目录
加速器功能
Window2D()函数
实现代码
变量解释
ARRAY_PARTITION
DEPENDENCE
LOOP_TRIPCOUNT
ramp_up
更新Window
更新LineBuffer
Filter2D()函数
ARRAY_PARTITION
window_stream.read()
计算过程
备注
加速器功能
- 硬件加速单元从全局内存(DDR)中读取图像数据和卷积核系数矩阵;
- 计算卷积;
- 计算结果返回全局内存(DDR)中;
加速器顶层代码
void Filter2DKernel(
const char coeffs[256],
float factor,
short bias,
unsigned short width,
unsigned short height,
unsigned short stride,
const unsigned char src[MAX_IMAGE_WIDTH*MAX_IMAGE_HEIGHT],
unsigned char dst[MAX_IMAGE_WIDTH*MAX_IMAGE_HEIGHT])
{
#pragma HLS INTERFACE m_axi port=src offset=slave bundle=gmem0
#pragma HLS INTERFACE m_axi port=coeffs offset=slave bundle=gmem1
#pragma HLS INTERFACE m_axi port=dst offset=slave bundle=gmem1
// Stream of pixels from kernel input to filter, and from filter to output
hls::stream<char,2> coefs_stream;
hls::stream<U8,2> src_stream;
hls::stream<window,3> window_stream; // Set FIFO depth to 0 to minimize resources
hls::stream<U8,64> dst_stream;
#pragma HLS DATAFLOW
// Read image data from global memory over AXI4 MM, and stream pixels out
ReadFromMem(width, height, stride, coeffs, coefs_stream, src, src_stream);
// Read incoming pixels and form valid HxV windows
Window2D(width, height, src_stream, window_stream);
// Process incoming stream of pixels, and stream pixels out
Filter2D(width, height, factor, bias, coefs_stream, window_stream, dst_stream);
// Write incoming stream of pixels and write them to global memory over AXI4 MM
WriteToMem(width, height, stride, dst_stream, dst);
}加速单元占用了两个AXI Master端口,AXI M1用于读取图像数据;AXI M2用于读取卷积核系数,并回传计算结果。
Window2D()函数
该函数(硬件)实现如下功能:
实现代码
struct window {
U8 pix[FILTER_V_SIZE][FILTER_H_SIZE];
};
hls::stream<U8> &src_stream
hls::stream<window> &window_stream
void Window2D(
unsigned short width,
unsigned short height,
hls::stream<U8> &src_stream,
hls::stream<window> &window_stream) {
U8 LineBuffer[FILTER_V_SIZE-1][MAX_IMAGE_WIDTH];
#pragma HLS ARRAY_PARTITION variable=LineBuffer dim=1 complete
#pragma HLS DEPENDENCE variable=LineBuffer inter false
#pragma HLS DEPENDENCE variable=LineBuffer intra false
window Window;
unsigned col_ptr = 0;
unsigned ramp_up = width*((FILTER_V_SIZE-1)/2)+(FILTER_H_SIZE-1)/2;
unsigned num_pixels = width*height;
unsigned num_iterations = num_pixels + ramp_up;
const unsigned max_iterations = MAX_IMAGE_WIDTH*MAX_IMAGE_HEIGHT +
MAX_IMAGE_WIDTH*((FILTER_V_SIZE-1)/2) +
(FILTER_H_SIZE-1)/2;
update_window: for (int n=0; n<num_iterations; n++)
{
#pragma HLS LOOP_TRIPCOUNT max=max_iterations
#pragma HLS PIPELINE II=1
U8 new_pixel = (n<num_pixels) ? src_stream.read() : 0;
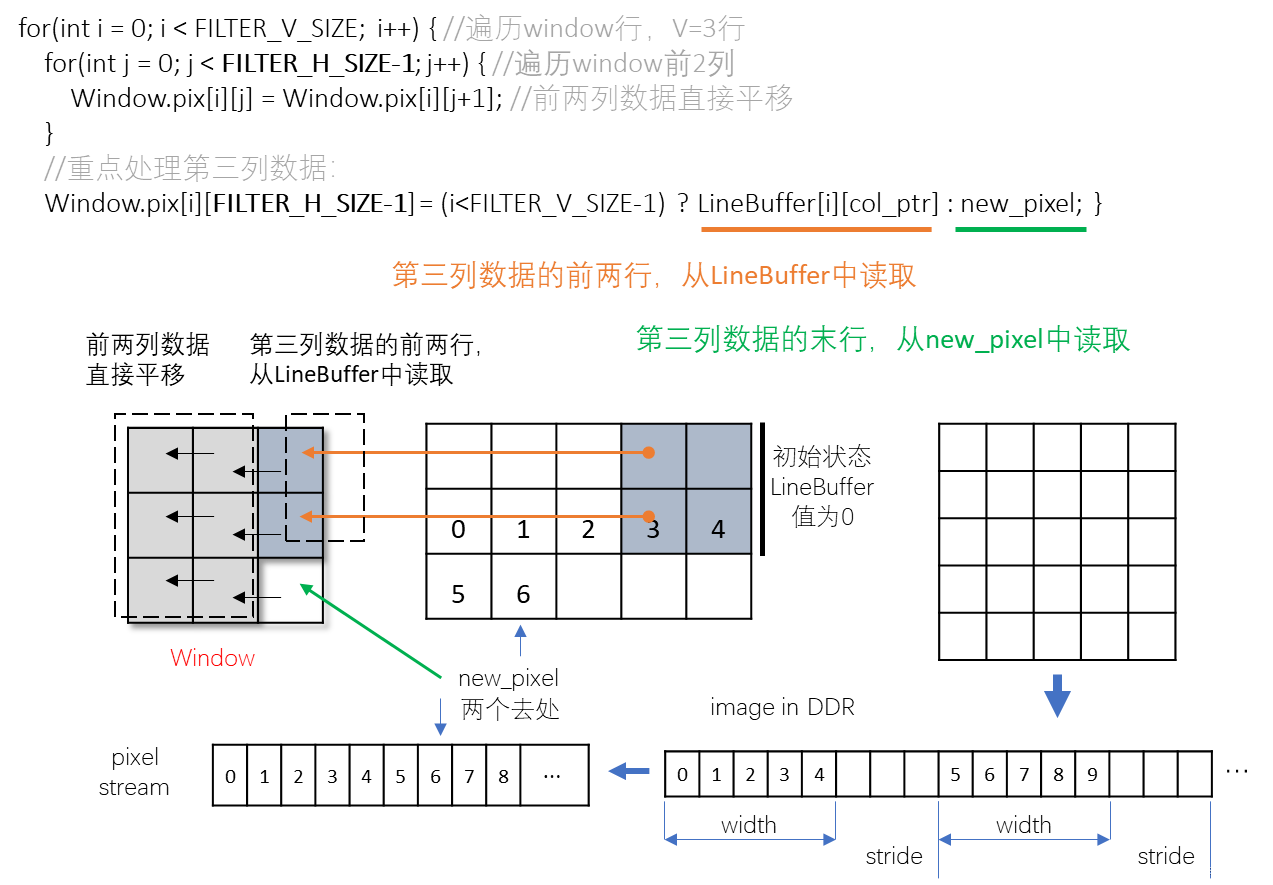
for(int i = 0; i < FILTER_V_SIZE; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < FILTER_H_SIZE-1; j++) {
Window.pix[i][j] = Window.pix[i][j+1];
}
Window.pix[i][FILTER_H_SIZE-1] = (i<FILTER_V_SIZE-1) ? LineBuffer[i][col_ptr] : new_pixel;
}
for(int i = 0; i < FILTER_V_SIZE-2; i++) {
LineBuffer[i][col_ptr] = LineBuffer[i+1][col_ptr];
}
LineBuffer[FILTER_V_SIZE-2][col_ptr] = new_pixel;
if (col_ptr==(width-1)) {
col_ptr = 0;
} else {
col_ptr++;
}
if (n>=ramp_up) { window_stream.write(Window); }
}
}
变量解释
- window_stream变量:窗口缓冲区
- LineBuffer只缓存了两行图像数据!
- ramp_up:初始化滑动窗口需要的像素数
ARRAY_PARTITION
#pragma HLS ARRAY_PARTITION variable=LineBuffer dim=1 complete
这条指令的效果是将LineBuffer数组完全分解为单个元素。这种分解可以将一个大的存储器解析为多个寄存器,从而增加LineBuffer的端口数,从而提高设计的吞吐量,但也会增加存储器实例或寄存器的数量。
DEPENDENCE
#pragma HLS DEPENDENCE variable=LineBuffer inter false //循环间无依赖
指示LineBuffer在不同的循环迭代之间没有数据相关性,即每一次循环对LineBuffer的读写操作都不会影响其他循环的读写操作。如果这个指令指定为true,就表示有数据相关性,那么编译器就会保证每一次循环的读写操作都按照顺序执行,不能并行化。如果指定为false,就表示没有数据相关性,那么编译器就可以在流水线化或展开循环时并行执行多个循环的读写操作,从而提高吞吐量。
#pragma HLS DEPENDENCE variable=LineBuffer intra false //循环内无依赖
指示LineBuffer在同一个循环迭代内没有数据相关性,即同一循环内对LineBuffer的读写操作互不相关。如果这个指令指定为true,就表示有数据相关性,那么编译器就会保证每一次循环内的读写操作都按照顺序执行,不能移动位置。如果指定为false,就表示没有数据相关性,那么编译器就可以在同一个循环内自由地移动读写操作的位置,从而提高操作的可调度性和潜在的性能或面积优化。
LOOP_TRIPCOUNT
#pragma HLS LOOP_TRIPCOUNT max=max_iterations
手动指定一个循环的最大迭代次数。只是用于分析,不会影响综合的结果。它可以帮助HLS工具计算循环的延迟,从而在报告中显示循环对总设计延迟的贡献,并帮助确定适合的优化方法。
ramp_up
window Window;
unsigned col_ptr = 0;
unsigned ramp_up = width*((FILTER_V_SIZE-1)/2)+(FILTER_H_SIZE-1)/2;
unsigned num_pixels = width*height;
unsigned num_iterations = num_pixels + ramp_up;代入计算:
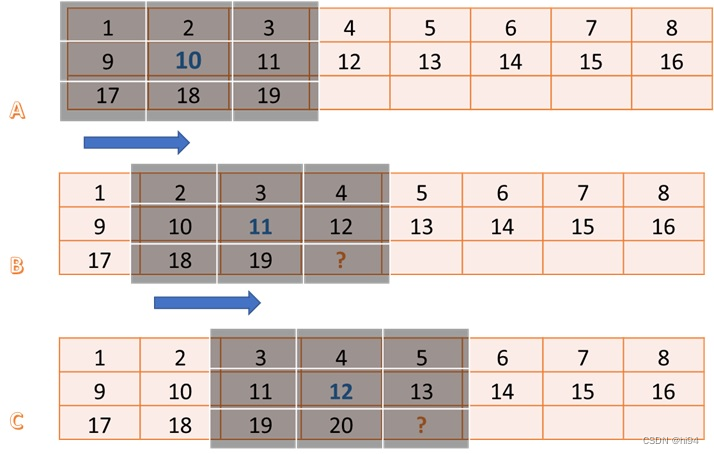
unsigned ramp_up = width*((FILTER_V_SIZE-1)/2)+(FILTER_H_SIZE-1)/2;
ramp_up = 5*((3-1)/2)+(3-1)/2 = 5+1 = 6
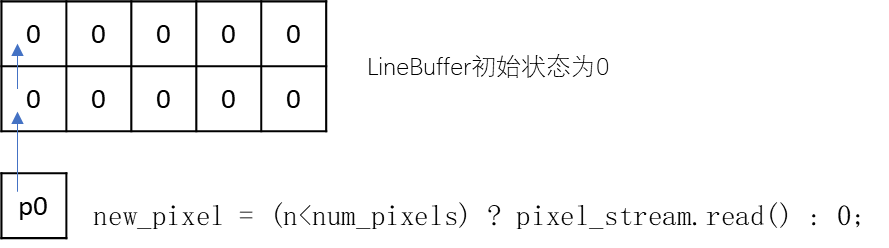
这个值表示了在输出滑动窗口stream之前,需要从输入流中读取多少个像素。也就是说,第一个滑动窗输出时,至少要读取0~6(7)个像素。如下图所示:

更新Window
U8 new_pixel = (n<num_pixels) ? pixel_stream.read() : 0;
前num_pixels个像素,每次从stream中读取,之后的pixel赋值为0。
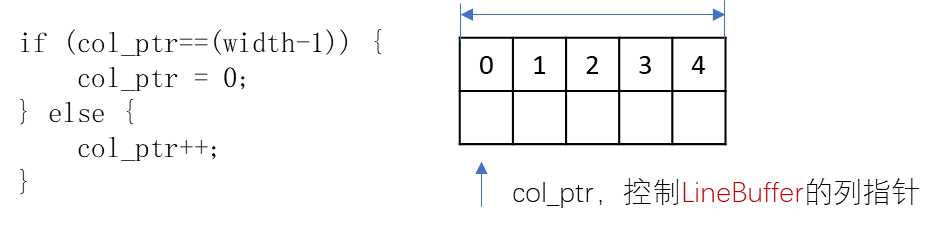
更新LineBuffer
FILTER_V_SIZE-2 = 3-2 = 1
for(int i = 0; i < FILTER_V_SIZE-2; i++) {
LineBuffer[i][col_ptr] = LineBuffer[i+1][col_ptr];
}
LineBuffer[FILTER_V_SIZE-2][col_ptr] = new_pixel;
FILTER_V_SIZE-2 = 3-2 = 1
表示:对于一个高度为v的kernel,其最后一列由new_pixel更新,前v-1列由原kernel上移更新,因此v=3时,只需更新一个数。
每次update_window迭代,LineBuffer仅更新一个pixel。
Filter2D()函数
void Filter2D(
unsigned short width,
unsigned short height,
float factor,
short bias,
hls::stream<char> &coeff_stream,
hls::stream<window> &window_stream,
hls::stream<U8> &pixel_stream ) {
char coeffs[FILTER_V_SIZE][FILTER_H_SIZE];
#pragma HLS ARRAY_PARTITION variable=coeffs complete dim=0
load_coefs: for (int i=0; i<FILTER_V_SIZE; i++) {
for (int j=0; j<FILTER_H_SIZE; j++) {
#pragma HLS PIPELINE II=1
coeffs[i][j] = coeff_stream.read(); } }
apply_filter: for (int y = 0; y < height; y++) {
for (int x = 0; x < width; x++) {
#pragma HLS PIPELINE II=1
window w = window_stream.read();
int sum = 0;
for(int row=0; row<FILTER_V_SIZE; row++) {
for(int col=0; col<FILTER_H_SIZE; col++) {
unsigned char pixel;
int xoffset = (x+col-(FILTER_H_SIZE/2));
int yoffset = (y+row-(FILTER_V_SIZE/2));
// Deal with boundary conditions : clamp pixels to 0 when outside of image
if ( (xoffset<0) || (xoffset>=width) || (yoffset<0) || (yoffset>=height) ) {
pixel = 0;
} else {
pixel = w.pix[row][col];
}
sum += pixel*(char)coeffs[row][col];
} }
unsigned char outpix = MIN(MAX((int(factor * sum)+bias), 0), 255);
pixel_stream.write(outpix);
}
} }
ARRAY_PARTITION
#pragma HLS ARRAY_PARTITION variable=coeffs complete dim=?
| B[0][0] | B[0][1] | B[0][2] | B[0][3] |
| B[1][0] | B[1][1] | B[1][2] | B[1][3] |
dim=0:则相当于将B[2][4]拆分成两个四元素数组B[0][0:3]、B[1][0:3],每一行都可以同时访问四个元素,但是每一列只能访问一个元素。
dim=1:则相当于将B[2][4]拆分成四个双元素数组B[0:1][0]、B[0:1][1]、B[0:1][2]、B[0:1][3],每一列都可以同时访问两个元素,但是每一行只能访问一个元素。
window_stream.read()
window w = window_stream.read();
此语句所在循环中,每个像素点都会读取stream,但不是所有window都会参与coeffs计算。
计算过程
for(int row=0; row<FILTER_V_SIZE; row++) {
for(int col=0; col<FILTER_H_SIZE; col++) {
unsigned char pixel;
int xoffset = (x+col-(FILTER_H_SIZE/2));
int yoffset = (y+row-(FILTER_V_SIZE/2));
// Deal with boundary conditions : clamp pixels to 0 when outside of image
if ( (xoffset<0) || (xoffset>=width) || (yoffset<0) || (yoffset>=height) ) {
pixel = 0;
} else {
pixel = w.pix[row][col];
}
sum += pixel*(char)coeffs[row][col];
}
}
备注
本文所称的函数,并非函数,最终映射为硬件电路。