一,框架介绍
-
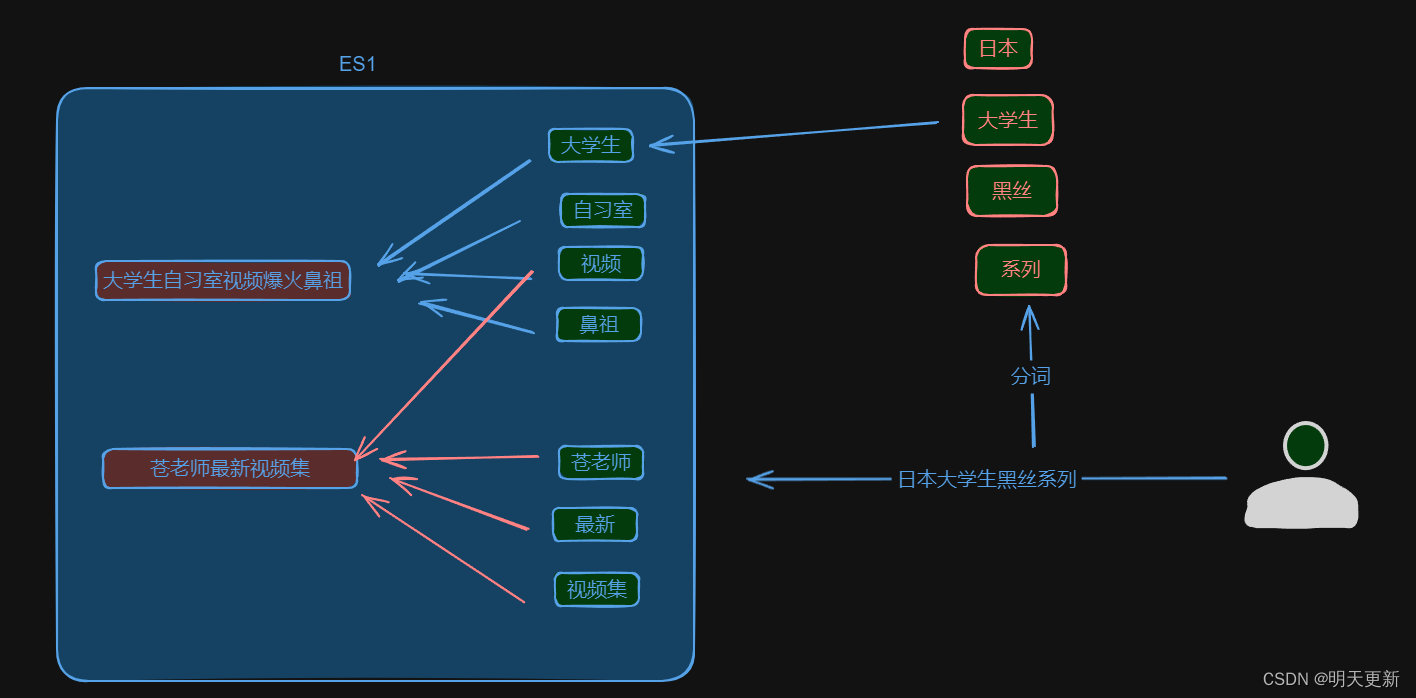
Spring 是一个非常流行和成功的 Java 应用开发框架。Spring Security 基于 Spring 框架,提供了一套 Web 应用安全性的完整解决方案。一般来说,Web 应用的安全性包括用户认证(Authentication)和用户授权(Authorization)两个部分。(1)用户认证指的是:验证某个用户是否为系统中的合法主体,也就是说用户能否访问该系统。用户认证一般要求用户提供用户名和密码。系统通过校验用户名和密码来完成认证过程。
(2)用户授权指的是验证某个用户是否有权限执行某个操作。在一个系统中,不同用户所具有的权限是不同的。比如对一个文件来说,有的用户只能进行读取,而有的用户可以进行修改。一般来说,系统会为不同的用户分配不同的角色,而每个角色则对应一系列的权限。
Spring Security其实就是用filter,多请求的路径进行过滤。
(1)如果是基于Session,那么Spring-security会对cookie里的sessionid进行解析,找到服务器存储的sesion信息,然后判断当前用户是否符合请求的要求。
(2)如果是token,则是解析出token,然后将当前请求加入到Spring-security管理的权限信息中去
-
认证与授权实现思路
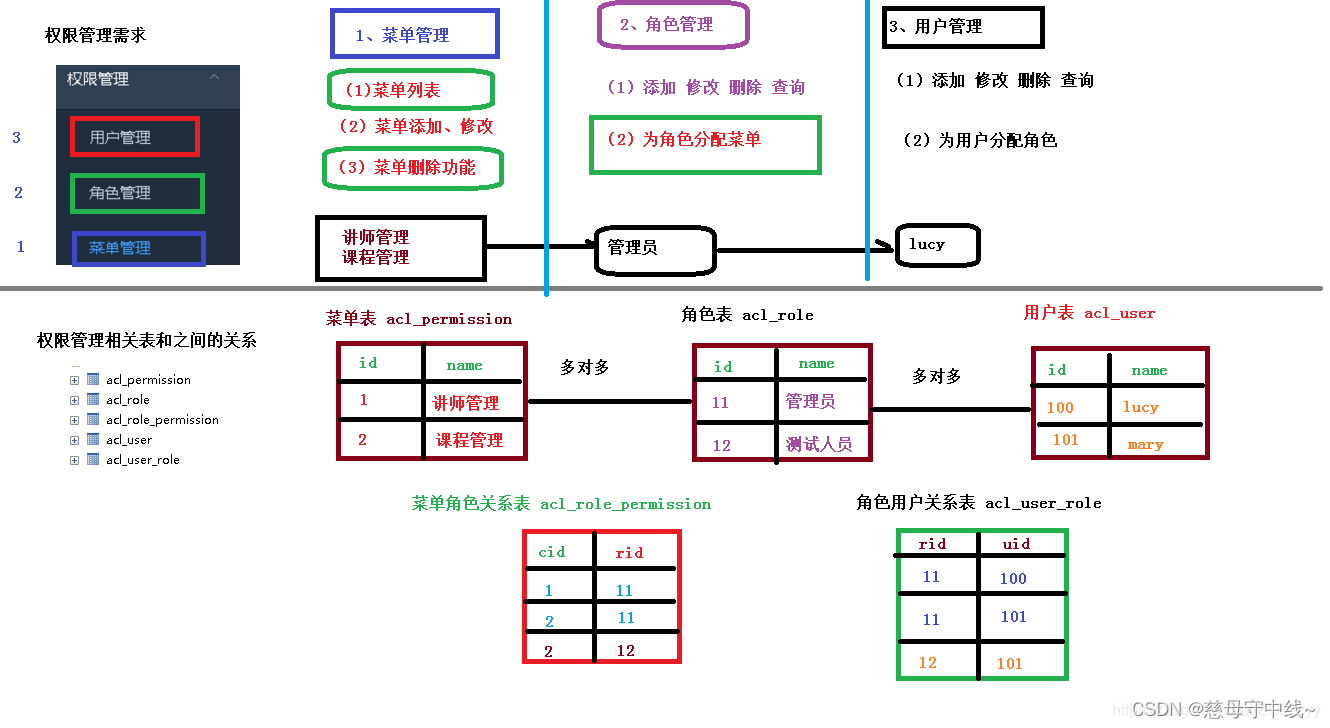
二 ,如何实现
1 ,导入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>2,代码
package com.demo.config;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.authentication.builders.AuthenticationManagerBuilder;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.EnableWebSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.WebSecurityConfiguration;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetails;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UsernameNotFoundException;
@EnableWebSecurity
public class Security extends WebSecurityConfiguration {
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/public/**").permitAll() // 允许访问公开路径
.antMatchers("/public/index").hasRole("vip") // 需要指定用户在可以使用
.antMatchers("/admin/**").hasRole("admin") // 需要指定用户在可以使用
.anyRequest().authenticated() // 其他请求需要认证
.and()
.formLogin() // 使用表单登录
.loginPage("/login") // 指定登录页面
.permitAll() // 允许所有用户访问登录页面
.and()
.logout() // 配置注销
.logoutUrl("/logout") // 注销路径
.logoutSuccessUrl("/login?logout") // 注销成功后跳转的页面
.permitAll();
}
//缓存中
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth.inMemoryAuthentication()
//添加 名字为 admin 密码 为 admin123 的用户 基于权限 ADMIN
.withUser("admin").password("admin123").roles("ADMIN")
.and()
.withUser("user").password("user123").roles("USER");
}
//从数据库中
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException {
// 从数据库或其他数据源加载用户信息
// 这里简单起见,直接使用内存中的用户信息
if ("admin".equals(username)) {
return org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.User.builder()
.username("admin")
.password("{noop}admin") // {noop}表示不加密,实际项目中应该使用加密的密码
.roles("ADMIN")
.build();
} else if ("user".equals(username)) {
return org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.User.builder()
.username("user")
.password("{noop}user")
.roles("USER")
.build();
} else {
throw new UsernameNotFoundException("User not found");
}
}
}
import org.springframework.security.access.annotation.Secured;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
@Controller
public class MyController {
@GetMapping("/user")
@Secured("ROLE_USER") // 要求用户具有ROLE_USER角色才能访问
public String userPage() {
return "user";
}
}import org.springframework.security.access.prepost.PreAuthorize;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
@Controller
public class MyController {
@GetMapping("/admin")
@PreAuthorize("hasRole('ADMIN')") // 要求用户具有ROLE_ADMIN角色才能访问
public String adminPage() {
return "admin";
}
@GetMapping("/user")
@PreAuthorize("hasRole('USER')") // 要求用户具有ROLE_USER角色才能访问
public String userPage() {
return "user";
}
}