output_bilinear_corner_False)
# output_bilinear_corner_False = F.interpolate(image_tensor, size = (512, 512), mode='bilinear', align_corners=False)
# output_bilinear_corner_False = output_bilinear_corner_False.squeeze().permute(1, 2, 0).numpy().astype(np.uint8)
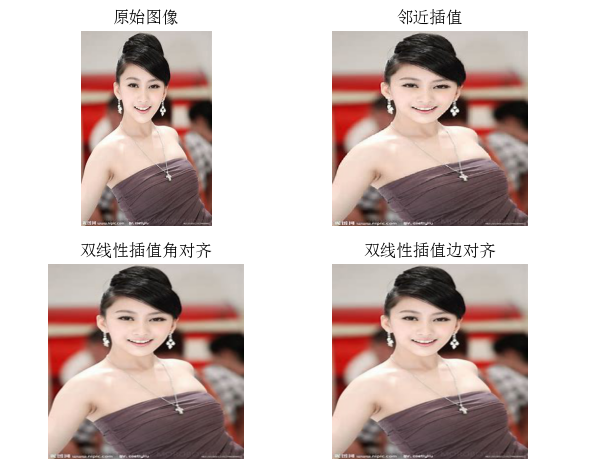
print('原始图像 :', image_array.shape )
print('邻近插值 :', output_array.shape )
print('双线性插值角对齐:', output_bilinear_corner_True.shape )
print('双线性插值边对齐 :', output_bilinear_corner_False.shape )
# 设置中文字体
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimSun']# 创建一个包含四个子图的画布
# 创建一个包含四个子图的画布
fig, axes = plt.subplots(2, 2)
# 第一张子图:原始图像
axes[0, 0].imshow(input_image)
axes[0, 0].set_title('原始图像')
axes[0, 0].axis('off')
# 第二张子图:插值后的图像
axes[0, 1].imshow(output_nearest_neighbor_interpolation)
axes[0, 1].set_title('邻近插值')
axes[0, 1].axis('off')
# 第三张子图:缩放后的图像
axes[1, 0].imshow(output_bilinear_corner_True)
axes[1, 0].set_title('双线性插值角对齐')
axes[1, 0].axis('off')
# 第四张子图:其他图像(你想添加的图像)
axes[1, 1].imshow(output_bilinear_corner_False)
axes[1, 1].set_title('双线性插值边对齐')
axes[1, 1].axis('off')
# 调整布局,防止标题重叠
plt.tight_layout()
# 展示图像
plt.show()
torch官方函数处理图像对比
from PIL import Image
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 读取图像
image_path = "D:\\My Data\\Figure\\下载.jpg"
image = Image.open(image_path)
# 将图像转换为 PyTorch 张量,并添加批量维度
image_tensor = torch.tensor(np.array(image), dtype=torch.float32).permute(2, 0, 1).unsqueeze(0)
# 目标图像大小
target_height, target_width = 512, 512
# 使用最近邻插值对图像进行缩放
output_nearest = F.interpolate(image_tensor, size=(target_height, target_width), mode='nearest')
# 将张量转换回 numpy 数组
output_nearest_array = output_nearest.squeeze().permute(1, 2, 0).numpy().astype(np.uint8)
# 使用双线性插值角对齐对图像进行缩放
output_bilinear_corners_True = F.interpolate(image_tensor, size=(target_height, target_width), mode='bilinear', align_corners=True)
# 将张量转换回 numpy 数组
output_bilinear_corners_True_array = output_bilinear_corners_True.squeeze().permute(1, 2, 0).numpy().astype(np.uint8)
# 使用双线性插值边对齐对图像进行缩放
output_bilinear_corners_False = F.interpolate(image_tensor, size=(target_height, target_width), mode='bilinear', align_corners=False)
# 将张量转换回 numpy 数组
output_bilinear_corners_False_array = output_bilinear_corners_False.squeeze().permute(1, 2, 0).numpy().astype(np.uint8)
print('原始图像:', np.array(image).shape )
print('邻近插值 :', output_nearest_array.shape )
print('双线性插值角对齐 :', output_bilinear_corners_True_array.shape )
print('双线性插值边对齐 :', output_bilinear_corners_False_array .shape )
# 设置中文字体
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimSun']# 创建一个包含四个子图的画布
fig, axes = plt.subplots(2, 2)
# 第一张子图:原始图像
axes[0, 0].imshow(image)
axes[0, 0].set_title('原始图像')
axes[0, 0].axis('off')
# 第二张子图:插值后的图像
axes[0, 1].imshow(output_nearest_array)
axes[0, 1].set_title('邻近插值')
axes[0, 1].axis('off')
# 第三张子图:缩放后的图像
axes[1, 0].imshow(output_bilinear_corners_True_array)
axes[1, 0].set_title('双线性插值角对齐')
axes[1, 0].axis('off')
# 第四张子图:其他图像(你想添加的图像)
axes[1, 1].imshow(output_bilinear_corners_False_array)
axes[1, 1].set_title('双线性插值边对齐')
axes[1, 1].axis('off')
# 调整布局,防止标题重叠
plt.tight_layout()
# 展示图像
plt.show()

参考视频:
插值算法 | 最近邻插值法_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
插值算法 |双线性插值法_哔哩哔哩_bilibili





![洛谷P1057 [NOIP2008 普及组] 传球游戏](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/ace643bca080445e94ec77ef24444b4c.png)