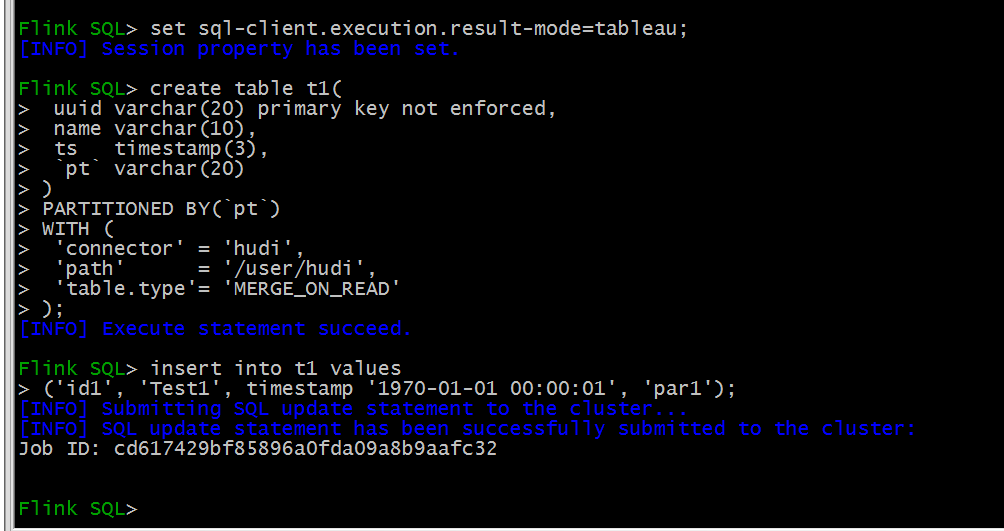
openlayers浅入(了解框架逻辑以及简单使用)
项目需求,使用openlayers替换天地图api开发,记录openlayer的使用
简介
OpenLayers是一个用于开发WebGIS客户端的JavaScript包,最初基于BSD许可发行。OpenLayers是一个开源的项目,其设计之意是为互联网客户端提供强大的地图展示功能,包括地图数据显示与相关操作,并具有灵活的扩展机制。目前OpenLayers已经成为一个拥有众多开发者和帮助社区的成熟、流行的框架。最新版本的OpenLayers采用纯面向对象的ECMA Script 6进行开发,可以说,在OpenLayers中万物皆对象
OpenLayers的官方网站
openlayers框架逻辑简单分析
在最新版本OpenLayers中万物皆对象,Map、Layer、Source和View是OpenLayers框架体系中的核心类,几乎所有的动作都围绕这几个核心类展开,以实现地图加载和相关操作。在OpenLayers的体系框架中:把整个地图看作一个容器(Map),核心为地图图层(Layer),每个图层有对应的数据源(Source),并由地图视图(View)进行地图表现。地图容器上还支持一些与用户交互的控件(Control和Interaction),另外,OpenLayers还支持事件机制

openlayers中常使用的坐标系统
使用WGS84(EPSG:4326) 存储数据,使用伪墨卡托(EPSG:3857)显示数据
使用openlayers
1.引入方式
写的demo使用的cdn方式引入openlayers,项目中使用npm导入openlayers依赖包
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>openlayer</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/ol@v7.1.0/ol.css">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="./index.css">
</head>
<body>
<div id="map"></div>
<div id="mouse-position" class="mouse-position-wrapper">
<div class="custom-mouse-position"></div>
</div>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/ol@v7.1.0/dist/ol.js"></script>
<script type="module" src="./app.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
2.具体js实现代码(app.js)
const url = 'http://服务器地址/tiles/{z}/{x}/{y}.png'
const epsg = 'EPSG:3857';
const projection = ol.proj.get(epsg);
new出map对象,部分参数使用
const map = new ol.Map({
target: 'map',
view: new ol.View({
center: ol.proj.transform([105.255396, 33.642909], 'EPSG:4326', epsg),
zoom: 4,
projection,
// minZoom: 3,
// 限制拖拽范围
extent: [
// ...ol.proj.fromLonLat([66.539576, 56.602398]),
// ...ol.proj.fromLonLat([139.137232, 9.785853]),
// 添加这个范围 经度-最小,纬度-最小,经度-最大,纬度-最大
...ol.proj.fromLonLat([73.32783475401652, 19.4243521114706]),
...ol.proj.fromLonLat([135.16017906160056, 53.83501005646246]),
], //长度为4的数组, 传入地图对角投影坐标
/*
`
lt:60.646255, 54.099069,
rt:141.628437, 55.359014,
rb:138.233974, 11.404207,
lb:72.284413, 12.590013
`
*/
showFullExtent: true,
}),
});
显示经纬度信息
map.addControl(ol.control.defaults.defaults().extend([
// 鼠标位置经纬度显示
new ol.control.MousePosition({
coordinateFormat: ol.coordinate.createStringXY(6),
projection: ol.proj.get('EPSG:4326'),
className: 'custom-mouse-position',
target: document.getElementById('mouse-position')
}),
]))
使用addLayer方法加载离线图层
*注:addLayer 方法添加层时 如果没有设置zIndex,根据添加顺序 后面添加的会覆盖前面添加的同位置的覆盖层
// 离线图层
map.addLayer(new ol.layer.Tile({
title: "tileLayer",
baseLayer: true,
willReadFrequently: true,
source: new ol.source.XYZ({
attributions: 'cdwx',
minZoom: 1,
maxZoom: 19,
projection: projection,
tileSize: 256,
url
})
}));
添加点Point,并设置点的样式图片等(注释代码是多种可设置样式的方式)
// 添加点
const iconFeature1 = new ol.Feature({
geometry: new ol.geom.Point(ol.proj.transform([104.13689, 33.96498], 'EPSG:4326', epsg)),
id: 9527,
// style: new ol.style.Style({
// image: new ol.style.Icon({
// anchor: [0.5, 50],
// anchorXUnits: 'fraction',
// anchorYUnits: 'pixels',
// src: "img/station_0_1.png",
// scale: .4
// })
// })
});
iconFeature1.setStyle(new ol.style.Style({
image: new ol.style.Icon({
anchor: [0.5, 50],
anchorXUnits: 'fraction',
anchorYUnits: 'pixels',
src: "img/station_0_1.png",
scale: .4
})
}))
const iconFeature2 = new ol.Feature({
geometry: new ol.geom.Point(ol.proj.transform([118.344251, 32.015470], 'EPSG:4326', epsg)),
id: 4388,
// style: new ol.style.Style({
// image: new ol.style.Icon({
// anchor: [0.5, 50],
// anchorXUnits: 'fraction',
// anchorYUnits: 'pixels',
// src: "img/station_0_1.png",
// scale: .4
// })
// })
});
iconFeature2.setStyle(new ol.style.Style({
image: new ol.style.Icon({
anchor: [0.5, 50],
anchorXUnits: 'fraction',
anchorYUnits: 'pixels',
src: "img/station_6_0.png",
scale: .3
})
}))
const tilerVectorSource = new ol.source.Vector({
features: [iconFeature1, iconFeature2]
});
/*
1.feature通过setStyle设置样式 layer通过 function (f) {return f.getStyle()} 设置样式 (能够在后期使用feature.setStyle(undefined)来隐藏feature)
2.
feature通过ObjectWithGeometry中设置style样式如下
new ol.Feature({
geometry: new ol.geom.Point(ol.proj.transform([118.344251, 32.015470], 'EPSG:4326', epsg)),
id: 4388,
style: new ol.style.Style({
image: new ol.style.Icon({
anchor: [0.5, 50],
anchorXUnits: 'fraction',
anchorYUnits: 'pixels',
src: "img/station_0_1.png",
scale: .4
})
})
})
layer通过 function (f) {return f.get('style')} 设置样式
3.feature不设置样式, layer通过属性设置样式
*/
map.addLayer(new ol.layer.VectorImage({
title: 'siteLayer',
source: tilerVectorSource,
zIndex: 1,
style: function (f) {
return f.getStyle()
// return f.get("style")
}
// style: new ol.style.Style({
// image: new ol.style.Icon({
// anchor: [0.5, 50],
// anchorXUnits: 'fraction',
// anchorYUnits: 'pixels',
// src: "img/station_0_1.png",
// scale: .4
// })
// })
}));
添加Polygon多边形,并设置点的样式图片等(注释代码是多种可设置样式的方式)
// Polygon多边形
let pointArr1 = [[115.668,25.811],[115.746,25.769],[116.533,25.2],[116.621,25.123],[117.275,24.448],[117.348,24.357],[117.774,23.783],[118.125,23.127],[118.248,22.775],[118.351,22.478],[118.474,21.836],[118.501,21.2],[118.484,21.016],[118.441,20.57],[118.283,19.945],[118.041,19.401],[118.003,19.326],[117.563,18.713],[117.494,18.639],[116.912,18.16],[116.823,18.108],[116.311,17.839],[115.692,17.64],[115.059,17.544],[114.41,17.54],[113.744,17.629],[113.059,17.811],[112.349,18.111],[112.202,18.193],[111.605,18.563],[111.253,18.834],[110.807,19.246],[110.585,19.474],[110.063,20.115],[109.906,20.354],[109.646,20.758],[109.348,21.403],[109.155,22.05],[109.052,22.699],[109.049,23.35],[109.129,23.853],[109.156,24.002],[109.41,24.654],[109.583,24.939],[109.865,25.305],[110.144,25.594],[110.62,25.952],[110.757,26.04],[111.409,26.324],[112.089,26.484],[112.788,26.544],[113.505,26.513],[114.236,26.384],[114.982,26.146],[115.668,25.811]]
let pointArr2 = [[120.55,24.385],[120.657,24.325],[121.259,23.72],[121.417,23.41],[121.55,23.067],[121.547,22.425],[121.531,22.384],[121.135,21.792],[120.971,21.663],[120.35,21.51],[119.702,21.571],[119.106,21.825],[119.019,21.886],[118.542,22.475],[118.367,23.122],[118.498,23.769],[118.715,24.116],[119.032,24.412],[119.311,24.563],[119.966,24.596],[120.55,24.385]]
const corrds1 = [pointArr1]
const corrds2 = [pointArr2]
const sourcePolygon = new ol.source.Vector() // 1.创建数据源
const layerPolygon = new ol.layer.Vector({ // 2.创建图层
zIndex: 1, // 图层的层级
// style: {
// 'fill-color': 'rgba(255, 0, 0, 0.3)',
// 'stroke-color': 'rgba(255, 0, 0, 0.9)',
// 'stroke-width': 1,
// },
// style: new ol.style.Style({
// stroke: new ol.style.Stroke({
// color: 'rgba(255, 0, 0, 0.9)',
// width: 1
// }),
// fill: new ol.style.Fill({
// color: 'rgba(255, 0, 0, 0.3)'
// })
// }),
style: function (f) {
return f.getStyle()
},
title: 'beamLayer'
})
const featureCollection = new ol.Collection()
const polygon1 = new ol.geom.Polygon(corrds1)
polygon1.applyTransform(ol.proj.getTransform('EPSG:4326', 'EPSG:3857'));
const polygon2 = new ol.geom.Polygon(corrds2)
polygon2.applyTransform(ol.proj.getTransform('EPSG:4326', 'EPSG:3857'));
const feature1 = new ol.Feature({
title: 'beam1',
geometry: polygon1,
})
feature1.setStyle(new ol.style.Style({
stroke: new ol.style.Stroke({
color: 'rgba(255, 0, 0, 0.9)',
width: 1
}),
fill: new ol.style.Fill({
color: 'rgba(255, 0, 0, 0.3)'
})
}))
const feature2 = new ol.Feature({
title: 'beam2',
geometry: polygon2
})
feature2.setStyle(new ol.style.Style({
stroke: new ol.style.Stroke({
color: 'rgba(255, 0, 0, 0.9)',
width: 1
}),
fill: new ol.style.Fill({
color: 'rgba(255, 0, 0, 0.3)'
})
}))
featureCollection.push(feature1)
featureCollection.push(feature2)
sourcePolygon.addFeatures(featureCollection.getArray())
layerPolygon.setSource(sourcePolygon) // 3.把数据源绑定到图层上面
map.addLayer(layerPolygon) // 4.图层通过addlayer添加到map对象上在界面显示
获取所有添加的layer图层,进行操作
*注:map.getPixelFromCoordinate 必须在map加载生成完毕后使用 否则会返回null
// 控制图标隐藏显示
map.getAllLayers().forEach(item => {
// console.log(item)
if (item.get('title') === 'siteLayer') {
console.log(item.getSource().getFeatures())
// console.log(item.getSource().getFeatures()[0].getStyle())
item.getSource().getFeatures()[1].setStyle()
// item.getSource().getFeatures()[1].setStyle(null)
// item.getSource().getFeatures()[1].setGeometry(null)
setTimeout(() => {
// map.getPixelFromCoordinate 必须在map加载生成完毕后使用 否则会返回null
console.log(map.getFeaturesAtPixel(map.getPixelFromCoordinate([118.344251, 32.015470])))
// const { style, geometry } = showOneSite(0, 1, [118.344251, 32.015470])
// item.getSource().getFeatures()[1].setStyle(style)
// item.getSource().getFeatures()[1].setGeometry(geometry)
}, 5000)
// item.setVisible(false) // 根据状态显示隐藏可以使用setVisible方法
}
if (item.get('title') === 'beamLayer') {
// console.log('----------')
// console.log(item.getSource().getFeatures(), '1')
// console.log(item.getSource().getFeatures()[0].get('title'))
item.getSource().getFeatures()[0].setStyle()
}
})
相比天地图api,openlayer的使用感觉功能更全面,api调用更方便,可扩展性更强,并且openlayer可以很方便的支持离线开发,离线图层等;因为自己使用cesium多处理的是3d界面数据显示,而openlayer使用不多并且是2d界面的数据展示。所以不好对比cesium,只是感觉openlayer的api调用更方便,cesium中Viewer类就是一切API的入口,代码过重。例如在cesium处理地图切换时监听事件代码如下:
viewer.sceneModePicker.viewModel.morphToColumbusView.beforeExecute.addEventListener(function(a) {
viewer.camera.setView({
destination: Cesium.Cartesian3.fromDegrees(105, 33, 10000000)
});
});