一、AOP概述
- AOP:Aspect Oriented Programming(面向切面编程、面向方面编程),其实就是面向特定方法编程。
- 使用场景:①记录操作日志;②权限控制;③事务管理等。
- 优势:①代码无侵入;②减少重复代码;③提高开发效率;④维护方便。
- 示例:案例部分功能运行较慢,定位执行耗时较长的业务方法,此时需要统计每一个业务方法的执行耗时。
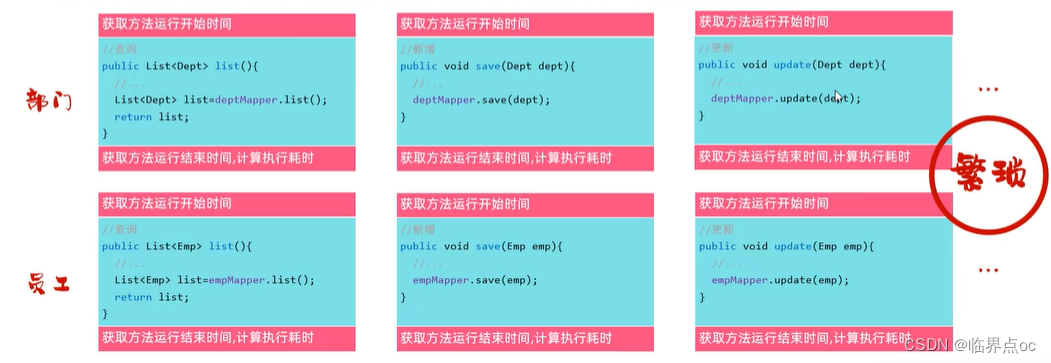
- 解决:
- 实现:动态代理是面向切面编程最主流的实现。而SpringAOP是Spring框架的高级技术,旨在管理bean对象的过程中,主要通过底层动态代理机制,对特定的方法进行编程。
- Spring AOP 入门程序:统计各个业务层方法执行耗时
①导入依赖:在pom.xml中导入AOP的依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactId>
</dependency>②编写AOP程序:针对特定方法根据业务需求进行编程
package com.itheima.aop;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Slf4j
@Component
//@Aspect //AOP类
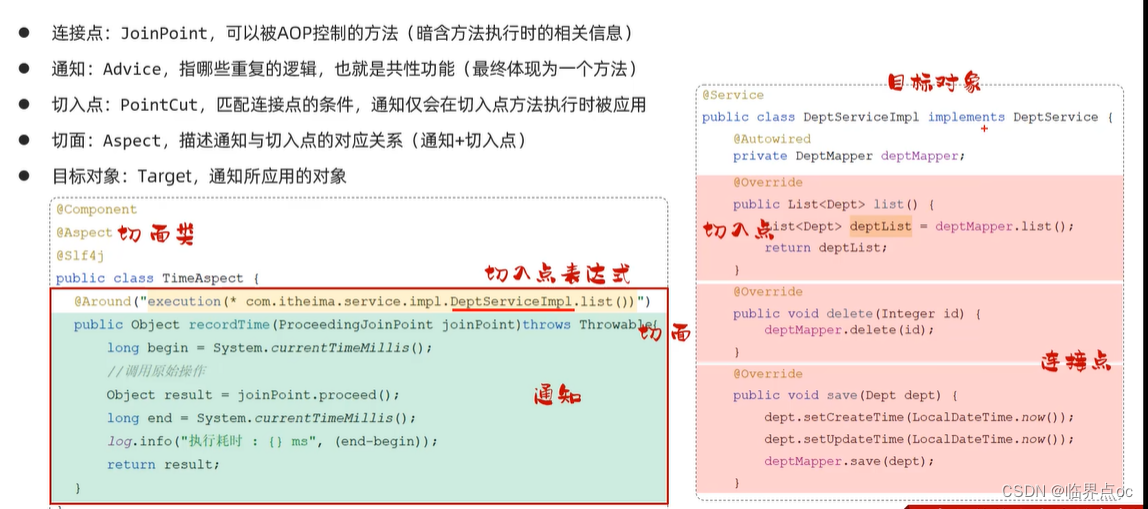
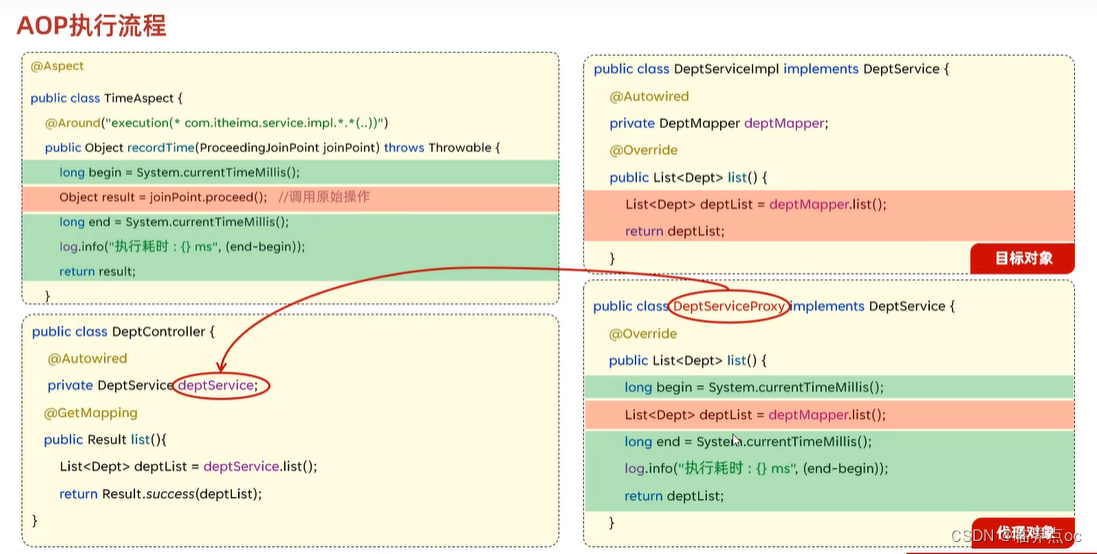
public class TimeAspect {
@Around("execution(* com.itheima.service.impl.DeptServiceImpl.*(..))") //切入点表达式
// @Around("com.itheima.aop.MyAspect1.pt()")
public Object recordTime(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
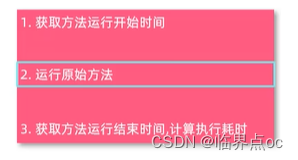
//1. 记录开始时间
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
//2. 调用原始方法运行
Object result = joinPoint.proceed();
//3. 记录结束时间, 计算方法执行耗时
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
log.info(joinPoint.getSignature()+"方法执行耗时: {}ms", end-begin);
return result;
}
}
二、AOP核心概念
- 连接点:JoinPoint,可以被AOP控制的方法(暗含方法执行时的相关信息)
- 通知:Advice,指那些重复的逻辑,也就是共性功能(最终体现为一个方法)
- 切入点:PointCut,匹配连接点的条件,通知仅会在切入点方法执行时被应用
- 切面:Aspect,描述通知与切入点的对应关系(通知+切入点)
- 目标对象:Target,通知所应用的对象
三、AOP进阶
1. 通知类型
| 通知类型 | 含义 |
| @Around | 环绕通知,此注解标注的通知方法在目标方法前、后都被执行 |
| @Before | 前置通知,此注解标注的通知方法在目标方法前被执行 |
| @After | 后置通知,此注解标注的通知方法在目标方法后被执行,无论是否有异常都会执行 |
| @AfterReturning | 返回后通知,此注解标注的通知方法在目标方法后被执行,有异常不会执行 |
| @AfterThrowing | 异常后通知,此注解标注的通知方法发生异常后运行 |
注意事项
@Around环绕通知需要自己调用ProceedingJoinPoint.proceed()来让原始方法执行,其他通知不需要考虑目标方法执行
@Around环绕通知方法的返回值,必须指定为Object,来接收原始方法的返回值。
@PointCut
该注解的作用是将公共的切入点表达式抽取出来,需要用到时引用该切入点表达式即可。
private:仅能在当前切面类中引用该表达式
public:在其他外部的切面类中也可以引用该表达式
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Slf4j // 开启日志
@Component
@Aspect
public class MyAspect1 {
// 抽取共同方法
// 切入点表达式
@Pointcut("execution(* com.itheima.service.impl.DeptServiceImpl.*(..))")
public void pt(){}
@Before("pt()")
public void before(){
log.info("before ...");
}
@Around("pt()")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint) throws Throwable {
log.info("around before ...");
//调用目标对象的原始方法执行
Object result = proceedingJoinPoint.proceed();
log.info("around after ...");
return result;
}
@After("pt()")
public void after(){
log.info("after ...");
}
@AfterReturning("pt()")
public void afterReturning(){
log.info("afterReturning ...");
}
@AfterThrowing("pt()")
public void afterThrowing(){
log.info("afterThrowing ...");
}
}
2. 通知顺序
当有多个切面的切入点都匹配到了目标方法,目标方法运行时,多个通知都会被执行。
执行顺序:
1. 不同切面类中,默认按照切面类的类名字母排序:①目标方法前的通知方法:字母排名靠前的先执行;②目标方法后的通知方法:字母排名靠前的前后执行。
2. 用@Order(数字)加在切面类上来控制顺序:①目标方法前的通知方法:数字小的先执行;②目标方法后的通知方法:数字小的后执行。
示例1:没加@order注解
package com.itheima.aop;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.After;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.Order;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
// @Order(3)
@Slf4j
@Component
@Aspect
public class MyAspect2 {
@Before("execution(* com.itheima.service.impl.DeptServiceImpl.*(..))")
public void before(){
log.info("before ...2");
}
@After("execution(* com.itheima.service.impl.DeptServiceImpl.*(..))")
public void after(){
log.info("after ...2");
}
}
package com.itheima.aop;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.After;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.Order;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
// @Order(1)
@Slf4j
@Component
@Aspect
public class MyAspect3 {
@Before("execution(* com.itheima.service.impl.DeptServiceImpl.*(..))")
public void before(){
log.info("before ...3");
}
@After("execution(* com.itheima.service.impl.DeptServiceImpl.*(..))")
public void after(){
log.info("after ...3");
}
}
package com.itheima.aop;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.After;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.Order;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
// @Order(2)
@Slf4j
@Component
@Aspect
public class MyAspect4 {
@Before("execution(* com.itheima.service.impl.DeptServiceImpl.*(..))")
public void before(){
log.info("before ...4");
}
@After("execution(* com.itheima.service.impl.DeptServiceImpl.*(..))")
public void after(){
log.info("after ...4");
}
}
运行结果:

示例2:加了@Order注解
package com.itheima.aop;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.After;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.Order;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Order(3)
@Slf4j
@Component
@Aspect
public class MyAspect3 {
@Before("execution(* com.itheima.service.impl.DeptServiceImpl.*(..))")
public void before(){
log.info("before ...3");
}
@After("execution(* com.itheima.service.impl.DeptServiceImpl.*(..))")
public void after(){
log.info("after ...3");
}
}
package com.itheima.aop;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.After;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.Order;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Order(1)
@Slf4j
@Component
@Aspect
public class MyAspect4 {
@Before("execution(* com.itheima.service.impl.DeptServiceImpl.*(..))")
public void before(){
log.info("before ...4");
}
@After("execution(* com.itheima.service.impl.DeptServiceImpl.*(..))")
public void after(){
log.info("after ...4");
}
}
package com.itheima.aop;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.After;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.Order;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Order(2)
@Slf4j
@Component
@Aspect
public class MyAspect5 {
@Before("execution(* com.itheima.service.impl.DeptServiceImpl.*(..))")
public void before(){
log.info("before ...5");
}
@After("execution(* com.itheima.service.impl.DeptServiceImpl.*(..))")
public void after(){
log.info("after ...5");
}
}
运行结果:

3. 切入点表达式
定义:描述切入点方法的一种表达式。
作用:主要用来决定项目中的哪些方法需要加入通知
常见形式:
1. execution(……):根据方法的签名来匹配
2. @annotation(……):根据注解匹配
①切入点表达式——execution
execution主要根据方法的返回值、包名、类名、方法名、方法参数等信息来匹配,语法为:
execution(访问修饰符? 返回值 包名.类名.?方法名(方法参数) throws 异常?)
其中带 '?' 的表示可以省略的部分
访问修饰符:可省略(比如:public、protected)
包名.类名:可省略,但不建议省略,否则匹配范围太大了,降低性能
throws异常:可省略(注意是方法上声明抛出的异常,不是实际抛出的异常)
可以使用通配符描述切入点
- * :单个独立的任意符号,可以统配任意返回值、包名、类名、方法名、任意类型的一个参数,也可以通配包、类、方法名的一部分
execution(* com.*.service.*.update*(*))
- .. :多个连续的任意符号,可以通配任意层级的包,或任意类型、任意个数的参数
execution(*com.itheima.DeptService.*(..))
书写建议
- 所有业务方法名在命名时尽量规范,方便切入点表达式快速匹配。如,查询类方法都是find开头,更新类方法都是update开头;
- 描述切入点方法通常基于接口描述,而不是直接描述实现类,增强拓展性;
- 在满足业务需要的前提下,尽量缩小切入点的匹配范围。如,包名匹配尽量不适用 .. ,使用 * 匹配单个包。
示例:
package com.itheima.aop;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
//切面类
@Slf4j
@Aspect
@Component
public class MyAspect6 {
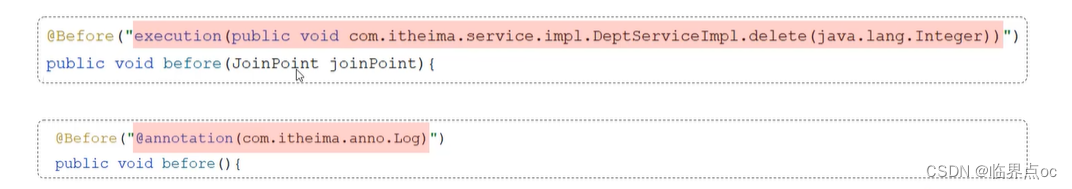
//@Pointcut("execution(public void com.itheima.service.impl.DeptServiceImpl.delete(java.lang.Integer))")
//@Pointcut("execution(void com.itheima.service.impl.DeptServiceImpl.delete(java.lang.Integer))")
//@Pointcut("execution(void delete(java.lang.Integer))") //包名.类名不建议省略
//@Pointcut("execution(void com.itheima.service.DeptService.delete(java.lang.Integer))")
//@Pointcut("execution(void com.itheima.service.DeptService.*(java.lang.Integer))")
//@Pointcut("execution(* com.*.service.DeptService.*(*))")
//@Pointcut("execution(* com.itheima.service.*Service.delete*(*))")
//@Pointcut("execution(* com.itheima.service.DeptService.*(..))")
//@Pointcut("execution(* com..DeptService.*(..))")
//@Pointcut("execution(* com..*.*(..))")
//@Pointcut("execution(* *(..))") //慎用
@Pointcut("execution(* com.itheima.service.DeptService.list()) || " +
"execution(* com.itheima.service.DeptService.delete(java.lang.Integer))")
private void pt(){}
@Before("pt()")
public void before(){
log.info("MyAspect6 ... before ...");
}
}
package com.itheima.service.impl;
import com.itheima.aop.MyLog;
import com.itheima.mapper.DeptMapper;
import com.itheima.pojo.Dept;
import com.itheima.service.DeptService;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.util.List;
@Slf4j
@Service
public class DeptServiceImpl implements DeptService {
@Autowired
private DeptMapper deptMapper;
//@MyLog
@Override
public List<Dept> list() {
List<Dept> deptList = deptMapper.list();
return deptList;
}
//@MyLog
@Override
public void delete(Integer id) {
//1. 删除部门
deptMapper.delete(id);
}
@Override
public void save(Dept dept) {
dept.setCreateTime(LocalDateTime.now());
dept.setUpdateTime(LocalDateTime.now());
deptMapper.save(dept);
}
@Override
public Dept getById(Integer id) {
return deptMapper.getById(id);
}
@Override
public void update(Dept dept) {
dept.setUpdateTime(LocalDateTime.now());
deptMapper.update(dept);
}
}
②切入点表达式——@annotation
@annotation切入点表达式,用于匹配标识有特定注解的方法。
@annotation(com.itheima.anno.Log)
示例:
package com.itheima.aop;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
// 定义注解
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) // 注解生效时间
@Target(ElementType.METHOD) // 注解作用域
public @interface MyLog {
}
package com.itheima.service.impl;
import com.itheima.aop.MyLog;
import com.itheima.mapper.DeptMapper;
import com.itheima.pojo.Dept;
import com.itheima.service.DeptService;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.util.List;
@Slf4j
@Service
public class DeptServiceImpl implements DeptService {
@Autowired
private DeptMapper deptMapper;
@MyLog
@Override
public List<Dept> list() {
List<Dept> deptList = deptMapper.list();
return deptList;
}
@MyLog
@Override
public void delete(Integer id) {
//1. 删除部门
deptMapper.delete(id);
}
}
package com.itheima.aop;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
//切面类
@Slf4j
//@Aspect
@Component
public class MyAspect7 {
//匹配DeptServiceImpl中的 list() 和 delete(Integer id)方法
//@Pointcut("execution(* com.itheima.service.DeptService.list()) || execution(* com.itheima.service.DeptService.delete(java.lang.Integer))")
@Pointcut("@annotation(com.itheima.aop.MyLog)")
private void pt(){}
@Before("pt()")
public void before(){
log.info("MyAspect7 ... before ...");
}
}
4. 连接点
在Spring中用JoinPoint抽象了连接点,用它可以获得方法执行时的相关信息,如目标类名、方法名、方法参数等。
- 对于@Around通知,获取连接点信息只能使用ProceedingJoinPoint
- 对于其他四种通知,获取连接点信息只能使用JoinPoint,它是ProceedingJoinPoint的父类型。
package com.itheima.aop;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.Signature;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.Arrays;
//切面类
@Slf4j
@Aspect
@Component
public class MyAspect8 {
@Pointcut("execution(* com.itheima.service.DeptService.*(..))")
private void pt(){}
@Before("pt()")
public void before(JoinPoint joinPoint){
log.info("MyAspect8 ... before ...");
String className = joinPoint.getTarget().getClass().getName(); // 获取目标类名
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature(); // 获取目标方法签名
String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName(); // 获取目标方法名
Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs(); // 获取目标方法进行参数
}
@Around("pt()")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
log.info("MyAspect8 around before ...");
//1. 获取 目标对象的类名 .
String className = joinPoint.getTarget().getClass().getName();
log.info("目标对象的类名:{}", className);
//2. 获取 目标方法的方法名 .
String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
log.info("目标方法的方法名: {}",methodName);
//3. 获取 目标方法运行时传入的参数 .
Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();
log.info("目标方法运行时传入的参数: {}", Arrays.toString(args));
//4. 放行 目标方法执行 .
Object result = joinPoint.proceed();
//5. 获取 目标方法运行的返回值 .
log.info("目标方法运行的返回值: {}",result);
log.info("MyAspect8 around after ...");
return result; // 在此处可以对返回结果进行篡改
}
}
四、AOP案列
案例1:将案列中增、删、改相关接口的操作日志记录到数据库表中。
操作日志:日志信息包括:操作人、操作时间、执行方法的全类名、执行方法名、方法运行时参数、返回值、方法执行时长。
思路分析:需要对所有业务类中的增、删、改方法添加统一功能,使用AOP技术最为方便。@Around环绕通知。

在案例工程中引入AOP的起步依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactId>
</dependency>导入资料中准备好的数据库表结构,并引入对应的实体类
-- 操作日志表
create table operate_log(
id int unsigned primary key auto_increment comment 'ID',
operate_user int unsigned comment '操作人ID',
operate_time datetime comment '操作时间',
class_name varchar(100) comment '操作的类名',
method_name varchar(100) comment '操作的方法名',
method_params varchar(1000) comment '方法参数',
return_value varchar(2000) comment '返回值',
cost_time bigint comment '方法执行耗时, 单位:ms'
) comment '操作日志表';
package com.itheima.pojo;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor // 无参构造
@AllArgsConstructor // 全参构造
public class OperateLog {
private Integer id; //ID
private Integer operateUser; //操作人ID
private LocalDateTime operateTime; //操作时间
private String className; //操作类名
private String methodName; //操作方法名
private String methodParams; //操作方法参数
private String returnValue; //操作方法返回值
private Long costTime; //操作耗时
}
package com.itheima.mapper;
import com.itheima.pojo.OperateLog;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Insert;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper;
@Mapper
public interface OperateLogMapper {
//插入日志数据
@Insert("insert into operate_log (operate_user, operate_time, class_name, method_name, method_params, return_value, cost_time) " +
"values (#{operateUser}, #{operateTime}, #{className}, #{methodName}, #{methodParams}, #{returnValue}, #{costTime});")
public void insert(OperateLog log);
}
自定义注解@Log
package com.itheima.anno;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) // 注解生效时间
@Target(ElementType.METHOD) // 注解作用范围
public @interface Log {
}
定义切面类,完成记录操作日志的逻辑
package com.itheima.utils;
import io.jsonwebtoken.Claims;
import io.jsonwebtoken.Jwts;
import io.jsonwebtoken.SignatureAlgorithm;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.Map;
public class JwtUtils {
private static String signKey = "itheima";
private static Long expire = 43200000L;
/**
* 生成JWT令牌
* @param claims JWT第二部分负载 payload 中存储的内容
* @return
*/
public static String generateJwt(Map<String, Object> claims){
String jwt = Jwts.builder()
.addClaims(claims)
.signWith(SignatureAlgorithm.HS256, signKey)
.setExpiration(new Date(System.currentTimeMillis() + expire))
.compact();
return jwt;
}
/**
* 解析JWT令牌
* @param jwt JWT令牌
* @return JWT第二部分负载 payload 中存储的内容
*/
public static Claims parseJWT(String jwt){
Claims claims = Jwts.parser()
.setSigningKey(signKey)
.parseClaimsJws(jwt)
.getBody();
return claims;
}
}
package com.itheima.aop;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject;
import com.itheima.mapper.OperateLogMapper;
import com.itheima.pojo.OperateLog;
import com.itheima.utils.JwtUtils;
import io.jsonwebtoken.Claims;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.util.Arrays;
@Slf4j
@Component
@Aspect //切面类
public class LogAspect {
@Autowired
private HttpServletRequest request;
@Autowired
private OperateLogMapper operateLogMapper;
@Around("@annotation(com.itheima.anno.Log)")
public Object recordLog(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
//操作人ID - 当前登录员工ID
//获取请求头中的jwt令牌, 解析令牌
String jwt = request.getHeader("token");
Claims claims = JwtUtils.parseJWT(jwt);
Integer operateUser = (Integer) claims.get("id");
//操作时间
LocalDateTime operateTime = LocalDateTime.now();
//操作类名
String className = joinPoint.getTarget().getClass().getName();
//操作方法名
String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
//操作方法参数
Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();
String methodParams = Arrays.toString(args);
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
//调用原始目标方法运行
Object result = joinPoint.proceed();
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
//方法返回值
String returnValue = JSONObject.toJSONString(result);
//操作耗时
Long costTime = end - begin;
//记录操作日志
OperateLog operateLog = new OperateLog(null,operateUser,operateTime,className,methodName,methodParams,returnValue,costTime);
operateLogMapper.insert(operateLog);
log.info("AOP记录操作日志: {}" , operateLog);
return result;
}
}
在需要用到操作日志的方法上加上"@Log"注解
package com.itheima.controller;
import com.itheima.anno.Log;
import com.itheima.pojo.Dept;
import com.itheima.pojo.Result;
import com.itheima.service.DeptService;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import java.util.List;
/**
* 部门管理Controller
*/
@Slf4j
@RequestMapping("/depts")
@RestController
public class DeptController {
//private static Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(DeptController.class);
@Autowired
private DeptService deptService;
/**
* 查询部门数据
* @return
*/
//@RequestMapping(value = "/depts",method = RequestMethod.GET) //指定请求方式为GET
@GetMapping
public Result list(){
log.info("查询全部部门数据");
//调用service查询部门数据
List<Dept> deptList = deptService.list();
return Result.success(deptList);
}
/**
* 删除部门
* @return
*/
@Log
@DeleteMapping("/{id}")
public Result delete(@PathVariable Integer id) throws Exception {
log.info("根据id删除部门:{}",id);
//调用service删除部门
deptService.delete(id);
return Result.success();
}
/**
* 新增部门
* @return
*/
@Log
@PostMapping
public Result add(@RequestBody Dept dept){
log.info("新增部门: {}" , dept);
//调用service新增部门
deptService.add(dept);
return Result.success();
}
}