前言
本文主要讲述不同SQL语句的优化策略。
SQL | DML语句
insert语句
-
插入数据的时候,改为批量插入
-
插入数据的时候,按照主键顺序插入
-
大批量插入数据的时候(百万),用load指令,从本地文件载入(需要在全局变量中开启,从而允许load指令)
update
注意更新语句的检索条件,尽量选择有索引的列;尽量选择主键索引。
- 当使用索引的时候:InnoDB引擎下执行update语句,添加的是行锁;当使用主键索引的时候,能减少回表查询
# 该事务下使用的锁是:行锁
update course set name = 'javaEE' where id = 1;
- 当没有索引或者索引失效的时候,会从行锁升级为表锁:
# 该事务下使用的锁是:表锁
update course set name = 'SpringBoot' where name = 'PHP' ;
SQL | DQL语句
order by
MySQL的排序有两种方式,尽量使用Using index:
-
Using filesort:将满足条件的数据行放到sort buffer中完成排序操作。使用索引或不使用索引的情况,都有可能出现该种排序方式 -
Using index:通过有序索引,按照顺序扫描,直接返回有序数据,不需要额外排序。效率要高于Using filesort
不同场景下,会选用不同的排序方式,也有某些场景,两种排序方式都存在。
使用Using filesort的情况:
- 无索引排序
- 多列排序,各列都单独创建索引
# 无索引
explain select id,age,phone from tb_user order by age;
explain select id,age,phone from tb_user order by age, phone;
# 多列排序,均为单列索引
explain select id,age,phone from tb_user order by age, phone;
使用Using index的情况:
- 单列排序,有单列索引
- 联合索引正常使用
# 单列索引
explain select age from tb_user order by age;
# 联合索引正常使用。给(age、phone)创建联合索引
explain select id,age,phone from tb_user order by age;
explain select id,age,phone from tb_user order by age, phone;
其他情况:
# 给(age、phone)创建联合索引
# Using index; Using filesort
explain select id,age,phone from tb_user order by phone;
explain select id,age,phone from tb_user order by phone, age;
# Backward index scan; Using index;
explain select id,age,phone from tb_user order by age, phone desc;
联合索引默认是增序的,在MySQL8版本中,可以建立降序索引:
CREATE [UNIQUE | FULLTEXT] INDEX index_name ON table_name(index_col_name asc, index_col_name_2 desc, ...);
group by
在分组操作的时候,通过索引可以提升效率,但是同时也遵循最左匹配原则:
# === 无索引
# Using temporary
explain select profession , count(*) from tb_user group by profession;
# === 建立单独索引
# Using index
explain select profession , count(*) from tb_user group by profession;
# === 建立联合索引:(profession,age)
# Using index
explain select profession , count(*) from tb_user group by profession;
# Using index,Using temporary
explain select age , count(*) from tb_user group by age;
limit
limit查询,查询的数据越往后,时间消耗越大:
# 0.00sec
select * from tb_sku limit 0, 10;
# 10.79sec
select * from tb_sku limit 100000, 10;
可以通过:覆盖索引 + 子查询(根据位置分类,属于from后面的子查询;根据返回结果分类,属于列子查询),对SQL进行优化:
explain select * from tb_sku t , (select id from tb_sku order by id limit 2000000,10) a where t.id = a.id;
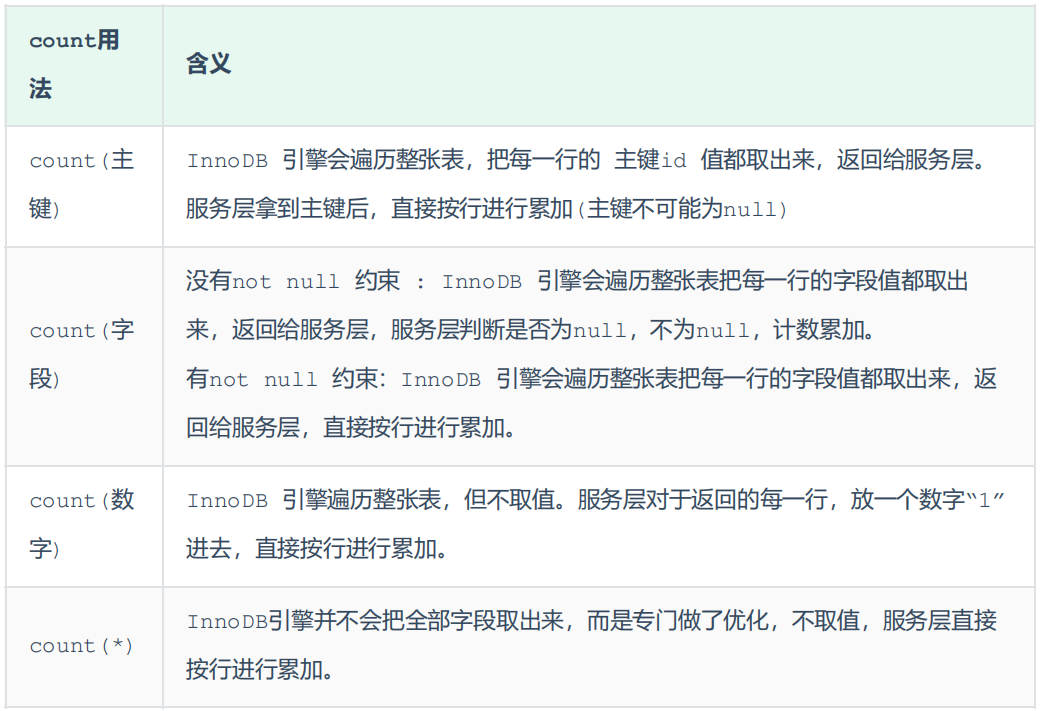
count
MySQl中统计数量的函数是count()。针对count的优化:
- 方案1:不使用count,自己计数(难搞)
- 方案2:合理的选用count用法。效率:count(字段) < count(主键) < count(1) = count(*)
其余 | 主键优化
- 满足业务的前提下,尽量减低主键的长度
- 插入数据尽量顺主键插入,可以选择自增主键
- 尽量不要用uuid或身份证号作为主键,插入数据不具备排序性质
- 业务操作,避免对主键进行修改
![MySQL中的SQL高级语句[二]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/fb3fbe9f067f4f34add079e870bca726.png)