基于深度学习的花卉检测系统(含PyQt界面)
- 前言
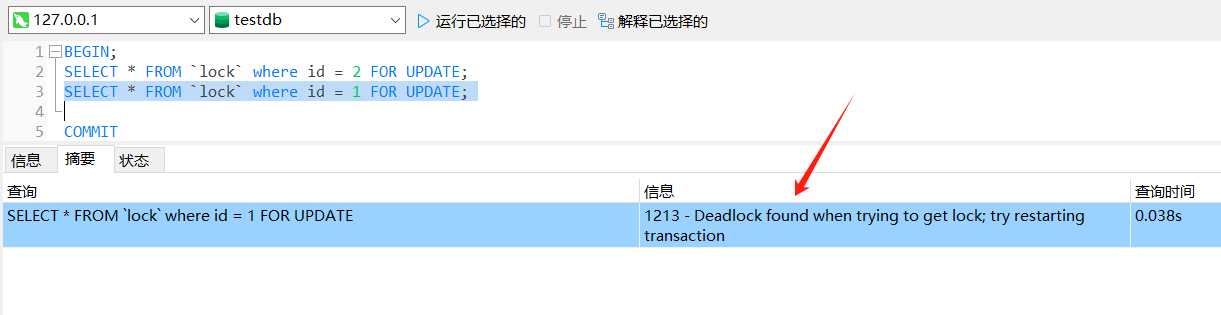
- 一、数据集
- 1.1 数据集介绍
- 1.2 数据预处理
- 二、模型搭建
- 三、训练与测试
- 3.1 模型训练
- 3.2 模型测试
- 四、PyQt界面实现
- 参考资料
前言
本项目是基于swin_transformer深度学习网络模型的花卉检测系统,目前能够检测daisy、dandelion、roses、sunflowers、tulips五类花卉,可以自己添加花卉种类进行训练。本文将详述数据集处理、模型构建、训练代码、以及基于PyQt5的应用界面设计。在应用中可以对花卉的图片进行识别,输出花卉的类别和模型对其预测结果的置信度。本文附带了完整的应用界面设计、深度学习模型代码和训练数据集的下载链接。
完整资源下载链接:博主在面包多网站上的完整资源下载页
项目演示视频:
【项目分享】基于深度学习的花卉检测系统(含PyQt界面)
一、数据集
1.1 数据集介绍
本项目使用的数据集是由谷歌创建的一个用于机器学习和计算机视觉任务的图像数据集,称为花卉数据集(Flower Photos Dataset)。它包含了来自五种不同花卉类别的图像,每个类别大约有几百到一千张图像。这些花卉类别包括:雏菊(Daisy)、蒲公英(Dandelion)、玫瑰(Roses)、向日葵(Sunflowers)、郁金香(Tulips) 。
下载链接:http://download.tensorflow.org/example_images/flower_photos.tgz
下载后得到一个.tgr文件,解压后,文件夹下包含了5个子文件夹,每个子文件夹都存储了一种类别的花的图片,子文件夹的名称就是花的类别的名称,如下图:

1.2 数据预处理
使用MyDataSet类在 PyTorch 中加载图像数据并将其与相应的类别标签配对,完成自定义数据集的生成。它包含初始化方法__init__来接收图像文件路径列表和对应的类别标签列表,并提供了__getitem__方法来获取图像及其标签,同时还可以使用collate_fn将多个样本进行批处理。
class MyDataSet(Dataset):
"""自定义数据集"""
def __init__(self, images_path: list, images_class: list, transform=None):
self.images_path = images_path
self.images_class = images_class
self.transform = transform
def __len__(self):
return len(self.images_path)
def __getitem__(self, item):
img = Image.open(self.images_path[item])
# RGB为彩色图片,L为灰度图片
if img.mode != 'RGB':
raise ValueError("image: {} isn't RGB mode.".format(self.images_path[item]))
label = self.images_class[item]
if self.transform is not None:
img = self.transform(img)
return img, label
@staticmethod
def collate_fn(batch):
# 官方实现的default_collate可以参考
# https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/blob/67b7e751e6b5931a9f45274653f4f653a4e6cdf6/torch/utils/data/_utils/collate.py
images, labels = tuple(zip(*batch))
images = torch.stack(images, dim=0)
labels = torch.as_tensor(labels)
return images, labels
二、模型搭建
我们使用的是一种称为 Swin_Transformer 的新视觉 Transformer,它可以作为 CV 的通用主干。将 Transformer 从语言适应到视觉方面的挑战来自两个域之间的差异,例如视觉实体的规模以及相比于文本单词的高分辨率图像像素的巨大差异。为解决这些差异,我们提出了一种 层次化 (hierarchical) Transformer,其表示是用移位窗口 (Shifted Windows) 计算的。移位窗口方案通过将自注意力计算限制在不重叠的局部窗口的同时,还允许跨窗口连接来提高效率。这种分层架构具有在各种尺度上建模的灵活性,并且相对于图像大小具有线性计算复杂度。Swin Transformer 的这些特性使其与广泛的视觉任务兼容,包括图像分类(ImageNet-1K 的 87.3 top-1 Acc)和密集预测任务,例如目标检测(COCO test dev 的 58.7 box AP 和 51.1 mask AP)和语义分割(ADE20K val 的 53.5 mIoU)。它的性能在 COCO 上以 +2.7 box AP 和 +2.6 mask AP 以及在 ADE20K 上 +3.2 mIoU 的大幅度超越了SOTA 技术,证明了基于 Transformer 的模型作为视觉主干的潜力。分层设计和移位窗口方法也证明了其对全 MLP 架构是有益的。Swin_Transformer模型的整体架构,如下图所示:

而我们代码的模型具体实现主要包括如下几个模块:PatchEmbed 模块、WindowAttention模块、SwinTransformerBlock模块 BasicLayer模块、SwinTransformer模块以及辅助函数drop_path_f等。
PatchEmbed 模块:将输入图像划分为不重叠的图像块,并将每个图像块转换为嵌入向量。
class PatchEmbed(nn.Module):
"""
2D Image to Patch Embedding
"""
def __init__(self, patch_size=4, in_c=3, embed_dim=96, norm_layer=None):
super().__init__()
patch_size = (patch_size, patch_size)
self.patch_size = patch_size
self.in_chans = in_c
self.embed_dim = embed_dim
self.proj = nn.Conv2d(in_c, embed_dim, kernel_size=patch_size, stride=patch_size)
self.norm = norm_layer(embed_dim) if norm_layer else nn.Identity()
def forward(self, x):
_, _, H, W = x.shape
# padding
# 如果输入图片的H,W不是patch_size的整数倍,需要进行padding
pad_input = (H % self.patch_size[0] != 0) or (W % self.patch_size[1] != 0)
if pad_input:
# to pad the last 3 dimensions,
# (W_left, W_right, H_top,H_bottom, C_front, C_back)
x = F.pad(x, (0, self.patch_size[1] - W % self.patch_size[1],
0, self.patch_size[0] - H % self.patch_size[0],
0, 0))
# 下采样patch_size倍
x = self.proj(x)
_, _, H, W = x.shape
# flatten: [B, C, H, W] -> [B, C, HW]
# transpose: [B, C, HW] -> [B, HW, C]
x = x.flatten(2).transpose(1, 2)
x = self.norm(x)
return x, H, W
WindowAttention 模块:基于窗口的多头自注意力机制,用于捕获图像块之间的全局关系。
class WindowAttention(nn.Module):
r""" Window based multi-head self attention (W-MSA) module with relative position bias.
It supports both of shifted and non-shifted window.
Args:
dim (int): Number of input channels.
window_size (tuple[int]): The height and width of the window.
num_heads (int): Number of attention heads.
qkv_bias (bool, optional): If True, add a learnable bias to query, key, value. Default: True
attn_drop (float, optional): Dropout ratio of attention weight. Default: 0.0
proj_drop (float, optional): Dropout ratio of output. Default: 0.0
"""
def __init__(self, dim, window_size, num_heads, qkv_bias=True, attn_drop=0., proj_drop=0.):
super().__init__()
self.dim = dim
self.window_size = window_size # [Mh, Mw]
self.num_heads = num_heads
head_dim = dim // num_heads
self.scale = head_dim ** -0.5
# define a parameter table of relative position bias
self.relative_position_bias_table = nn.Parameter(
torch.zeros((2 * window_size[0] - 1) * (2 * window_size[1] - 1), num_heads)) # [2*Mh-1 * 2*Mw-1, nH]
# get pair-wise relative position index for each token inside the window
coords_h = torch.arange(self.window_size[0])
coords_w = torch.arange(self.window_size[1])
coords = torch.stack(torch.meshgrid([coords_h, coords_w])) # [2, Mh, Mw]
coords_flatten = torch.flatten(coords, 1) # [2, Mh*Mw]
# [2, Mh*Mw, 1] - [2, 1, Mh*Mw]
relative_coords = coords_flatten[:, :, None] - coords_flatten[:, None, :] # [2, Mh*Mw, Mh*Mw]
relative_coords = relative_coords.permute(1, 2, 0).contiguous() # [Mh*Mw, Mh*Mw, 2]
relative_coords[:, :, 0] += self.window_size[0] - 1 # shift to start from 0
relative_coords[:, :, 1] += self.window_size[1] - 1
relative_coords[:, :, 0] *= 2 * self.window_size[1] - 1
relative_position_index = relative_coords.sum(-1) # [Mh*Mw, Mh*Mw]
self.register_buffer("relative_position_index", relative_position_index)
self.qkv = nn.Linear(dim, dim * 3, bias=qkv_bias)
self.attn_drop = nn.Dropout(attn_drop)
self.proj = nn.Linear(dim, dim)
self.proj_drop = nn.Dropout(proj_drop)
nn.init.trunc_normal_(self.relative_position_bias_table, std=.02)
self.softmax = nn.Softmax(dim=-1)
def forward(self, x, mask: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None):
"""
Args:
x: input features with shape of (num_windows*B, Mh*Mw, C)
mask: (0/-inf) mask with shape of (num_windows, Wh*Ww, Wh*Ww) or None
"""
# [batch_size*num_windows, Mh*Mw, total_embed_dim]
B_, N, C = x.shape
# qkv(): -> [batch_size*num_windows, Mh*Mw, 3 * total_embed_dim]
# reshape: -> [batch_size*num_windows, Mh*Mw, 3, num_heads, embed_dim_per_head]
# permute: -> [3, batch_size*num_windows, num_heads, Mh*Mw, embed_dim_per_head]
qkv = self.qkv(x).reshape(B_, N, 3, self.num_heads, C // self.num_heads).permute(2, 0, 3, 1, 4)
# [batch_size*num_windows, num_heads, Mh*Mw, embed_dim_per_head]
q, k, v = qkv.unbind(0) # make torchscript happy (cannot use tensor as tuple)
# transpose: -> [batch_size*num_windows, num_heads, embed_dim_per_head, Mh*Mw]
# @: multiply -> [batch_size*num_windows, num_heads, Mh*Mw, Mh*Mw]
q = q * self.scale
attn = (q @ k.transpose(-2, -1))
# relative_position_bias_table.view: [Mh*Mw*Mh*Mw,nH] -> [Mh*Mw,Mh*Mw,nH]
relative_position_bias = self.relative_position_bias_table[self.relative_position_index.view(-1)].view(
self.window_size[0] * self.window_size[1], self.window_size[0] * self.window_size[1], -1)
relative_position_bias = relative_position_bias.permute(2, 0, 1).contiguous() # [nH, Mh*Mw, Mh*Mw]
attn = attn + relative_position_bias.unsqueeze(0)
if mask is not None:
# mask: [nW, Mh*Mw, Mh*Mw]
nW = mask.shape[0] # num_windows
# attn.view: [batch_size, num_windows, num_heads, Mh*Mw, Mh*Mw]
# mask.unsqueeze: [1, nW, 1, Mh*Mw, Mh*Mw]
attn = attn.view(B_ // nW, nW, self.num_heads, N, N) + mask.unsqueeze(1).unsqueeze(0)
attn = attn.view(-1, self.num_heads, N, N)
attn = self.softmax(attn)
else:
attn = self.softmax(attn)
attn = self.attn_drop(attn)
# @: multiply -> [batch_size*num_windows, num_heads, Mh*Mw, embed_dim_per_head]
# transpose: -> [batch_size*num_windows, Mh*Mw, num_heads, embed_dim_per_head]
# reshape: -> [batch_size*num_windows, Mh*Mw, total_embed_dim]
x = (attn @ v).transpose(1, 2).reshape(B_, N, C)
x = self.proj(x)
x = self.proj_drop(x)
return x
SwinTransformerBlock 模块:Swin Transformer 的基本模块,包含了窗口注意力机制和MLP前馈网络。
class SwinTransformerBlock(nn.Module):
r""" Swin Transformer Block.
Args:
dim (int): Number of input channels.
num_heads (int): Number of attention heads.
window_size (int): Window size.
shift_size (int): Shift size for SW-MSA.
mlp_ratio (float): Ratio of mlp hidden dim to embedding dim.
qkv_bias (bool, optional): If True, add a learnable bias to query, key, value. Default: True
drop (float, optional): Dropout rate. Default: 0.0
attn_drop (float, optional): Attention dropout rate. Default: 0.0
drop_path (float, optional): Stochastic depth rate. Default: 0.0
act_layer (nn.Module, optional): Activation layer. Default: nn.GELU
norm_layer (nn.Module, optional): Normalization layer. Default: nn.LayerNorm
"""
def __init__(self, dim, num_heads, window_size=7, shift_size=0,
mlp_ratio=4., qkv_bias=True, drop=0., attn_drop=0., drop_path=0.,
act_layer=nn.GELU, norm_layer=nn.LayerNorm):
super().__init__()
self.dim = dim
self.num_heads = num_heads
self.window_size = window_size
self.shift_size = shift_size
self.mlp_ratio = mlp_ratio
assert 0 <= self.shift_size < self.window_size, "shift_size must in 0-window_size"
self.norm1 = norm_layer(dim)
self.attn = WindowAttention(
dim, window_size=(self.window_size, self.window_size), num_heads=num_heads, qkv_bias=qkv_bias,
attn_drop=attn_drop, proj_drop=drop)
self.drop_path = DropPath(drop_path) if drop_path > 0. else nn.Identity()
self.norm2 = norm_layer(dim)
mlp_hidden_dim = int(dim * mlp_ratio)
self.mlp = Mlp(in_features=dim, hidden_features=mlp_hidden_dim, act_layer=act_layer, drop=drop)
def forward(self, x, attn_mask):
H, W = self.H, self.W
B, L, C = x.shape
assert L == H * W, "input feature has wrong size"
shortcut = x
x = self.norm1(x)
x = x.view(B, H, W, C)
# pad feature maps to multiples of window size
# 把feature map给pad到window size的整数倍
pad_l = pad_t = 0
pad_r = (self.window_size - W % self.window_size) % self.window_size
pad_b = (self.window_size - H % self.window_size) % self.window_size
x = F.pad(x, (0, 0, pad_l, pad_r, pad_t, pad_b))
_, Hp, Wp, _ = x.shape
# cyclic shift
if self.shift_size > 0:
shifted_x = torch.roll(x, shifts=(-self.shift_size, -self.shift_size), dims=(1, 2))
else:
shifted_x = x
attn_mask = None
# partition windows
x_windows = window_partition(shifted_x, self.window_size) # [nW*B, Mh, Mw, C]
x_windows = x_windows.view(-1, self.window_size * self.window_size, C) # [nW*B, Mh*Mw, C]
# W-MSA/SW-MSA
attn_windows = self.attn(x_windows, mask=attn_mask) # [nW*B, Mh*Mw, C]
# merge windows
attn_windows = attn_windows.view(-1, self.window_size, self.window_size, C) # [nW*B, Mh, Mw, C]
shifted_x = window_reverse(attn_windows, self.window_size, Hp, Wp) # [B, H', W', C]
# reverse cyclic shift
if self.shift_size > 0:
x = torch.roll(shifted_x, shifts=(self.shift_size, self.shift_size), dims=(1, 2))
else:
x = shifted_x
if pad_r > 0 or pad_b > 0:
# 把前面pad的数据移除掉
x = x[:, :H, :W, :].contiguous()
x = x.view(B, H * W, C)
# FFN
x = shortcut + self.drop_path(x)
x = x + self.drop_path(self.mlp(self.norm2(x)))
return x
BasicLayer 模块:用于构建 Swin Transformer 的一个阶段,可以包含多个 SwinTransformerBlock 模块。
class BasicLayer(nn.Module):
"""
A basic Swin Transformer layer for one stage.
Args:
dim (int): Number of input channels.
depth (int): Number of blocks.
num_heads (int): Number of attention heads.
window_size (int): Local window size.
mlp_ratio (float): Ratio of mlp hidden dim to embedding dim.
qkv_bias (bool, optional): If True, add a learnable bias to query, key, value. Default: True
drop (float, optional): Dropout rate. Default: 0.0
attn_drop (float, optional): Attention dropout rate. Default: 0.0
drop_path (float | tuple[float], optional): Stochastic depth rate. Default: 0.0
norm_layer (nn.Module, optional): Normalization layer. Default: nn.LayerNorm
downsample (nn.Module | None, optional): Downsample layer at the end of the layer. Default: None
use_checkpoint (bool): Whether to use checkpointing to save memory. Default: False.
"""
def __init__(self, dim, depth, num_heads, window_size,
mlp_ratio=4., qkv_bias=True, drop=0., attn_drop=0.,
drop_path=0., norm_layer=nn.LayerNorm, downsample=None, use_checkpoint=False):
super().__init__()
self.dim = dim
self.depth = depth
self.window_size = window_size
self.use_checkpoint = use_checkpoint
self.shift_size = window_size // 2
# build blocks
self.blocks = nn.ModuleList([
SwinTransformerBlock(
dim=dim,
num_heads=num_heads,
window_size=window_size,
shift_size=0 if (i % 2 == 0) else self.shift_size,
mlp_ratio=mlp_ratio,
qkv_bias=qkv_bias,
drop=drop,
attn_drop=attn_drop,
drop_path=drop_path[i] if isinstance(drop_path, list) else drop_path,
norm_layer=norm_layer)
for i in range(depth)])
# patch merging layer
if downsample is not None:
self.downsample = downsample(dim=dim, norm_layer=norm_layer)
else:
self.downsample = None
def create_mask(self, x, H, W):
# calculate attention mask for SW-MSA
# 保证Hp和Wp是window_size的整数倍
Hp = int(np.ceil(H / self.window_size)) * self.window_size
Wp = int(np.ceil(W / self.window_size)) * self.window_size
# 拥有和feature map一样的通道排列顺序,方便后续window_partition
img_mask = torch.zeros((1, Hp, Wp, 1), device=x.device) # [1, Hp, Wp, 1]
h_slices = (slice(0, -self.window_size),
slice(-self.window_size, -self.shift_size),
slice(-self.shift_size, None))
w_slices = (slice(0, -self.window_size),
slice(-self.window_size, -self.shift_size),
slice(-self.shift_size, None))
cnt = 0
for h in h_slices:
for w in w_slices:
img_mask[:, h, w, :] = cnt
cnt += 1
mask_windows = window_partition(img_mask, self.window_size) # [nW, Mh, Mw, 1]
mask_windows = mask_windows.view(-1, self.window_size * self.window_size) # [nW, Mh*Mw]
attn_mask = mask_windows.unsqueeze(1) - mask_windows.unsqueeze(2) # [nW, 1, Mh*Mw] - [nW, Mh*Mw, 1]
# [nW, Mh*Mw, Mh*Mw]
attn_mask = attn_mask.masked_fill(attn_mask != 0, float(-100.0)).masked_fill(attn_mask == 0, float(0.0))
return attn_mask
def forward(self, x, H, W):
attn_mask = self.create_mask(x, H, W) # [nW, Mh*Mw, Mh*Mw]
for blk in self.blocks:
blk.H, blk.W = H, W
if not torch.jit.is_scripting() and self.use_checkpoint:
x = checkpoint.checkpoint(blk, x, attn_mask)
else:
x = blk(x, attn_mask)
if self.downsample is not None:
x = self.downsample(x, H, W)
H, W = (H + 1) // 2, (W + 1) // 2
return x, H, W
SwinTransformer 模块:整个 Swin Transformer 模型的主体结构,包含了多个 BasicLayer 模块。
class SwinTransformer(nn.Module):
r""" Swin Transformer
A PyTorch impl of : `Swin Transformer: Hierarchical Vision Transformer using Shifted Windows` -
https://arxiv.org/pdf/2103.14030
Args:
patch_size (int | tuple(int)): Patch size. Default: 4
in_chans (int): Number of input image channels. Default: 3
num_classes (int): Number of classes for classification head. Default: 1000
embed_dim (int): Patch embedding dimension. Default: 96
depths (tuple(int)): Depth of each Swin Transformer layer.
num_heads (tuple(int)): Number of attention heads in different layers.
window_size (int): Window size. Default: 7
mlp_ratio (float): Ratio of mlp hidden dim to embedding dim. Default: 4
qkv_bias (bool): If True, add a learnable bias to query, key, value. Default: True
drop_rate (float): Dropout rate. Default: 0
attn_drop_rate (float): Attention dropout rate. Default: 0
drop_path_rate (float): Stochastic depth rate. Default: 0.1
norm_layer (nn.Module): Normalization layer. Default: nn.LayerNorm.
patch_norm (bool): If True, add normalization after patch embedding. Default: True
use_checkpoint (bool): Whether to use checkpointing to save memory. Default: False
"""
def __init__(self, patch_size=4, in_chans=3, num_classes=1000,
embed_dim=96, depths=(2, 2, 6, 2), num_heads=(3, 6, 12, 24),
window_size=7, mlp_ratio=4., qkv_bias=True,
drop_rate=0., attn_drop_rate=0., drop_path_rate=0.1,
norm_layer=nn.LayerNorm, patch_norm=True,
use_checkpoint=False, **kwargs):
super().__init__()
self.num_classes = num_classes
self.num_layers = len(depths)
self.embed_dim = embed_dim
self.patch_norm = patch_norm
# stage4输出特征矩阵的channels
self.num_features = int(embed_dim * 2 ** (self.num_layers - 1))
self.mlp_ratio = mlp_ratio
# split image into non-overlapping patches
self.patch_embed = PatchEmbed(
patch_size=patch_size, in_c=in_chans, embed_dim=embed_dim,
norm_layer=norm_layer if self.patch_norm else None)
self.pos_drop = nn.Dropout(p=drop_rate)
# stochastic depth
dpr = [x.item() for x in torch.linspace(0, drop_path_rate, sum(depths))] # stochastic depth decay rule
# build layers
self.layers = nn.ModuleList()
for i_layer in range(self.num_layers):
# 注意这里构建的stage和论文图中有些差异
# 这里的stage不包含该stage的patch_merging层,包含的是下个stage的
layers = BasicLayer(dim=int(embed_dim * 2 ** i_layer),
depth=depths[i_layer],
num_heads=num_heads[i_layer],
window_size=window_size,
mlp_ratio=self.mlp_ratio,
qkv_bias=qkv_bias,
drop=drop_rate,
attn_drop=attn_drop_rate,
drop_path=dpr[sum(depths[:i_layer]):sum(depths[:i_layer + 1])],
norm_layer=norm_layer,
downsample=PatchMerging if (i_layer < self.num_layers - 1) else None,
use_checkpoint=use_checkpoint)
self.layers.append(layers)
self.norm = norm_layer(self.num_features)
self.avgpool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool1d(1)
self.head = nn.Linear(self.num_features, num_classes) if num_classes > 0 else nn.Identity()
self.apply(self._init_weights)
def _init_weights(self, m):
if isinstance(m, nn.Linear):
nn.init.trunc_normal_(m.weight, std=.02)
if isinstance(m, nn.Linear) and m.bias is not None:
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
elif isinstance(m, nn.LayerNorm):
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
nn.init.constant_(m.weight, 1.0)
def forward(self, x):
# x: [B, L, C]
x, H, W = self.patch_embed(x)
x = self.pos_drop(x)
for layer in self.layers:
x, H, W = layer(x, H, W)
x = self.norm(x) # [B, L, C]
x = self.avgpool(x.transpose(1, 2)) # [B, C, 1]
x = torch.flatten(x, 1)
x = self.head(x)
return x
辅助函数drop_path_f :用于实现随机深度路径(Stochastic Depth)以及一些用于处理窗口的辅助函数。
def drop_path_f(x, drop_prob: float = 0., training: bool = False):
"""Drop paths (Stochastic Depth) per sample (when applied in main path of residual blocks).
This is the same as the DropConnect impl I created for EfficientNet, etc networks, however,
the original name is misleading as 'Drop Connect' is a different form of dropout in a separate paper...
See discussion: https://github.com/tensorflow/tpu/issues/494#issuecomment-532968956 ... I've opted for
changing the layer and argument names to 'drop path' rather than mix DropConnect as a layer name and use
'survival rate' as the argument.
"""
if drop_prob == 0. or not training:
return x
keep_prob = 1 - drop_prob
shape = (x.shape[0],) + (1,) * (x.ndim - 1) # work with diff dim tensors, not just 2D ConvNets
random_tensor = keep_prob + torch.rand(shape, dtype=x.dtype, device=x.device)
random_tensor.floor_() # binarize
output = x.div(keep_prob) * random_tensor
return output
三、训练与测试
3.1 模型训练
我们训练的模型是在通用的预训练模型swin_base_patch4_window7_224.pth上再次训练的,通过模型训练微调,能给得到一个效果更好的花卉检测模型。
首先,设置模型训练的关键参数,如检测目标类别数目(可以按照自己的数据集和检测种类进行设置)、批量大小、训练周期、输入数据的维度等参数。
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument('--num_classes', type=int, default=5)
parser.add_argument('--epochs', type=int, default=100)
parser.add_argument('--batch-size', type=int, default=16)
parser.add_argument('--lr', type=float, default=0.0001)
# 数据集所在根目录
# http://download.tensorflow.org/example_images/flower_photos.tgz
parser.add_argument('--data-path', type=str,
default="flower_photos")
# 预训练权重路径,如果不想载入就设置为空字符
parser.add_argument('--weights', type=str, default='./swin_base_patch4_window7_224.pth',
help='initial weights path')
# 是否冻结权重
parser.add_argument('--freeze-layers', type=bool, default=False)
parser.add_argument('--device', default='cuda:0', help='device id (i.e. 0 or 0,1 or cpu)')
然后通过下面代码,设置模型训练设备和文件夹路径。接着对数据进行预处理并创建数据集和数据加载器。并根据命令行参数配置模型并加载预训练权重,可选择性地冻结部分模型参数。最后,使用AdamW优化器进行训练,并在每个epoch结束时保存模型权重。整个训练过程可以记录损失、准确率等指标,并将其写入TensorBoard。
def main(args):
device = torch.device(args.device if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
if os.path.exists("./weights") is False:
os.makedirs("./weights")
tb_writer = SummaryWriter()
train_images_path, train_images_label, val_images_path, val_images_label = read_split_data(args.data_path)
img_size = 224
data_transform = {
"train": transforms.Compose([transforms.RandomResizedCrop(img_size),
transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize([0.485, 0.456, 0.406], [0.229, 0.224, 0.225])]),
"val": transforms.Compose([transforms.Resize(int(img_size * 1.143)),
transforms.CenterCrop(img_size),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize([0.485, 0.456, 0.406], [0.229, 0.224, 0.225])])}
# 实例化训练数据集
train_dataset = MyDataSet(images_path=train_images_path,
images_class=train_images_label,
transform=data_transform["train"])
# 实例化验证数据集
val_dataset = MyDataSet(images_path=val_images_path,
images_class=val_images_label,
transform=data_transform["val"])
batch_size = args.batch_size
nw = min([os.cpu_count(), batch_size if batch_size > 1 else 0, 8]) # number of workers
print('Using {} dataloader workers every process'.format(nw))
train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(train_dataset,
batch_size=batch_size,
shuffle=True,
pin_memory=True,
num_workers=nw,
collate_fn=train_dataset.collate_fn)
val_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(val_dataset,
batch_size=batch_size,
shuffle=False,
pin_memory=True,
num_workers=nw,
collate_fn=val_dataset.collate_fn)
model = create_model(num_classes=args.num_classes).to(device)
if args.weights != "":
assert os.path.exists(args.weights), "weights file: '{}' not exist.".format(args.weights)
weights_dict = torch.load(args.weights, map_location=device)["model"]
# 删除有关分类类别的权重
for k in list(weights_dict.keys()):
if "head" in k:
del weights_dict[k]
print(model.load_state_dict(weights_dict, strict=False))
if args.freeze_layers:
for name, para in model.named_parameters():
# 除head外,其他权重全部冻结
if "head" not in name:
para.requires_grad_(False)
else:
print("training {}".format(name))
pg = [p for p in model.parameters() if p.requires_grad]
optimizer = optim.AdamW(pg, lr=args.lr, weight_decay=5E-2)
for epoch in range(args.epochs):
# train
train_loss, train_acc = train_one_epoch(model=model,
optimizer=optimizer,
data_loader=train_loader,
device=device,
epoch=epoch)
# validate
val_loss, val_acc = evaluate(model=model,
data_loader=val_loader,
device=device,
epoch=epoch)
train_acc_list.append(train_acc)
train_loss_list.append(train_loss)
val_acc_list.append(val_acc)
val_loss_list.append(val_loss)
tags = ["train_loss", "train_acc", "val_loss", "val_acc", "learning_rate"]
tb_writer.add_scalar(tags[0], train_loss, epoch)
tb_writer.add_scalar(tags[1], train_acc, epoch)
tb_writer.add_scalar(tags[2], val_loss, epoch)
tb_writer.add_scalar(tags[3], val_acc, epoch)
tb_writer.add_scalar(tags[4], optimizer.param_groups[0]["lr"], epoch)
torch.save(model.state_dict(), "./weights/model-{}.pth".format(epoch))
整个训练过程可以记录损失、准确率等指标:

3.2 模型测试
可以分别使用predict.py对单张花卉图片和predict-batch.py批量进行检测。
# predict.py
def main(img_path):
import os
os.environ['KMP_DUPLICATE_LIB_OK'] = 'TRUE'
device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
img_size = 224
data_transform = transforms.Compose(
[transforms.Resize(int(img_size * 1.143)),
transforms.CenterCrop(img_size),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize([0.485, 0.456, 0.406], [0.229, 0.224, 0.225])])
# load image
# img_path = "./tulip.jpg"
assert os.path.exists(img_path), "file: '{}' dose not exist.".format(img_path)
img = Image.open(img_path)
plt.imshow(img)
# [N, C, H, W]
img = data_transform(img)
# expand batch dimension
img = torch.unsqueeze(img, dim=0)
# read class_indict
json_path = './class_indices.json'
assert os.path.exists(json_path), "file: '{}' dose not exist.".format(json_path)
json_file = open(json_path, "r")
class_indict = json.load(json_file)
# create model
model = create_model(num_classes=5).to(device)
# load model weights
model_weight_path = "./weights/model-86.pth"
model.load_state_dict(torch.load(model_weight_path, map_location=device))
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
# predict class
output = torch.squeeze(model(img.to(device))).cpu()
predict = torch.softmax(output, dim=0)
predict_cla = torch.argmax(predict).numpy()
# print_res = "class: {} prob: {:.3}".format(class_indict[str(predict_cla)],
# predict[predict_cla].numpy())
# plt.title(print_res)
for i in range(len(predict)):
print("class: {:10} prob: {:.3}".format(class_indict[str(i)],
predict[i].numpy()))
# plt.show()
res = class_indict[str(list(predict.numpy()).index(max(predict.numpy())))]
num= "%.2f" % (max(predict.numpy()) * 100) + "%"
print(res,num)
return res,max(predict.numpy())
# print(class_indict[str(list(predict.numpy()).index(max(predict.numpy())))])
def main():
device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
img_size = 224
data_transform = transforms.Compose(
[transforms.Resize(int(img_size * 1.143)),
transforms.CenterCrop(img_size),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize([0.485, 0.456, 0.406], [0.229, 0.224, 0.225])])
# read class_indict
json_path = './class_indices.json'
assert os.path.exists(json_path), "file: '{}' dose not exist.".format(json_path)
json_file = open(json_path, "r")
class_indict = json.load(json_file)
# create model
model = create_model(num_classes=5).to(device)
# load model weights
model_weight_path = "./weights/model-86.pth"
model.load_state_dict(torch.load(model_weight_path, map_location=device))
model.eval()
# load image
data_root = os.path.abspath(os.path.join(os.getcwd(), "../")) # get data root path
all_dir = os.path.join(data_root, "data_set") # flower data set path
# img_path_list = ["../tulip.jpg", "../rose.jpg"]
img_list = []
test_dir = os.path.join(all_dir, "jpg") # test
test_datasets = datasets.ImageFolder(test_dir, transform=data_transform)
for img_path, idx in test_datasets.imgs:
assert os.path.exists(img_path), "file: '{}' dose not exist.".format(img_path)
# img_path = "./tulip.jpg"
assert os.path.exists(img_path), "file: '{}' dose not exist.".format(img_path)
img = Image.open(img_path)
plt.imshow(img)
# [N, C, H, W]
img = data_transform(img)
# expand batch dimension
img = torch.unsqueeze(img, dim=0)
with torch.no_grad():
# predict class
output = torch.squeeze(model(img.to(device))).cpu()
predict = torch.softmax(output, dim=0)
predict_cla = torch.argmax(predict).numpy()
print_res = "image: {} class: {} prob: {:.3}".format(img_path, class_indict[str(predict_cla)],
predict[predict_cla].numpy())
print(print_res)
测试结果:

四、PyQt界面实现
当整个项目构建完成后,使用PyQt5编写可视化界面,可以支持花卉图像的检测。运行主界面.py,然后点击文件夹图片传入待检测的花卉图像即可。经过花卉识别系统识别后,会输出相应的类别和置信度。

参考资料
- 论文:https://arxiv.org/pdf/2103.14030.pdf
- 代码:https://github.com/microsoft/Swin-Transformer
- timm:https://hub.fastgit.org/rwightman/pytorch-image-models/blob/master/timm/models/swin_transformer.py
- Swin_Transformer网络模型详解资料:详解Swin_Transformer (SwinT)



![[管理者与领导者-163] :团队管理 - 高效执行力 -1- 高效沟通的架构、关键问题、注意事项](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/364a6da3aa4e4fe2affb311e89c33c71.png)