前言
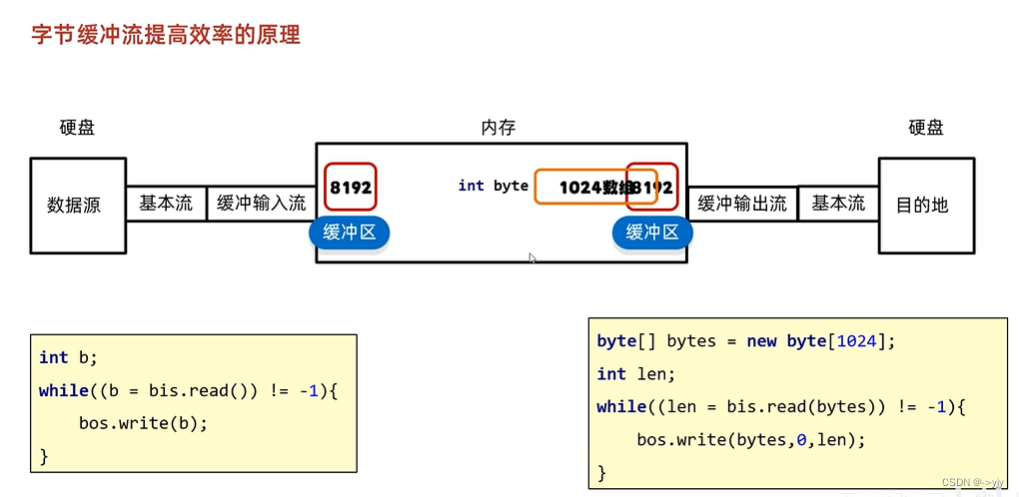
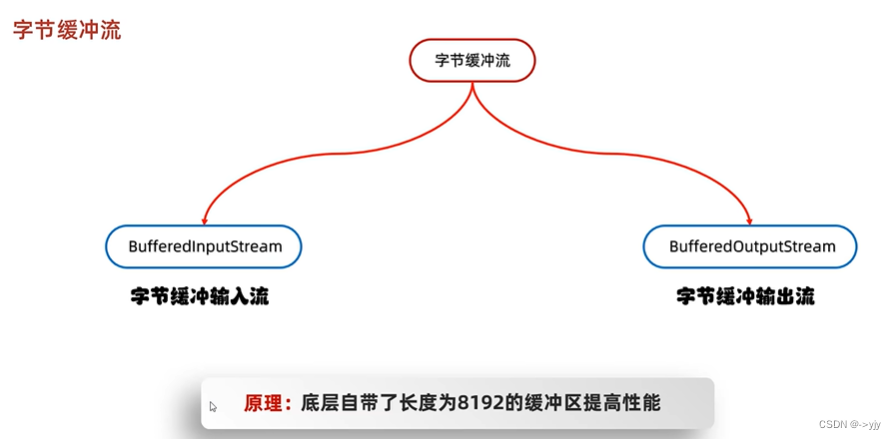
缓冲区能够提升输入输出的效率
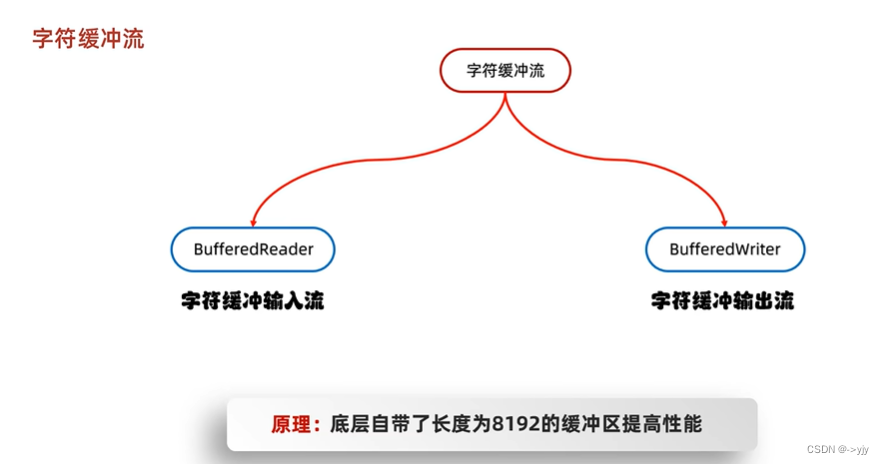
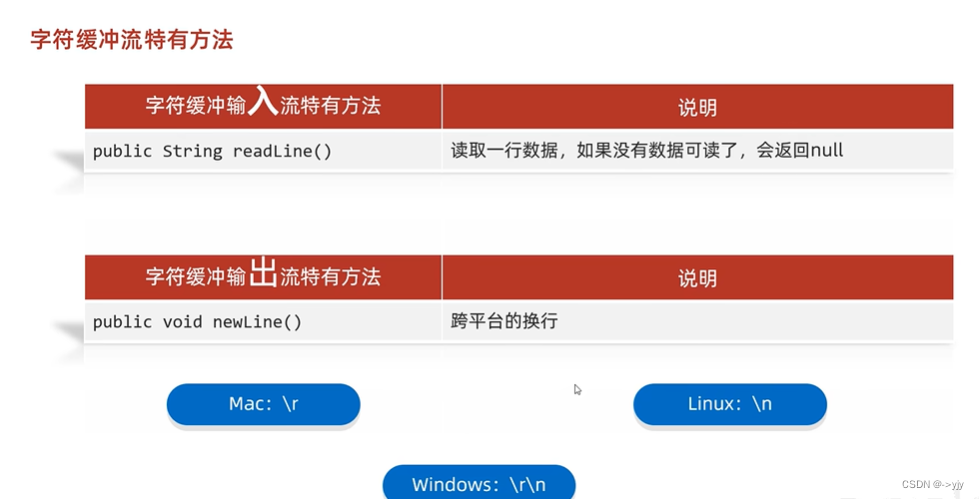
虽然FileReader和FileWriter中也有缓冲区 但是BufferedReader和BufferWriter有两个非常好用的方法.
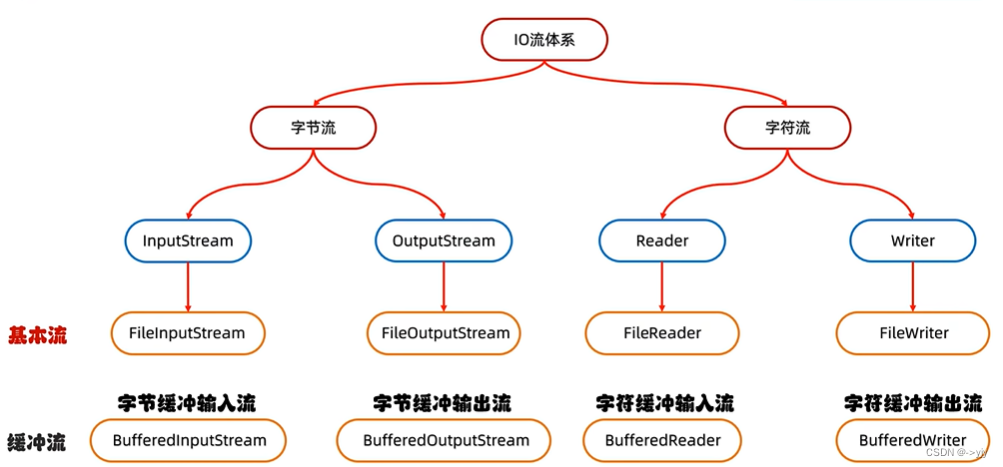
缓冲流
字节缓冲流
import java.io.*;
public class BufferedStreamDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1.创建缓冲流的对象
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("Myio\\a.txt"));
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("Myio\\copy.txt"));
//2.循环读取并写到目的地
int b;
while((b=bis.read())!=-1){
bos.write(b);
}
//3.释放资源
bos.close();//内部把基本流关闭了
bis.close();
}
}import java.io.*;
public class BufferedStreamDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1.创建缓冲流的对象
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("Myio\\a.txt"));
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("Myio\\copy2.txt"));
//2.拷贝(一次读写多个字节)
byte[] bytes= new byte[1024];
int len;
while((len=bis.read(bytes))!=-1){
bos.write(bytes,0,len);
}
bis.close();
bos.close();
}
}字符缓冲流
import java.io.*;
public class BufferedStreamDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1.创建字符缓冲输入流的对象
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("Myio\\a.txt"));
//2.读取数据
//细节:readLine方法在读取的时候,一次读一整行,遇到回车换行结束
// 但是他不会把回车换行读到内存当中
// String line = br.readLine();
// System.out.println(line);
String line;
while((line=br.readLine())!=null){
System.out.println(line);
}
//3.释放资源
br.close();
}
}import java.io.*;
public class BufferedStreamDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1.创建字符缓冲输出流的对象
BufferedWriter bw= new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("b.txt",true));
//2.写出数据
bw.write("ggg");
bw.newLine();
bw.write("dddd");
bw.newLine();
//释放资源
bw.close();
}
}
练习

import java.io.*;
public class BufferedStreamDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
/*
四种方法拷贝文件,并统计各自用时
*/
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
method1();
method2(); //16.235
method3();//137.391秒
method4();//18.488秒
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println((end-start)/1000.0+"秒");
}
//字节流的基本流,一次读写一个字节
public static void method1() throws IOException {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("Myio\\a.txt");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("Myio\\b.txt");
int ch;
while((ch=fis.read())!=-1){
fos.write(ch);
}
fis.close();
fos.close();
}
//字节流的基本流,一次读写一个字节数组
public static void method2() throws IOException {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("Myio\\a.txt");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("Myio\\b.txt");
byte[] bytes = new byte[8192];
int len;
while((len=fis.read(bytes))!=-1){
fos.write(bytes,0,len);
}
fos.close();
fis.close();
}
//字节流的基本流:一次读写一个字节数组
public static void method3() throws IOException {
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("Myio\\a.txt"));
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("Myio\\b.txt"));
int b;
while((b=bis.read())!=-1){
bos.write(b);
}
bos.close();
bis.close();
}
//字节流的基本流,一次读写一个字节数组
public static void method4() throws IOException {
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("Myio\\a.txt"));
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("Myio\\b.txt"));
byte[] bytes = new byte[8192];
int b;
while((b=bis.read(bytes))!=-1){
bos.write(bytes,0,b);
}
bis.close();
bos.close();
}
}


import java.io.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Comparator;
public class BufferedStreamDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
/*
需求:把<出师表>的文章顺序进行回复到一个新文件中
*/
//1.读取数据
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("Myio\\csb.txt"));
String line;
ArrayList<String>list = new ArrayList<>();
while((line=br.readLine())!=null){
// System.out.println(line);
list.add(line);
}
br.close();
//2.排序
//排序规则:按照每一行前面的序号进行排序
Collections.sort(list, new Comparator<String>() {
@Override
public int compare(String o1, String o2) {
//获取o1和o2的序号
int i1 = Integer.parseInt(o1.split("\\.")[0]);
int i2 = Integer.parseInt(o2.split("\\.")[0]);
return i1- i2;
}
});
//3.写出
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("Myio\\result.txt"));
for(String str:list){
bw.write(str);
bw.newLine();
}
bw.close();
}
}import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class BufferedStreamDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
/*
需求:把<出师表>的文章顺序进行回复到一个新文件中
*/
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("Myio\\a.txt"));
String line;
TreeMap<Integer,String>tm = new TreeMap<>();
while((line=br.readLine())!=null){
String[] arr = line.split("\\.");
//0:序号 1:内容
tm.put(Integer.parseInt(arr[0]),arr[1]);
}
br.close();
//2.写出数据
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("Myio\\result2.txt"));
Set<Map.Entry<Integer,String>>entries = tm.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<Integer, String> entry : entries) {
String value = entry.getValue();
bw.write(value);
bw.newLine();
}
bw.close();
}
}

public class BufferedStreamDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//次数 计算器 因为变量在内存中每次会被清0 但是可以保存在文件中记录当前次数
//1.把文件中的数字读取到内存中
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("Myio\\count.txt"));
String line = br.readLine();
int count = Integer.parseInt(line);
//表示当前文件又运行了一次
count++;
//2.判断
if(count<=3){
System.out.println("欢迎使用本软件,第"+count+"次使用免费");
}else{
System.out.println("本软件只能免费使用3次,欢迎注册会员后继续使用");
}
//3.把当前自增之后的写到文件当中
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("Myio\\count.txt"));
//不能写到上面 原则:IO:随时随用,什么时候不用什么时候关闭 不然会出错
bw.write(count+"");//97 + ""
bw.close();
}
}
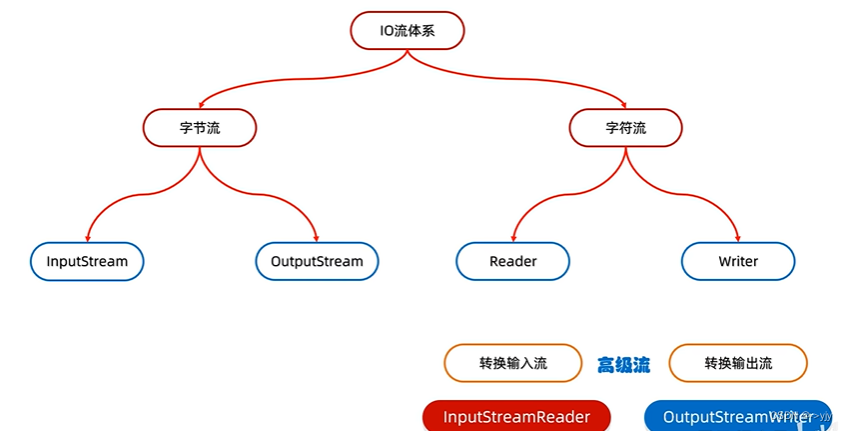
转换流
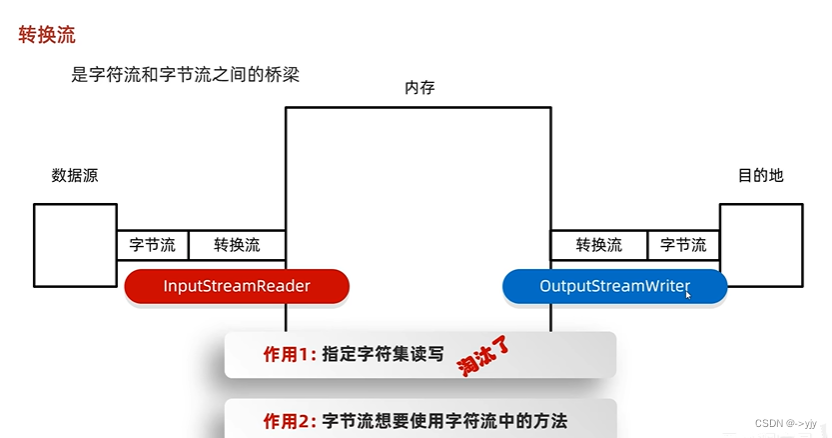

import java.io.*;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
public class BufferedStreamDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
/*
利用转换流按照指定字符编码读取(了解)
因为JDK11:这种方式被淘汰了,替代方案(掌握)
D:\yjy\test.txt
*/
// //1.创建对象并指定字符编码
// InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("Myio\\test.txt"),"GBK");
// //2.读取数据
// int ch;
// while((ch=isr.read())!=-1){
// System.out.print((char)ch);
//
// }
// //3.释放资源
// isr.close();
FileReader fr = new FileReader("Myio\\test.txt", Charset.forName("GBK"));
int ch;
while((ch=fr.read())!=-1){
System.out.print((char)ch);
}
fr.close();
}
}
import java.io.*;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
public class BufferedStreamDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
/*
利用转换流按照指定字符编码写出
*/
// //1.创建转换流的对象
// OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("Myio\\test.txt"),"GBK");
// //2.写出数据
// osw.write("你好你好");
// osw.close(); 淘汰
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("Myio\\c.txt",Charset.forName("GBK"));
fw.write("你好你好");
fw.close();
}
}
public class BufferedStreamDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
/*
将本地文件中的GBK文件,转成UTF-8
*/
//1.JDK11以前
// InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("Myio\\test.txt"),"GBK");
// OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("Myio\\d.txt"),"UTF-8");
//
// int b;
// while((b=isr.read())!=-1){
// osw.close();
// }
// osw.close();
// isr.close();
//2.替代方案
FileReader fr = new FileReader("Myio\\b.txt",Charset.forName("GBK"));
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("Myio\\e.txt",Charset.forName("UTF-8"));
int b;
while((b=fr.read())!=-1){
fw.write(b);
}
fr.close();
fw.close();
}
}

import java.io.*;
public class Main {
/*
利用字节流读取文件中的数据,每一次读一整行,而且不能出现乱码
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1.字节流读取不出现乱码 -- 字符流
//2.一次读一整行 -- 字符缓冲流
// FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("C:\\大一学习\\Java\\DailyRoutine\\b.txt");
// InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(fis);
// BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(isr);
//
// String s = br.readLine();
// System.out.println(s);
// br.close();
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("C:\\大一学习\\Java\\DailyRoutine\\b.txt")));
String line;
while((line=br.readLine())!=null){
System.out.println(line);
}
br.close();
}
}序列化流
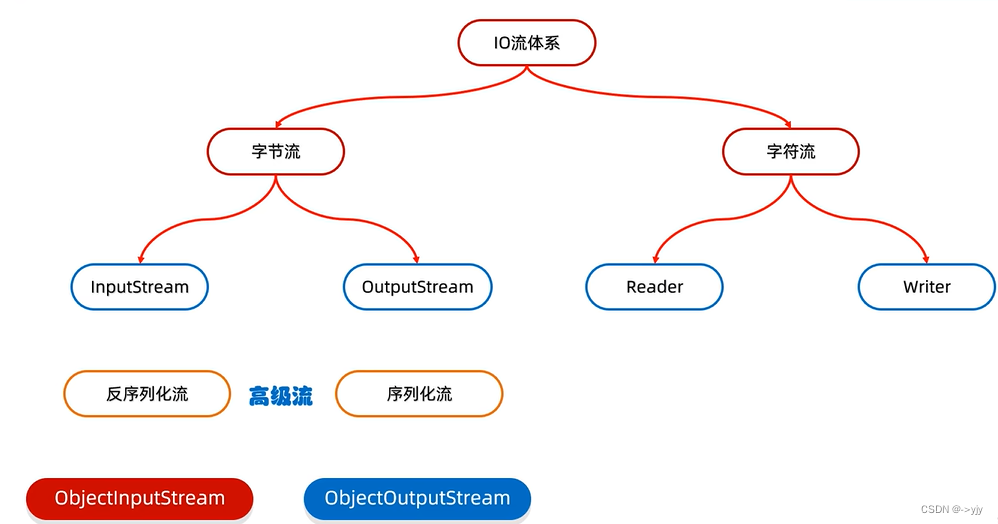


Serializable 是一个没有抽象方法的接口它是一种符号型接口,理解:物品的合格证
import java.io.Serializable;
public class Student implements Serializable {
private String name;
private int age;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
/**
* 获取
* @return name
*/
public String getName() {
return name;
}
/**
* 设置
* @param name
*/
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
/**
* 获取
* @return age
*/
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
/**
* 设置
* @param age
*/
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String toString() {
return "Student{name = " + name + ", age = " + age + "}";
}
}
import java.io.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
//1.创建对象
Student s = new Student("zhangsan",23);
//2.创建序列化流
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("Myio\\a.txt"));
oos.writeObject(s);
oos.close();
}
}
import java.io.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("Myio\\a.txt"));
Object o = ois.readObject();
System.out.println(o);//Student{name = zhangsan, age = 23}
ois.close();
}
} 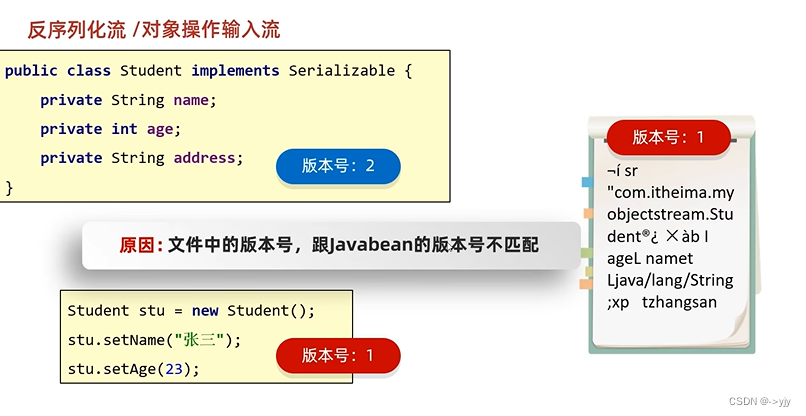
解释一下为什么版本一版本二
可以来看一下这样一个场景假如上面的实现代码不变 但是我们把javabean多加了一个属性address
报错:

如果一个类实现了Serializable接口说明这个类是可被序列化的,那么Java的底层会根据这个类的成员变量,静态变量,构造方法,成员方法,计算出一个long类型的序列号.那么我们假设计算出的版本号是1,我们所创建的对象中也包含这样一个版本号,但是如果修改了javabean,版本号就会更改,不匹配,导致报错
我们可以固定版本号
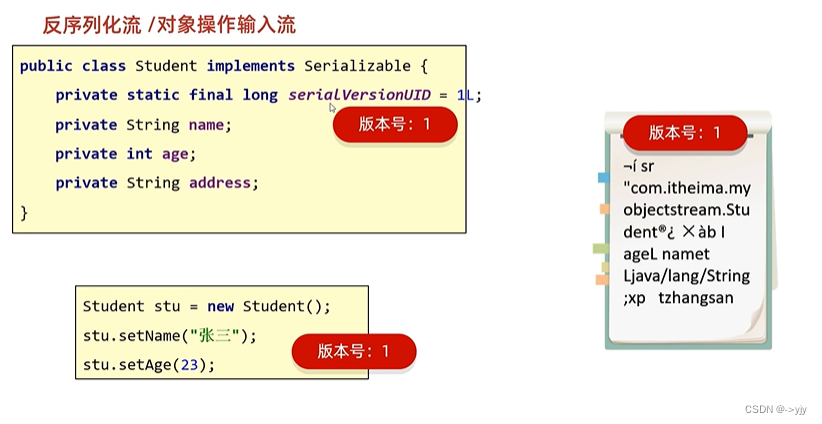
可以手动写版本号
也可以设置:
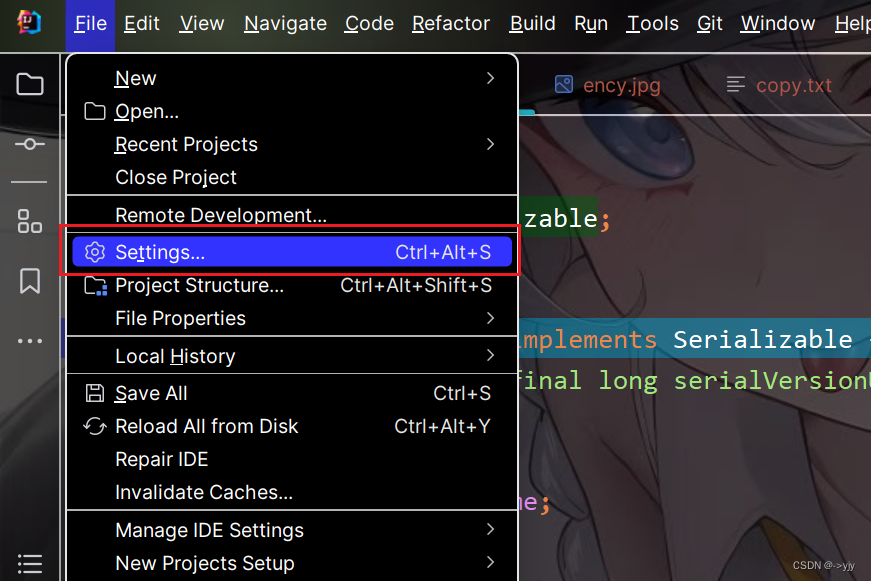
在搜索框搜索Serializable
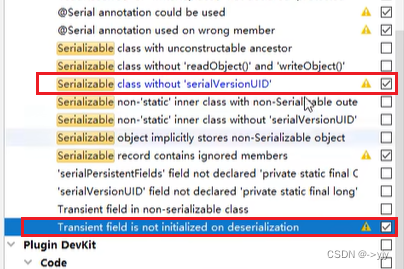
![]()
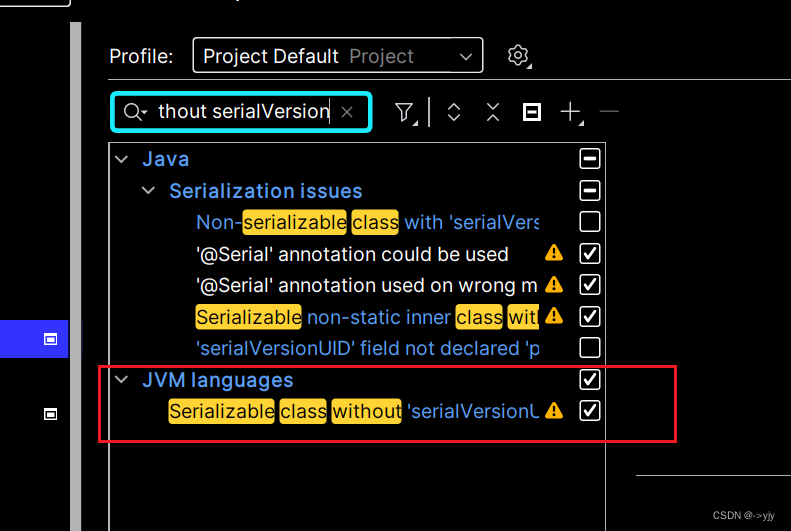
被深褐色包括 alt + 回车 添加一个UID即可

如果记不住也可以在源码中查找比如在ArrayList中粘贴复制修改



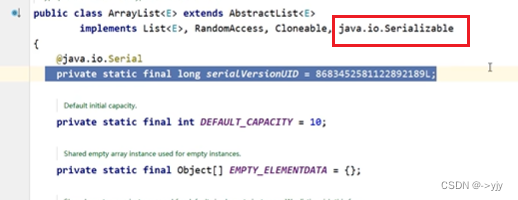
public class Student implements Serializable {
@Serial
private static final long serialVersionUID = 4974302185636640060L;
private String name;
private int age;
private String address;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, int age, String address) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.address = address;
}
/**
* 获取
* @return name
*/
public String getName() {
return name;
}
/**
* 设置
* @param name
*/
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
/**
* 获取
* @return age
*/
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
/**
* 设置
* @param age
*/
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
/**
* 获取
* @return address
*/
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
/**
* 设置
* @param address
*/
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
public String toString() {
return "Student{name = " + name + ", age = " + age + ", address = " + address + "}";
}
}
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class test {
//需求:将多个自定义对象序列化到文件中,但是对象的个数不确定,该如何操作呢?
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1.序列化多个对象
Student s1 = new Student("zhangsan",23,"南京");
Student s2 = new Student("lisi",24,"重庆");
Student s3 = new Student("wangwu",25,"北京");
ArrayList<Student> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(s1);
list.add(s2);
list.add(s3);
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("Myio\\a.txt"));
oos.writeObject(list);
// oos.writeObject(s1);
// oos.writeObject(s2);
// oos.writeObject(s3);
oos.close();
}
}
import java.io.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
//1.创建反序列流的对象
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("Myio\\a.txt"));
//
// //2.读取数据
// Student o = (Student)ois.readObject();
// Student o1 =(Student) ois.readObject();
// Student o2 =(Student) ois.readObject();
// //但是这样写其实不好因为要是你不知道里面有多少对象怎么办?
// //所以我们序列化对象的时候其实可以把对象们都放到一个集合中
//
// System.out.println(o);
// System.out.println(o1);
// System.out.println(o2);
//2.读取数据
ArrayList<Student> list = (ArrayList<Student>)ois.readObject();
for (Student student : list) {
System.out.println(student);
}
ois.close();
}
}
打印流


字节打印流

public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException {
//1.创建字节打印流的对象
PrintStream ps = new PrintStream(new FileOutputStream("Myio\\a.txt"), true, Charset.forName("UTF-8"));
ps.println(97);//写出 + 自动刷新 + 自动换行
ps.print(true);
ps.printf("%s 爱上了 %s","阿珍","阿强");
ps.close();
}
}
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.PrintStream;
import java.util.Date;
public class PrintStreamDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException {
PrintStream ps = new PrintStream("a.txt");
//% n表示换行
ps.printf("我叫%s %n", "阿玮");
ps.printf("%s喜欢%s %n", "阿珍", "阿强");
ps.printf("字母H的大写:%c %n", 'H');
ps.printf("8>3的结果是:%b %n", 8 > 3);
ps.printf("100的一半是:%d %n", 100 / 2);
ps.printf("100的16进制数是:%x %n", 100);
ps.printf("100的8进制数是:%o %n", 100);
ps.printf("50元的书打8.5折扣是:%f元%n", 50 * 0.85);
ps.printf("计算的结果转16进制:%a %n", 50 * 0.85);
ps.printf("计算的结果转科学计数法表示:%e %n", 50 * 0.85);
ps.printf("计算的结果转成指数和浮点数,结果的长度较短的是:%g %n", 50 * 0.85);
ps.printf("带有百分号的符号表示法,以百分之85为例:%d%% %n", 85);
ps.println("---------------------");
double num1 = 1.0;
ps.printf("num: %.4g %n", num1);
ps.printf("num: %.5g %n", num1);
ps.printf("num: %.6g %n", num1);
float num2 = 1.0F;
ps.printf("num: %.4f %n", num2);
ps.printf("num: %.5f %n", num2);
ps.printf("num: %.6f %n", num2);
ps.println("---------------------");
ps.printf("数字前面带有0的表示方式:%03d %n", 7);
ps.printf("数字前面带有0的表示方式:%04d %n", 7);
ps.printf("数字前面带有空格的表示方式:% 8d %n", 7);
ps.printf("整数分组的效果是:%,d %n", 9989997);
ps.println("---------------------");
//最终结果是10位,小数点后面是5位,不够在前面补空格,补满10位
//如果实际数字小数点后面过长,但是只规定两位,会四舍五入
//如果整数部分过长,超出规定的总长度,会以实际为准
ps.printf("一本书的价格是:%2.5f元%n", 49.8);
ps.printf("%(f%n", -76.04);
//%f,默认小数点后面7位,
//<,表示采取跟前面一样的内容
ps.printf("%f和%3.2f %n", 86.04, 1.789651);
ps.printf("%f和%<3.2f %n", 86.04, 1.789651);
ps.println("---------------------");
Date date = new Date();
// %t 表示时间,但是不能单独出现,要指定时间的格式
// %tc 周二 12月 06 22:08:40 CST 2022
// %tD 斜线隔开
// %tF 冒号隔开(12小时制)
// %tr 冒号隔开(24小时制)
// %tT 冒号隔开(24小时制,带时分秒)
ps.printf("全部日期和时间信息:%tc %n", date);
ps.printf("月/日/年格式:%tD %n", date);
ps.printf("年-月-日格式:%tF %n", date);
ps.printf("HH:MM:SS PM格式(12时制):%tr %n", date);
ps.printf("HH:MM格式(24时制):%tR %n", date);
ps.printf("HH:MM:SS格式(24时制):%tT %n", date);
System.out.println("---------------------");
ps.printf("星期的简称:%ta %n", date);
ps.printf("星期的全称:%tA %n", date);
ps.printf("英文月份简称:%tb %n", date);
ps.printf("英文月份全称:%tB %n", date);
ps.printf("年的前两位数字(不足两位前面补0):%tC %n", date);
ps.printf("年的后两位数字(不足两位前面补0):%ty %n", date);
ps.printf("一年中的第几天:%tj %n", date);
ps.printf("两位数字的月份(不足两位前面补0):%tm %n", date);
ps.printf("两位数字的日(不足两位前面补0):%td %n", date);
ps.printf("月份的日(前面不补0):%te %n", date);
System.out.println("---------------------");
ps.printf("两位数字24时制的小时(不足2位前面补0):%tH %n", date);
ps.printf("两位数字12时制的小时(不足2位前面补0):%tI %n", date);
ps.printf("两位数字24时制的小时(前面不补0):%tk %n", date);
ps.printf("两位数字12时制的小时(前面不补0):%tl %n", date);
ps.printf("两位数字的分钟(不足2位前面补0):%tM %n", date);
ps.printf("两位数字的秒(不足2位前面补0):%tS %n", date);
ps.printf("三位数字的毫秒(不足3位前面补0):%tL %n", date);
ps.printf("九位数字的毫秒数(不足9位前面补0):%tN %n", date);
ps.printf("小写字母的上午或下午标记(英):%tp %n", date);
ps.printf("小写字母的上午或下午标记(中):%tp %n", date);
ps.printf("相对于GMT的偏移量:%tz %n", date);
ps.printf("时区缩写字符串:%tZ%n", date);
ps.printf("1970-1-1 00:00:00 到现在所经过的秒数:%ts %n", date);
ps.printf("1970-1-1 00:00:00 到现在所经过的毫秒数:%tQ %n", date);
ps.close();
}
}
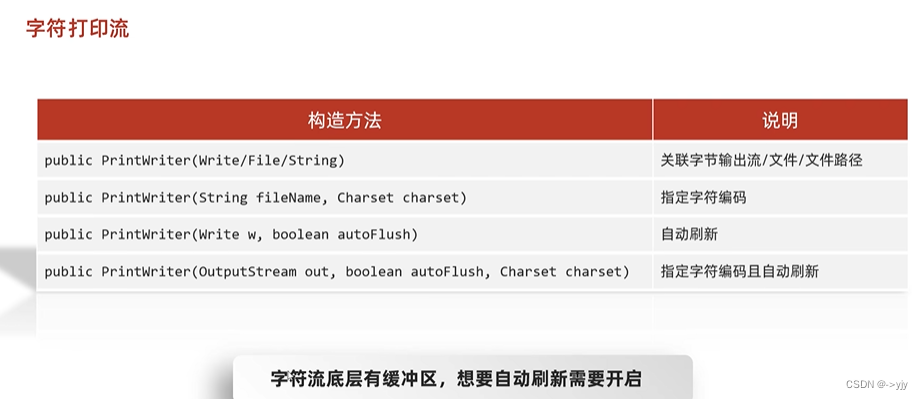
字符打印流

public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1.创建字符打印流的对象
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(new FileWriter("Myio\\a.txt"),true);
//2.写出数据
pw.println("筛选入脑内容,不要被情绪所左右 静坐冥想");
pw.print("自身价值高比啥都强");
pw.printf("%s和%s","建造","成长");
//3.释放资源
pw.close();
}
}
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//打印流的应用场景
// System.out.println("123");
//获取打印流的对象,此打印流在虚拟机启动的时候,由虚拟机创建,默认指向控制台
//特殊的打印流,系统中的标准输出流,是不能关闭的,在系统中是唯一的.
PrintStream ps = System.out;
//调用打印流中的方法
//写出数据 自动换行 自动刷新
ps.println("123");
}
}
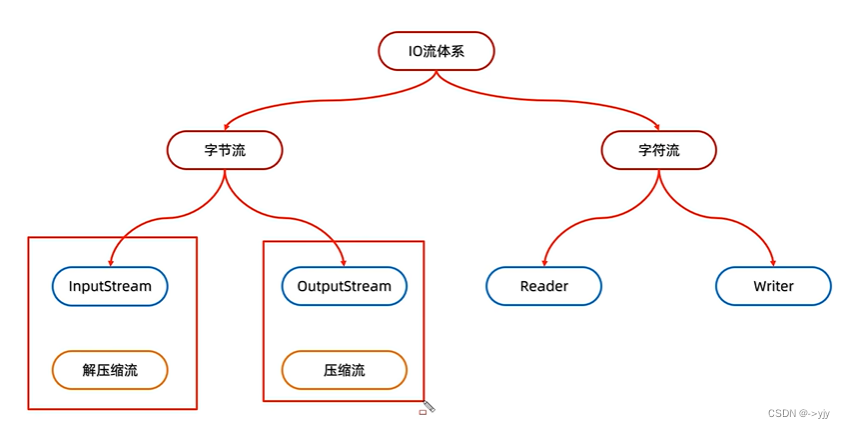
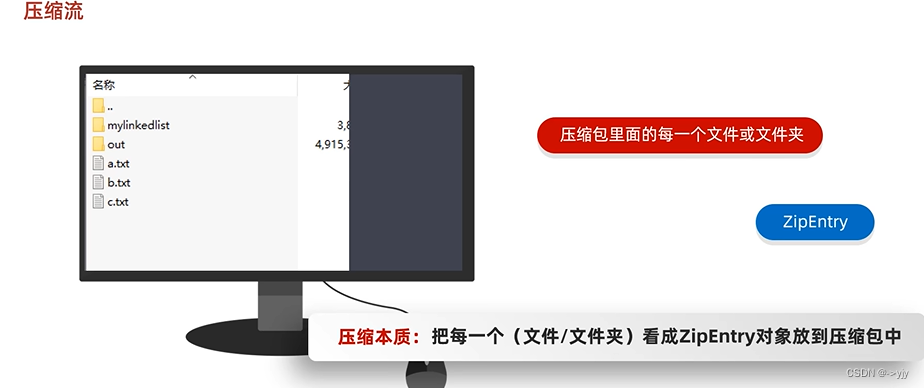
压缩流



import java.io.*;
import java.util.zip.ZipEntry;
import java.util.zip.ZipInputStream;
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File src = new File("D:\\yjy.zip");
File dest = new File("D:");
unzip(src,dest);
}
//定义一个方法来解压
private static void unzip(File src, File dest) throws IOException {
//解压的本质,把压缩包里面的每一个文件或者文件夹读取出来,按照层级拷贝到目的地当中
//创建一个压缩流用来读取压缩包的数据
ZipInputStream zip = new ZipInputStream(new FileInputStream(src));
//要先获取到压缩包里面的每一个zipentry对象
//表示当前在压缩包中获取到的文件或文件夹
ZipEntry entry;
while((entry=zip.getNextEntry())!=null){
System.out.println(entry);
//文件夹:需要在目的地dest处创建一个同样的文件夹
//文件:需要读取到压缩包中的文件,并把他存放在目的地dest文件夹中(按照层级目录进行存放
if(entry.isDirectory()){
File file = new File(dest,entry.toString());
file.mkdirs();
}else{
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(new File(dest,entry.toString()));
int b;
while((b=zip.read())!=-1){
//写到目的地
fos.write(b);
}
fos.close();
//表示在压缩包中的一个文件处理完毕了
zip.closeEntry();
}
}
zip.close();
}
}
import java.io.*;
import java.util.zip.ZipEntry;
import java.util.zip.ZipOutputStream;
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
/*
* 压缩流
* 需求:
* 把D:\\a.txt打包成一个压缩包
*
*/
//1.创建File对象表示要压缩的文件
File src = new File("D:\\a.txt");
//2.创建File对象表示压缩包的位置
File dest = new File("D:\\");
//3.调用方法来压缩
toZip(src,dest);
}
/*
* 作用:压缩
* 参数一:表示要压缩的文件
* 参数二:表示压缩包的位置
*/
public static void toZip(File src,File dest) throws IOException {
//1.创建压缩流去创建压缩包
ZipOutputStream zos = new ZipOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(new File(dest,"a.zip")));
//2.创建zipEntry对象,表示压缩包里面的每一个文件和文件夹
ZipEntry entry = new ZipEntry("a.txt");//压缩包中叫a.txt
//3.把ZipEntry对象放到压缩包当中
zos.putNextEntry(entry);
//4.把src文件中的数据写到压缩包当中
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(src);
int b;
while((b=fis.read())!=-1){
zos.write(b);
}
zos.closeEntry();
zos.close();
}
}
import java.io.*;
import java.util.zip.ZipEntry;
import java.util.zip.ZipOutputStream;
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
/*
* 压缩流:
* 需求:
* 把D:\\aaa对象表示要压缩的文件夹
*/
//1.创建File对象表示要压缩的文件夹
File src = new File("D:\\aaa");
//2.创建File对象表示压缩包的路径 放在哪里 (压缩包放在哪里)
File destParent = src.getParentFile();//
//3.创建File对象
File dest = new File(destParent,src.getName()+".zip");
System.out.println(dest);
//4.创建压缩流关联压缩包
ZipOutputStream zos = new ZipOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(dest));
//5.获取src里面的每一个文件,变成ZipEntry对象,放入到压缩包当中
toZip(src,zos,src.getName());
//6.释放资源
zos.close();
}
/**
* 作用:获取src里面的每一个文件,变成ZipEntry对象,放入到压缩包当中
* @param src :数据源
* @param zos :压缩流
* @param name : 压缩包内部的路径
*/
public static void toZip(File src,ZipOutputStream zos,String name) throws IOException {
//1.进入src文件夹
File[] files = src.listFiles();
//2.遍历数组
for (File file : files) {
//3.判断 + 文件 ,变成ZipEntry对象,放入到压缩包当中
if(file.isFile()){
ZipEntry entry = new ZipEntry(name+"\\"+file.getName());//aaa\\haha.txt
zos.putNextEntry(entry);
//读取文件数据,写到压缩包
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
int b;
while((b=fis.read())!=-1){
zos.close();
}
fis.close();
zos.closeEntry();
}else{
//递归
toZip(file,zos,name+"\\"+file.getName());
}
}
}
}
Commons-io






import org.apache.commons.io.FileUtils;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// File src= new File("yjy.txt");
// File dest = new File("YJY\\copy.txt");
// FileUtils.copyFile(src,dest);
// System.out.println("Hello world!");
//
// File src = new File("D:\\yjy1");
// File dest = new File("D:\\bbb");
// FileUtils.copyDirectory(src,dest);
File src = new File("D:\\yjy");
// FileUtils.deleteDirectory(src);
FileUtils.cleanDirectory(new File("D:\\yjy1"));
}
}更多方法看这里: commons-io

官网:
https://hutool.cn/
API文档:
https://apidoc.gitee.com/dromara/hutool/
中文使用文档:
https://hutool.cn/docs/#/
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import cn.hutool.core.io.FileUtil;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
/*
FileUtil类:
file:根据参数创建一个file对象
touch:根据参数创建文件
writeLines:把集合中的数据写出到文件中,续写模式
readLines:指定字符编码,把文件编码,把文件中的数据,读到集合中
readUtf8Lines:按照UTF-8的形式,把文件中的数据,读到集合中
copy:拷贝文件或者文件夹
*/
File file = FileUtil.file("D:\\aaa", "bbb", "a.txt");
System.out.println(file);//D:\aaa\bbb\a.txt
// File f = new File("a.txt");
// f.createNewFile();//父级路径不存在会报错
//touch方法父级路径不存在也仍然能够创建
File touch = FileUtil.touch(file);
System.out.println(touch);//
//
// ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
// list.add("aaa");
// list.add("aaa");
// list.add("aaa");
// FileUtil.writeLines(list,"D:\\a.txt","UTF-8",true);
//
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("aaa");
list.add("aaa");
list.add("aaa");
File file1 = FileUtil.appendLines(list, "D:\\a.txt", "UTF-8");
System.out.println(file1);
ArrayList<String> strings = FileUtil.readLines("D:\\a.txt", "UTF-8", new ArrayList<String>());
List<String> strings1 = FileUtil.readLines("D:\\a.txt", "UTF-8");
System.out.println(strings1);
}
}