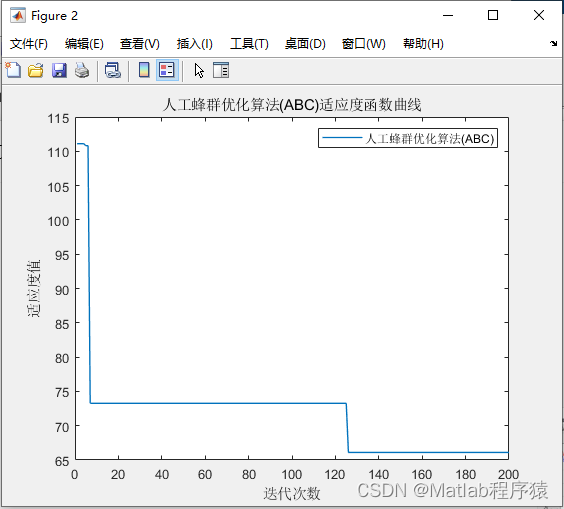
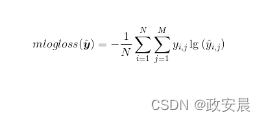
1、元素内容
| 属性名称 | 说明 |
| 元素名.innerText | 输出一个字符串,设置或返回元素中的内容,不识别html标签 |
| 元素名.innerHTML | 输出一个字符串,设置或返回元素中的内容,识别html标签 |
| 元素名.textContent | 设置或返回指定节点的文本内容,不识别html标签 |
方法:
元素名.document.write():向文档写入指定内容。
元素名.document.writeln():向文档写入指定内容并换行。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
div{
height: 100px;
width: 250px;
font-size: 20px;
line-height: 100px;
text-align: center;
display: inline-block;
}
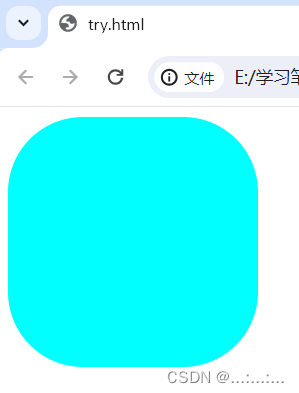
.it{
background-color: aqua;
}
.ih{
background-color: red;
color: white;
}
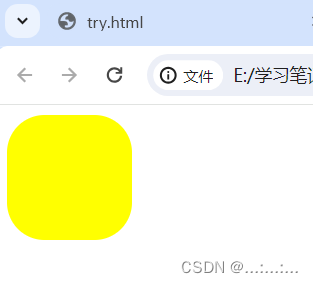
.tc{
background-color: yellow;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="it">innerText</div>
<div class="ih"></div>
<div class="tc">textContent</div>
<script>
let it=document.querySelector(".it")
let ih=document.querySelector(".ih")
let tc=document.querySelector(".tc")
it.innerText='<i>innerText</i>'
ih.innerHTML='<i>innerHTML</i>'//为他们增加倾斜效果
tc.textContent='<i>TextContent</i>'
</script>
</body>
</html>我们发现只有inner HTML识别倾斜标签 
写入文档就是写入网页里
<body>
<h2>注意write()方法不会在每个语句后面新增一行:</h2>
<pre>
<script>
document.write("哈哈哈哈哈哈");
document.write("666666");
</script>
</pre>
<h2>注意writeln()方法在每个语句后面新增一行:</h2>
<pre>
<script>
document.writeln("哈哈哈哈哈哈");
document.writeln("666666");
</script>
</pre>
</body>
练习
<body>
<div></div>
<script>
let arr = ["zhangsan", "lisi", "王麻子", "王总"]
function get_random(n, m) {
return Math.floor(Math.random() * ((m - n) + 1)) + n
}
// 1、获取元素
const box = document.querySelector("div")
// 2、产生随机数
let random = get_random(0, arr.length - 1)
// 3、更换div中的内容
box.innerText = arr[random]
</script>
</body>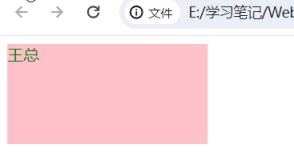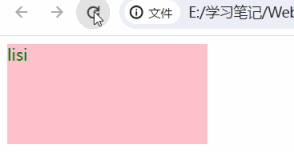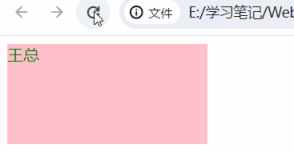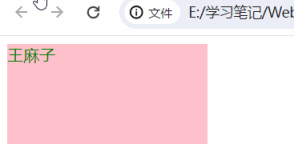
2、更改属性
对象.属性 = 值
<body>
<form action="">
<input type="button" name="" id="">
</form>
<script>
const ipt = document.querySelector("input")
ipt.type = "password"
</script>
</body>本来是按钮,但是属性值被改成密码了

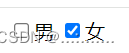
- 像是checked这样的属性名=属性值的属性,js在进行赋值时,通过true/false去控制属性值
- 比如说下面的例子,男的选择按钮我在input属性里用checked默认选中,女孩相反,利用更改属性值,使女的选择按钮默认选中,男相反
<body>
<form action="">
<input type="checkbox" checked name="sex" value="nan">男
<input type="checkbox" name="sex" value="nv">女
</form>
<script>
document.querySelector("input[value='nv']").checked="ture"
document.querySelector("input[value='nan']").checked=false
</script>
</body>
3、更改style样式
①、对象.style.样式 = ""
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
<style>
.box{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: greenyellow;
border: 3px solid yellow;
border-radius: 50%;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box"></div>
<script>
// 1、获取元素
const b = document.querySelector(".box")
// 2、对象.style.样式 = ""
b.style.backgroundColor="red"
</script>
</body>
</html>更改了属性,使原来绿色的背景色,变成了红色
|
|
|
②、利用className=" "
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
<style>
div{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: greenyellow;
border-radius: 50%;
}
.box{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: aqua;
border-radius: 50%;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div></div>
<script>
// 1、获取元素
const b = document.querySelector("div")
// 2、classname
b.className="box"
</script>
</body>
</html>利用ClassName为div盒子添加类名,从而更改样式
|
|
|
③、利用ClassList(" ")
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
<style>
div{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: yellow;
border-radius: 30%;
}
.box{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: aqua;
border-radius: 30%;
}
.bb{
border:5px dashed red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="bb"></div>
<script>
// 1、获取元素
const b = document.querySelector("div")
// 2、classList
b.classList.add("box")
b.classList.remove("bb")
</script>
</body>
</html>利用.bb类名为盒子设置红色边框, 使用 b.classList.remove("bb"),移除.bb类名
利用b.classList.add("box")增添box类名,改变背景色与大小的属性
|
|
|
补充:
如果类名存在,则移除,如果不存在,则添加
box.classList.toggle("box1")
4、查找节点
对象.属性
| 属性 | 说明 |
| parentNode | 可返回某节点的父节点。如果指定的节点没有父节点则返回 null 。 |
| children | children 属性返回元素的子元素的集合,是一个 HTML收集 对象。 提示: 根据子元素在元素中出现的先后顺序进行排序。使用 HTML收集对象的 length属性获取子元素的数量,然后使用序列号(index,起始值为0)访问每个子元素。 |
| childNodes | childNodes 属性返回包含被选节点的子节点的 NodeList。 提示: 如果选定的节点没有子节点,则该属性返回不包含节点的 NodeList。 |
| nextElementSibling | 返回指定元素之后的下一个兄弟元素 |
| previousElementSibling | 返回指定元素的前一个元素。 |
| nextSibling | 返回选定元素的下一个同级节点 |
children 属性与 childNodes属性的差别:
- childNodes 属性返回所有的节点,包括文本节点、注释节点;
- children 属性只返回元素节点;
nextSibling 属性与 nextElementSibling 属性的差别:
- nextSibling 属性返回元素节点之后的兄弟节点(包括文本节点、注释节点);
- nextElementSibling 属性只返回元素节点之后的兄弟元素节点(不包括文本节点、注释节点);
<script>
console.log(1)
console.log(document.querySelector(".son").parentNode)
console.log(2)
console.log(document.querySelector(".father").children)
console.log(3)
console.log(document.querySelector(".father").childNodes)
// 查找兄弟jiedian
console.log(4)
console.log(document.querySelector(".son").nextElementSibling)
console.log(5)
console.log(document.querySelector(".son1").previousElementSibling)
console.log(6)
console.log(document.querySelector(".son").nextSibling)
</script>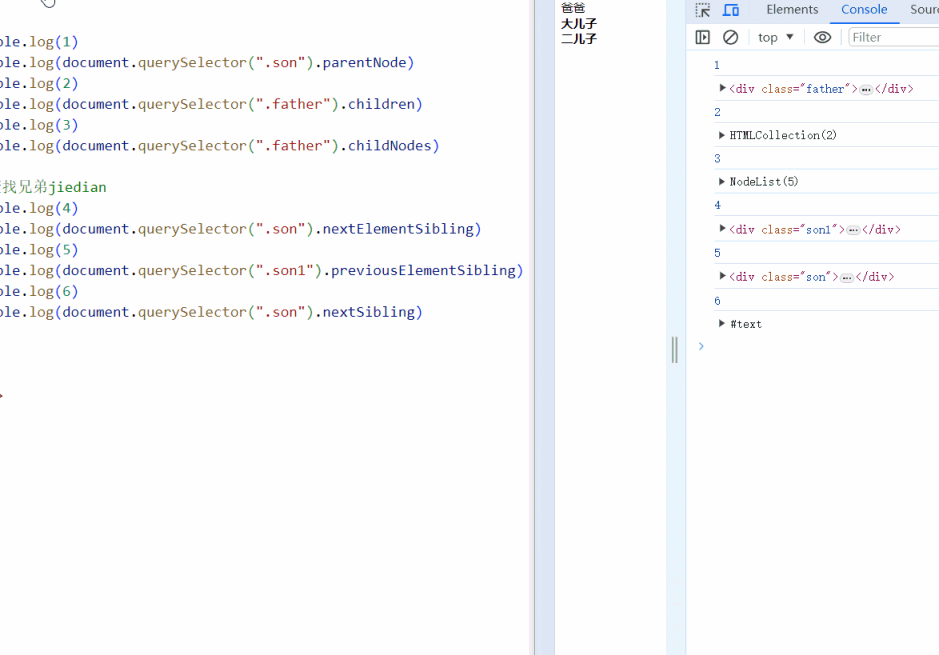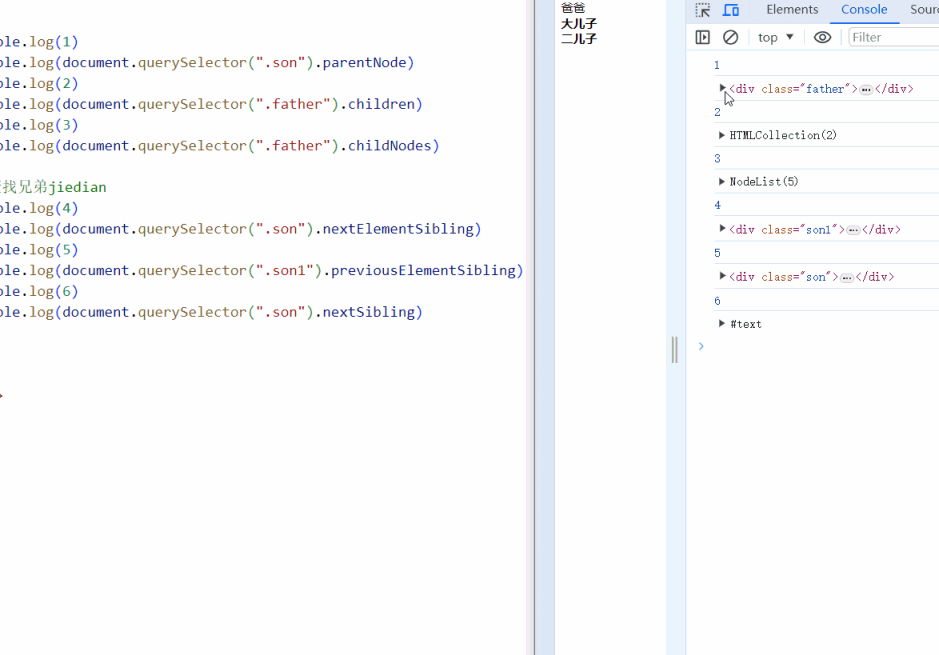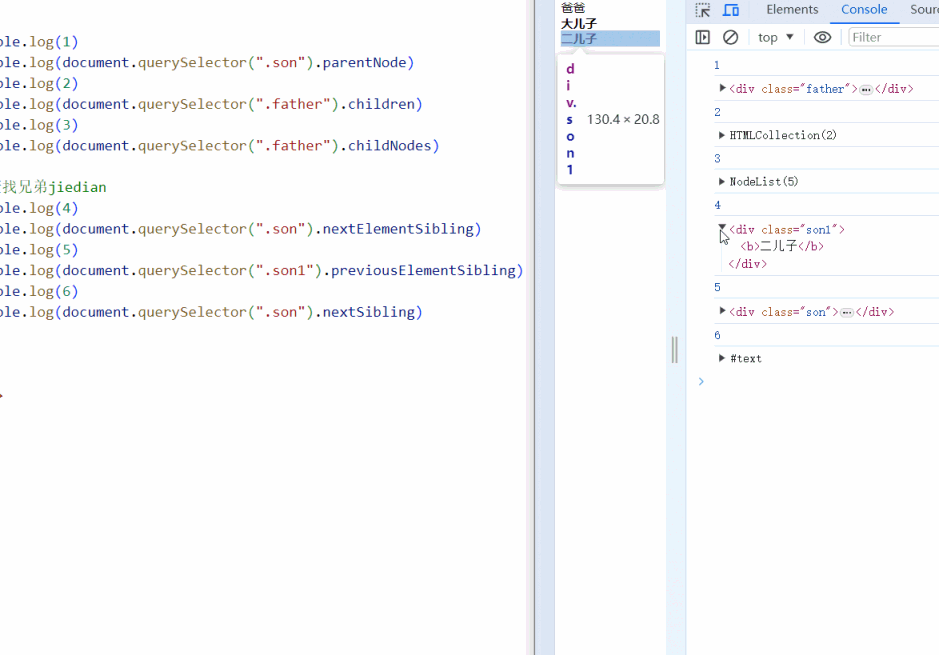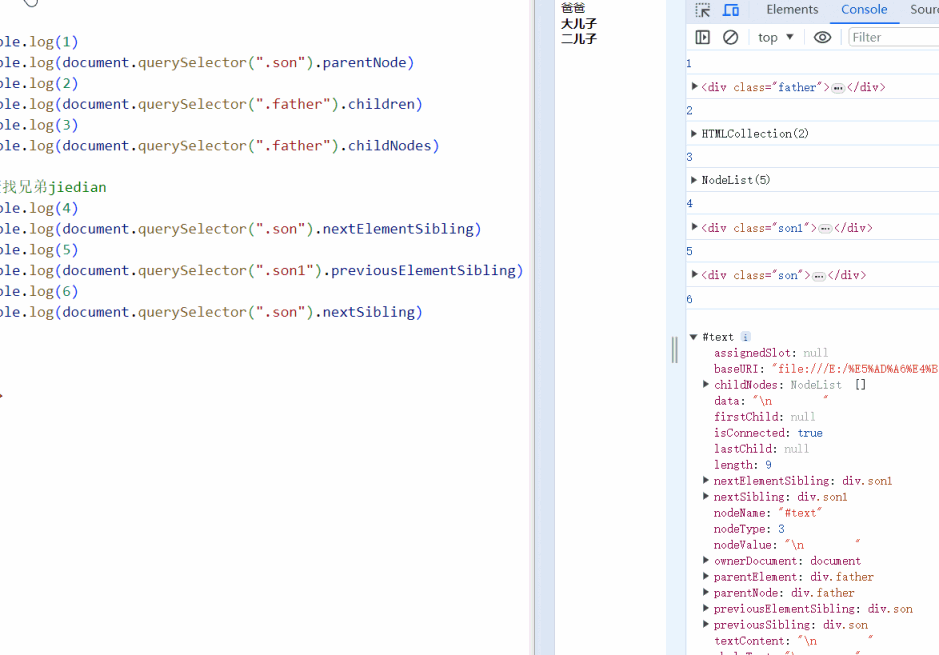
5、事件监听
①、事件源.on+事件类型=匿名函数
同一个事件源,后面注册的事件会对前面注册的事件进行覆盖
<body>
<button>点击</button>
<div></div>
<script>
const button = document.querySelector("button")
const box = document.querySelector("div")
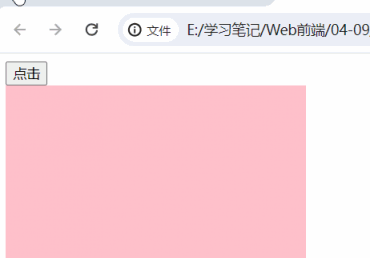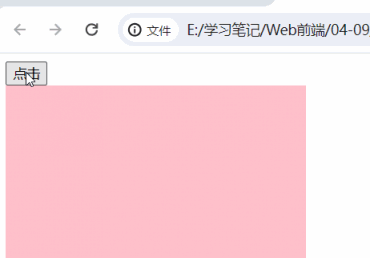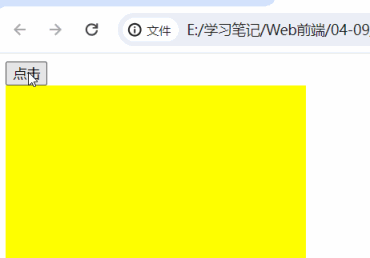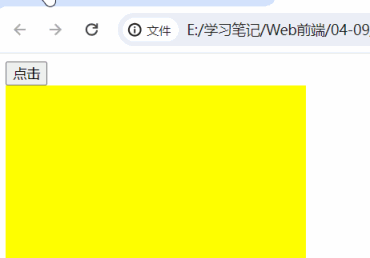
button.onclick = function () {
box.style.backgroundColor = "yellow"
}
button.onclick = function () {
box.innerHTML='<b>6666</b>'
}
</script>
</body>| 没有加 第二个功能块 的时候的时候 | 加 上第二个功能块之后 |
|
| 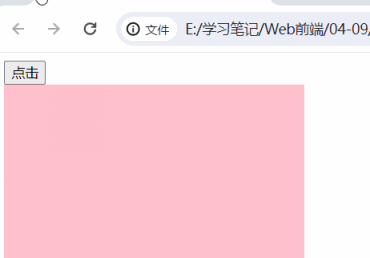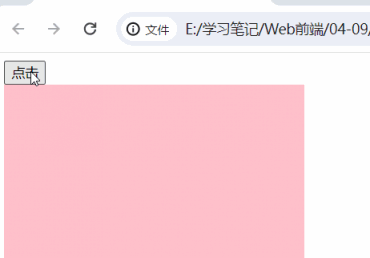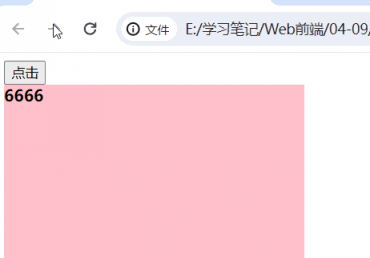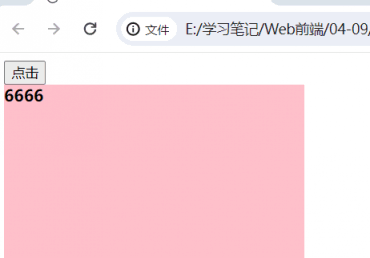 |
去除监听:
事件源.on+事件类型=null
②、事件源.addEventListener("事件类型",行为,【是否捕获】)
是否捕获是true或者false,选填
方法为元素附加事件处理程序而不会覆盖已有的事件处理程序。
<body>
<button>点击</button>
<div></div>
<script>
// 事件监听 不会覆盖
button.addEventListener("click",()=>{
box.style.backgroundColor = "yellow"
}, true)
button.addEventListener("click",()=>{
box.innerHTML='<b>6666</b>'
}, true)
</script>
</body>| 没有加 第二个功能块 的时候的时候 | 加 上第二个功能块之后 |
|
|  |
去除监听:
事件源.removeEventListener("事件", 行为,【是否捕获】)
6、练习
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title></title>
<style type="text/css">
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
ul {
list-style: none;
}
.wrapper {
width: 1000px;
height: 475px;
margin: 0 auto;
margin-top: 100px;
}
.tab {
border: 1px solid #ddd;
border-bottom: 0;
height: 36px;
width: 320px;
}
.tab li {
position: relative;
float: left;
width: 80px;
height: 34px;
line-height: 34px;
text-align: center;
cursor: pointer;
border-top: 4px solid #fff;
}
.tab span {
position: absolute;
right: 0;
top: 10px;
background: #ddd;
width: 1px;
height: 14px;
overflow: hidden;
}
.products {
width: 1002px;
border: 1px solid #ddd;
height: 476px;
}
.products .main {
float: left;
display: none;
width: 1000px;
height: 480px;
}
.products .main:nth-child(1) {
background-color: pink;
}
.products .main:nth-child(2) {
background-color: rgb(236, 5, 44);
}
.products .main:nth-child(3) {
background-color: rgb(59, 13, 228);
}
.products .main:nth-child(4) {
background-color: rgb(49, 216, 7);
}
.products .main.active {
display: block;
}
.tab li.active {
border-color: red;
border-bottom: 0;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="wrapper">
<ul class="tab">
<li class="tab-item active">国际大牌<span>◆</span></li>
<li class="tab-item">国妆名牌<span>◆</span></li>
<li class="tab-item">清洁用品<span>◆</span></li>
<li class="tab-item">男士精品</li>
</ul>
<div class="products">
<div class="main active">
</div>
<div class="main">
</div>
<div class="main">
</div>
<div class="main">
</div>
</div>
</div>
<script>
// 获取元素对象
let lis = document.querySelectorAll(".tab .tab-item")
let divs = document.querySelectorAll(".products .main")
//遍历
for (let i = 0; i < lis.length; i++) {
// li添加事件监听
lis[i].addEventListener("click", function () {
document.querySelector(".tab .active").classList.remove("active")
lis[i].classList.add("active")
document.querySelector(".products .active").classList.remove("active")
divs[i].classList.add("active")
})
}
</script>
</body>
</html>