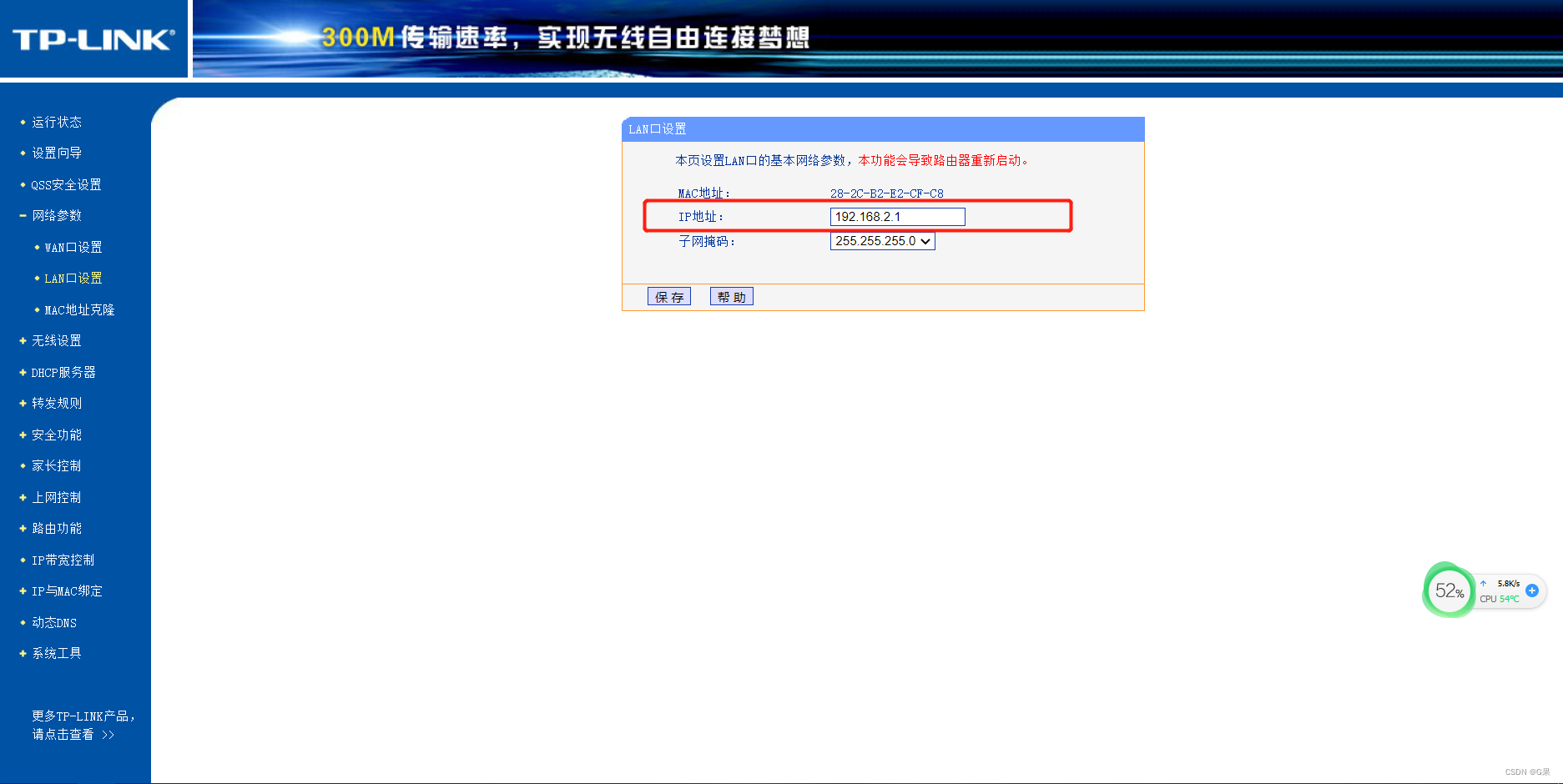
FFMpeg 作为音视频领域的开源工具,它几乎可以实现所有针对音视频的处理,本文主要利用 FFMpeg 官方提供的 SDK 实现音视频最简单的几个实例:编码、解码、封装、解封装、转码、缩放以及添加水印。
接下来会由发现问题->分析问题->解决问题->实现方案,循序渐进的完成。
参考代码:
GitHub - lazybing/ffmpeg-study-recording
FFMpeg 编码实现
本例子实现的是将视频域 YUV 数据编码为压缩域的帧数据,编码格式包含了 H.264/H.265/MPEG1/MPEG2 四种 CODEC 类型。
实现的过程,可以大致用如下图表示:
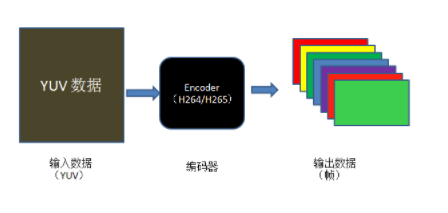
从图中可以大致看出视频编码的流程:
-
首先要有未压缩的 YUV 原始数据。
-
其次要根据想要编码的格式选择特定的编码器。
-
最后编码器的输出即为编码后的视频帧。
根据流程可以推倒出大致的代码实现:
-
存放待压缩的 YUV 原始数据。此时可以利用 FFMpeg 提供的 AVFrame 结构体,并根据 YUV 数据来填充 AVFrame 结构的视频宽高、像素格式;根据视频宽高、像素格式可以分配存放数据的内存大小,以及字节对齐情况。
-
获取编码器。利用想要压缩的格式,比如 H.264/H.265/MPEG1/MPEG2 等,来获取注册的编解码器,编解码器在 FFMpeg 中用 AVCodec 结构体表示,对于编解码器,肯定要对其进行配置,包括待压缩视频的宽高、像素格式、比特率等等信息,这些信息,FFMpeg 提供了一个专门的结构体 AVCodecContext 结构体。
-
存放编码后压缩域的视频帧。FFMpeg 中用来存放压缩编码数据相关信息的结构体为 AVPacket。最后将 AVPacket 存储的压缩数据写入文件即可。
AVFrame 结构体的分配使用av_frame_alloc()函数,该函数会对 AVFrame 结构体的某些字段设置默认值,它会返回一个指向 AVFrame 的指针或 NULL指针(失败)。
AVFrame 结构体的释放只能通过av_frame_free()来完成。
注意,该函数只能分配 AVFrame 结构体本身,不能分配它的 data buffers 字段指向的内容,该字段的指向要根据视频的宽高、像素格式信息手动分配,本例使用的是av_image_alloc()函数。
★文末名片可以免费领取音视频开发学习资料,内容包括(FFmpeg ,webRTC ,rtmp ,hls ,rtsp ,ffplay ,srs)以及音视频学习路线图等等。
见下方!↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓
代码实现大致如下:
//allocate AVFrame struct
AVFrame *frame = NULL;
frame = av_frame_alloc();
if(!frame){
printf("Alloc Frame Fail\n");
return -1;
}
//fill AVFrame struct fields
frame->width = width;
frame->height = height;
frame->pix_fmt = AV_PIX_FMT_YUV420P;
//allocate AVFrame data buffers field point
ret = av_image_alloc(frame->data, frame->linesize, frame->width, frame->height, frame->pix_fmt, 32);
if(ret < 0){
printf("Alloc Fail\n");
return -1;
}
//write input file data to frame->data buffer
fread(frame->data[0], 1, frame->width*frame->height, pInput_File);
...
av_frame_free(frame);
编解码器相关的 AVCodec 结构体的分配使用avcodec_find_encoder(enum AVCodecID id)完成,该函数的作用是找到一个与 AVCodecID 匹配的已注册过得编码器;成功则返回一个指向 AVCodec ID 的指针,失败返回 NULL 指针。
该函数的作用是确定系统中是否有该编码器,只是能够使用编码器进行特定格式编码的最基本的条件,要想使用它,至少要完成两个步骤:
-
根据特定的视频数据,对该编码器进行特定的配置;
-
打开该编码器。
针对第一步中关于编解码器的特定参数,FFMpeg 提供了一个专门用来存放 AVCodec 所需要的配置参数的结构体 AVCodecContext 结构。
它的分配使用avcodec_alloc_context3(const AVCodec *codec)完成,该函数根据特定的 CODEC 分配一个 AVCodecContext 结构体,并设置一些字段为默认参数,成功则返回指向 AVCodecContext 结构体的指针,失败则返回 NULL 指针。
分配完成后,根据视频特性,手动指定与编码器相关的一些参数,比如视频宽高、像素格式、比特率、GOP 大小等。最后根据参数信息,打开找到的编码器,此处使用avcodec_open2()函数完成。
代码实现大致如下:
AVCodec *codec = NULL;
AVCodecContext *codecCtx = NULL;
//register all encoder and decoder
avcodec_register_all();
//find the encoder
codec = avcodec_find_encoder(codec_id);
if(!codec){
printf("Could Not Find the Encoder\n");
return -1;
}
//allocate the AVCodecContext and fill it's fields
codecCtx = avcodec_alloc_context3(codec);
if(!codecCtx){
printf("Alloc AVCodecCtx Fail\n");
return -1;
}
codecCtx->bit_rate = 4000000;
codecCtx->width = frameWidth;
codecCtx->height = frameHeight;
codecCtx->time_base= (AVRational){1, 25};
//open the encoder
if(avcodec_open2(codecCtx, codec, NULL) < 0){
printf("Open Encoder Fail\n");
}
存放编码数据的结构体为 AVPacket,使用之前要对该结构体进行初始化,初始化函数为av_init_packet(AVPacket *pkt),该函数会初始化 AVPacket 结构体中一些字段为默认值,但它不会设置其中的 data 和 size 字段,需要单独初始化,如果此处将 data 设为 NULL、size 设为 0,编码器会自动填充这两个字段。
有了存放编码数据的结构体后,我们就可以利用编码器进行编码了。
FFMpeg 提供的用于视频编码的函数为avcodec_encode_video2,它作用是编码一帧视频数据,该函数比较复杂,单独列出如下:
int avcodec_encode_video2(AVCodecContext *avctx, AVPacket *avpkt, const AVFrame *frame, int *got_packet_ptr);
它会接收来自 AVFrame->data 的视频数据,并将编码数据放到 AVPacket->data 指向的位置,编码数据大小为 AVPacket->size。
其参数和返回值的意义:
-
avctx: AVCodecContext 结构,指定了编码的一些参数;
-
avPkt: AVPacket对象的指针,用于保存输出的码流;
-
frame:AVFrame结构,用于传入原始的像素数据;
-
got_packet_ptr:输出参数,用于标识是否已经有了完整的一帧;
-
返回值:编码成功返回 0, 失败返回负的错误码;
编码完成后就可将AVPacket->data内的编码数据写到输出文件中;代码实现大致如下:
AVPacket pkt;
//init AVPacket
av_init_packet(&pkt);
pkt.data = NULL;
pkt.size = 0;
//encode the image
ret = avcodec_encode_video2(codecCtx, &pkt, frame, &got_output);
if(ret < 0){
printf("Encode Fail\n");
return -1;
}
if(got_output){
fwrite(pkt.data, 1, pkt.size, pOutput_File);
}
编码的大致流程已经完成了,剩余的是一些收尾工作,比如释放分配的内存、结构体等等。
FFMpeg 解码实现
解码实现的是将压缩域的视频数据解码为像素域的 YUV 数据。实现的过程,可以大致用如下图所示。
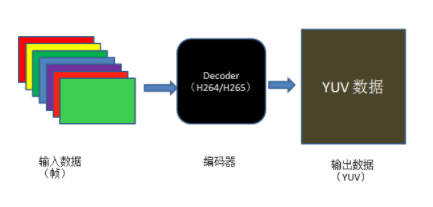
从图中可以看出,大致可以分为下面三个步骤:
-
首先要有待解码的压缩域的视频。
-
其次根据压缩域的压缩格式获得解码器。
-
最后解码器的输出即为像素域的 YUV 数据。
根据流程可以推倒出大致的代码实现:
-
关于输入数据。首先,要分配一块内存,用于存放压缩域的视频数据;之后,对内存中的数据进行预处理,使其分为一个一个的 AVPacket 结构(AVPacket 结构的简单介绍如上面的编码实现)。最后,将 AVPacket 结构中的 data 数据给到解码器。
-
关于解码器。首先,利用 CODEC_ID 来获取注册的解码器;之后,将预处理过得视频数据给到解码器进行解码。
-
关于输出。FFMpeg 中,解码后的数据存放在 AVFrame 中;之后就将 AVFrame 中的 data 字段的数据存放到输出文件中。
对于输入数据,首先,通过 fread 函数实现将固定长度的输入文件的数据存放到一块 buffer 内。
H.264中一个包的长度是不定的,读取固定长度的码流通常不可能刚好读出一个包的长度;
对此,FFMpeg 提供了一个 AVCoderParserContext 结构用于解析读到 buffer 内的码流信息,直到能够取出一个完整的 H.264 包。
为此,FFMpeg 提供的函数为av_parser_parse2,该函数比较复杂,定义如下:
int av_parser_parse2(AVCodecParserContext *s, AVCodecContext *avctx, uint8_t **poutbuf, int *poutbuf_size, const uint8_t *buf, int buf_size, int64_t pts, int64_t dts, int64_t pos);
函数的参数和返回值含义如下:
-
AVCodecParserContext *s:初始化过的 AVCodecParserContext 对象,决定了码流该以怎样的标准进行解析;
-
AVCodecContext *avctx:预先定义好的 AVCodecContext 对象;
-
uint8_t **poutbuf:AVPacket::data 的地址,保存解析完成的包数据。
-
int *poutbuf_size:AVPacket 的实际数据长度,如果没有解析出完整的一个包,该值为 0;
-
const uint8_t *but:待解码的码流的地址;
-
int buf_size:待解码的码流的长度;
-
int64_t pts, int64_t dts:显示和解码的时间戳;
-
int64_t pos:码流中的位置;
-
返回值为解析所使用的比特位的长度;
FFMpeg 中为我们提供的该函数常用的使用方式为:
while(in_len){
len = av_parser_parse2(myparser. AVCodecContext, &data, &size, in_data, in len, pts, dts, pos);
in_data += len;
in_len -= len;
if(size)
decode_frame(data, size);
}
如果参数poutbuf_size的值为0,那么应继续解析缓存中剩余的码流;如果缓存中的数据全部解析后依然未能找到一个完整的包,那么继续从输入文件中读取数据到缓存,继续解析操作,直到pkt.size不为0为止。
因此,关于输入数据的处理,代码大致如下:
//open input file
FILE *pInput_File = fopen(Input_FileName, "rb+");
if(!pInput_File){
printf("Open Input File Fail\n");
return -1;
}
//read compressed bitstream form file to buffer
uDataSize = fread(inbuf, 1, INBUF_SIZE, pInput_File);
if(uDataSize == 0){ //decode finish
return -1;
}
//decode the data in the buffer to AVPacket.data
while(uDataSize > 0){
len = av_parser_parse2(pCodecParserCtx, codecCtx,
&(pkt.data), &(pkt.size),
pDataPtr, uDataSize,
AV_NOPTS_VALUE, AV_NOPTS_VALUE,
AV_NOPTS_VALUE);
uDataSize -= len;
uDataPtr += len;
if(pkt.size == 0) continue;
decode_frame(pkt.data, pkt.size);
}
注意,上面提到的av_parser_parse2函数用的几个参数,其实是与具体的编码格式有关的,它们应该在之前已经分配好了,我们只是放到后面来讲一下,因为它们是与具体的解码器强相关的。
对于解码器。
与上面提到的编码实现类似,首先,根据 CODEC_ID 找到注册的解码器 AVCodec,FFMpeg 为此提供的函数为avcodec_find_decoder();
其次,根据找到的解码器获取与之相关的解码器上下文结构体 AVCodecC,使用的函数为编码中提到的avcodec_alloc_context3;
再者,如上面提到的要获取完整的一个 NALU,解码器需要分配一个 AVCodecParserContext 结构,使用函数av_parser_init;
最后,前面的准备工作完成后,打开解码器,即可调用 FFMpeg 提供的解码函数avcodec_decode_video2对输入的压缩域的码流进行解码,并将解码数据存放到 AVFrame->data 中。
代码实现大致如下:
AVFrame *frame = NULL;
AVCodec *codec = NULL;
AVCodecContext *codecCtx = NULL;
AVCodecParserContext *pCodecParserCtx = NULL;
//register all encoder and decoder
avcodec_register_all();
//Allocate AVFrame to Store the Decode Data
frame = av_frame_alloc();
if(!frame){
printf("Alloc Frame Fail\n");
return -1;
}
//Find the AVCodec Depending on the CODEC_ID
codec = avcodec_find_decoder(AV_CODEC_ID_H264);
if(!codec){
printf("Find the Decoder Fail\n");
return -1;
}
//Allocate the AVCodecContext
codecCtx = avcodec_alloc_context3(codec);
if(!codecCtx){
printf("Alloc AVCodecCtx Fail\n");
return -1;
}
//Allocate the AVCodecParserContext
pCodecParserCtx = av_parser_init(AV_CODEC_ID_H264);
if(!pCodecParserCtx){
printf("Alloc AVCodecParserContext Fail\n");
return -1;
}
//Open the Decoder
if(avcodec_open2(codecCtx, codec, NULL) < 0){
printf("Could not Open the Decoder\n");
return -1;
}
//read compressed bitstream form file to buffer
uDataSize = fread(inbuf, 1, INBUF_SIZE, pInput_File);
if(uDataSize == 0){ //decode finish
return -1;
}
//decode the data in the buffer to AVPacket.data
while(uDataSize > 0){
len = av_parser_parse2(pCodecParserCtx, codecCtx,
&(pkt.data), &(pkt.size),
pDataPtr, uDataSize,
AV_NOPTS_VALUE, AV_NOPTS_VALUE,
AV_NOPTS_VALUE);
uDataSize -= len;
uDataPtr += len;
if(pkt.size == 0) continue;
//decode start
avcodec_decode_video2(codecCtx, frame, &got_frame, pkt);
}
注意,上面解码的过程中,针对具体的实现,可能要做一些具体参数上的调整,此处只是理清解码的流程。
对于输出数据。
解码完成后,解码出来的像素域的数据存放在 AVFrame 的 data 字段内,只需要将该字段内存放的数据之间写文件到输出文件即可。
解码函数avcodec_decode_video2函数完成整个解码过程,对于它简单介绍如下:
int avcodec_decode_video2(AVCodecContext *avctx, AVFrame *picture, int *got_picture_ptr, const AVPacket *avpkt);
该函数各个参数的意义:
-
AVCodecContext *avctx:编解码器上下文对象,在打开编解码器时生成;
-
AVFrame *picture: 保存解码完成后的像素数据;我们只需要分配对象的空间,像素的空间codec会为我们分配好;
-
int *got_picture_ptr: 标识位,如果为1,那么说明已经有一帧完整的像素帧可以输出了;
-
const AVPacket *avpkt: 前面解析好的码流包;
由此可见,当标识位为1时,代表解码一帧结束,可以写数据到文件中。代码如下:
pOutput_File = fopen(Output_FileName, "wb");
if(!pOutput_File){
printf("Open Output File Fail\n");
return -1;
}
if(*got_picture_ptr){
fwrite(frame->data[0],1, Len, pOutput_File)
}
解码的大致流程已经完成了,剩余的是一些收尾工作,比如释放分配的内存、结构体等等。
作者:赖人李冰
★文末名片可以免费领取音视频开发学习资料,内容包括(FFmpeg ,webRTC ,rtmp ,hls ,rtsp ,ffplay ,srs)以及音视频学习路线图等等。
见下方!↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓



![[机器视觉]目标检测评价指标及其实现](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/f74a9f3d532647aebc9d079c4030b8d2.png)

![[数据结构] 详解链表(超详细)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/f5efe874514241c0965f4899996a1516.png)