目录
- 数据集划分与交叉验证
- 模型集成方法
- Titanic为例的简单应用
- kaggle比赛相关tips
数据集划分与交叉验证
数据集划分
通常有两种方法:
- 留出法(Hold-out) 适用于数据量大的情况
- K折交叉验证(K-fold CV) 适用于数据量一般情况 时间比较长
- 自助采样(Bootstrap) 较少使用
交叉验证得到的模型更加稳定.
数据一致性分析

理想情况下AUC接近0.5
sklearn中封装的一系列的数据划分的代码
# hold-out
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
# K折交叉验证
from sklearn.model_selection import KFold
from sklearn.model_selection import RepeatedKFold
# K折分布保持交叉验证
from sklearn.model_selection import StratifiedKFold
from sklearn.model_selection import RepeatedStratifiedKFold
# 时间序列划分方法
from sklearn.model_selection import TimeSeriesSplit
# booststrap 采样
from sklearn.utils import resample
构造数据集
X = np.zeros((20, 5))
Y = np.array([1]*5 + [2]*5 + [3]*5 + [4]*5)
print(X, Y)

留出法代码
# 直接按照比例拆分
train_X, val_X, train_y, val_y = train_test_split(X, Y, test_size = 0.2)
print(train_y, val_y)
# 按照比例 & 标签分布划分
train_X, val_X, train_y, val_y = train_test_split(X, Y, test_size = 0.2, stratify=Y)
print(train_y, val_y)
两种划分效果如下:

可以看到,第一种划分不均匀,当添加参数stratify=Y时,
第二种划分方式变的均匀了。
K折交叉验证
不均匀的分布方式 KFold
kf = KFold(n_splits=5)
for train_idx, test_idx, in kf.split(X, Y):
print(train_idx, test_idx)
print('Label', Y[test_idx])
print('')

均匀分布方式 StratifiedKFold
# 5折划分方式
kf = StratifiedKFold(n_splits=5)
for train_idx, test_idx, in kf.split(X, Y):
print(train_idx, test_idx)
print('Label', Y[test_idx])
print('')

均匀重复采样 RepeatedStratifiedKFold
kf = RepeatedStratifiedKFold(n_splits=5, n_repeats=2)
for train_idx, test_idx, in kf.split(X, Y):
print(train_idx, test_idx)
print('Label', Y[test_idx])
print('')

模型集成方法
机器学习的模型集成
-
模型集成和集成学习

-
Vote和Blend
Vote主要用于分类任务
Blend主要用于回归任务
主要方法:
对结果简单投票或者平均
加权权重可以修改 -
Stacking

多次学习
在第一次学习的基础上生成新的特征,
在将新的特征拼接到训练集上,进行新的学习
深度学习的模型集成
-
数据扩增

数据集和测试集都可以进行数据扩增 -
snapshot Ensemble

保存多个局部最优解,找到最终最优解
Titanic为例的简单应用
- Load data
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
%matplotlib inline
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
#import train and test CSV files
train_df = pd.read_csv("../input/train.csv")
test_df = pd.read_csv("../input/test.csv")
#take a look at the training data
train_df.describe(include="all")

print(train_df.columns)

train_df.sample(5)

#see a summary of the training dataset
train_df.describe(include = "all")
- Data Visualization
# 性别和幸存的关系
sns.barplot(x="Sex", y="Survived", data=train_df)

类似的查看其他字段和幸存率的关系
#draw a bar plot of survival by Pclass
sns.barplot(x="Pclass", y="Survived", data=train_df)
#draw a bar plot for SibSp vs. survival
sns.barplot(x="SibSp", y="Survived", data=train_df)
#draw a bar plot for Parch vs. survival
sns.barplot(x="Parch", y="Survived", data=train_df)
plt.show()
根据年龄进行分组,
(-1, 0) 是 Unknown
(0, 5) 是 Baby
(5, 12) 是 Child
(12, 18) 是 Teenager
(18, 24) 是 Student
(24, 35) 是 Young Adult
.。。。。。
查看年龄和幸存的关系
#sort the ages into logical categories
train_df["Age"] = train_df["Age"].fillna(-0.5)
test_df["Age"] = test_df["Age"].fillna(-0.5)
bins = [-1, 0, 5, 12, 18, 24, 35, 60, np.inf]
labels = ['Unknown', 'Baby', 'Child', 'Teenager', 'Student', 'Young Adult', 'Adult', 'Senior']
train_df['AgeGroup'] = pd.cut(train_df["Age"], bins, labels = labels)
test_df['AgeGroup'] = pd.cut(test_df["Age"], bins, labels = labels)
train_df["CabinBool"] = train_df["Cabin"].notnull().astype('int')
test_df["CabinBool"] = test_df["Cabin"].notnull().astype('int')

删除一些没太有用的信息
train = train.drop(['Cabin'], axis = 1)
test = test.drop(['Cabin'], axis = 1)
#we can also drop the Ticket feature since it's unlikely to yield any useful information
train = train.drop(['Ticket'], axis = 1)
test = test.drop(['Ticket'], axis = 1)
处理姓名字段
#replace various titles with more common names
for dataset in combine:
dataset['Title'] = dataset['Title'].replace(['Lady', 'Capt', 'Col',
'Don', 'Dr', 'Major', 'Rev', 'Jonkheer', 'Dona'], 'Rare')
dataset['Title'] = dataset['Title'].replace(['Countess', 'Lady', 'Sir'], 'Royal')
dataset['Title'] = dataset['Title'].replace('Mlle', 'Miss')
dataset['Title'] = dataset['Title'].replace('Ms', 'Miss')
dataset['Title'] = dataset['Title'].replace('Mme', 'Mrs')
train[['Title', 'Survived']].groupby(['Title'], as_index=False).mean()
# map each of the title groups to a numerical value
title_mapping = {"Mr": 1, "Miss": 2, "Mrs": 3, "Master": 4, "Royal": 5, "Rare": 6}
for dataset in combine:
dataset['Title'] = dataset['Title'].map(title_mapping)
dataset['Title'] = dataset['Title'].fillna(0)
train.head()
登陆口
#now we need to fill in the missing values in the Embarked feature
print("Number of people embarking in Southampton (S):")
southampton = train[train["Embarked"] == "S"].shape[0]
print(southampton)
print("Number of people embarking in Cherbourg (C):")
cherbourg = train[train["Embarked"] == "C"].shape[0]
print(cherbourg)
print("Number of people embarking in Queenstown (Q):")
queenstown = train[train["Embarked"] == "Q"].shape[0]
print(queenstown)

用出现次数最多的S做缺失值填充
#replacing the missing values in the Embarked feature with S
train = train.fillna({"Embarked": "S"})
年龄字段
#create a combined group of both datasets
combine = [train, test]
#extract a title for each Name in the train and test datasets
for dataset in combine:
dataset['Title'] = dataset.Name.str.extract(' ([A-Za-z]+)\.', expand=False)
pd.crosstab(train['Title'], train['Sex'])
#replace various titles with more common names
for dataset in combine:
dataset['Title'] = dataset['Title'].replace(['Lady', 'Capt', 'Col',
'Don', 'Dr', 'Major', 'Rev', 'Jonkheer', 'Dona'], 'Rare')
dataset['Title'] = dataset['Title'].replace(['Countess', 'Lady', 'Sir'], 'Royal')
dataset['Title'] = dataset['Title'].replace('Mlle', 'Miss')
dataset['Title'] = dataset['Title'].replace('Ms', 'Miss')
dataset['Title'] = dataset['Title'].replace('Mme', 'Mrs')
train[['Title', 'Survived']].groupby(['Title'], as_index=False).mean()

处理姓名字段的缺失值
# fill missing age with mode age group for each title
mr_age = train[train["Title"] == 1]["AgeGroup"].mode() #Young Adult
miss_age = train[train["Title"] == 2]["AgeGroup"].mode() #Student
mrs_age = train[train["Title"] == 3]["AgeGroup"].mode() #Adult
master_age = train[train["Title"] == 4]["AgeGroup"].mode() #Baby
royal_age = train[train["Title"] == 5]["AgeGroup"].mode() #Adult
rare_age = train[train["Title"] == 6]["AgeGroup"].mode() #Adult
age_title_mapping = {1: "Young Adult", 2: "Student", 3: "Adult", 4: "Baby", 5: "Adult", 6: "Adult"}
#使用众数来填充缺失值
for x in range(len(train["AgeGroup"])):
if train["AgeGroup"][x] == "Unknown":
train["AgeGroup"][x] = age_title_mapping[train["Title"][x]]
for x in range(len(test["AgeGroup"])):
if test["AgeGroup"][x] == "Unknown":
test["AgeGroup"][x] = age_title_mapping[test["Title"][x]]
性别字段转换成数值
#map each Sex value to a numerical value
sex_mapping = {"male": 0, "female": 1}
train['Sex'] = train['Sex'].map(sex_mapping)
test['Sex'] = test['Sex'].map(sex_mapping)
train.head()
登陆口岸转换为数值
#map each Embarked value to a numerical value
embarked_mapping = {"S": 1, "C": 2, "Q": 3}
train['Embarked'] = train['Embarked'].map(embarked_mapping)
test['Embarked'] = test['Embarked'].map(embarked_mapping)
train.head()
根据票类型的平均值填补缺失值
for x in range(len(test["Fare"])):
if pd.isnull(test["Fare"][x]):
pclass = test["Pclass"][x] #Pclass = 3
test["Fare"][x] = round(train[train["Pclass"] == pclass]["Fare"].mean(), 4)
# map Fare values into groups of numerical values
train['FareBand'] = pd.qcut(train['Fare'], 4, labels = [1, 2, 3, 4])
test['FareBand'] = pd.qcut(test['Fare'], 4, labels = [1, 2, 3, 4])
train = train.drop(['Fare'], axis = 1)
test = test.drop(['Fare'], axis = 1)

查看数据集结果
#check train data
train.head()

可以看到数据均被转换为合理的数值格式,供模型训练使用
3. Choosing the Best Model
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
predictors = train.drop(['Survived', 'PassengerId'], axis=1)
target = train["Survived"]
x_train, x_val, y_train, y_val = train_test_split(predictors, target, test_size = 0.22, random_state = 0)
高斯朴素贝叶斯
# Gaussian Naive Bayes
from sklearn.naive_bayes import GaussianNB
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
gaussian = GaussianNB()
gaussian.fit(x_train, y_train)
y_pred = gaussian.predict(x_val)
acc_gaussian = round(accuracy_score(y_pred, y_val) * 100, 2)
print(acc_gaussian)
逻辑回归
# Logistic Regression
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
logreg = LogisticRegression()
logreg.fit(x_train, y_train)
y_pred = logreg.predict(x_val)
acc_logreg = round(accuracy_score(y_pred, y_val) * 100, 2)
print(acc_logreg)
svm的分类模型
# Support Vector Machines
from sklearn.svm import SVC
svc = SVC()
svc.fit(x_train, y_train)
y_pred = svc.predict(x_val)
acc_svc = round(accuracy_score(y_pred, y_val) * 100, 2)
print(acc_svc)
线性SVC模型
# Linear SVC
from sklearn.svm import LinearSVC
linear_svc = LinearSVC()
linear_svc.fit(x_train, y_train)
y_pred = linear_svc.predict(x_val)
acc_linear_svc = round(accuracy_score(y_pred, y_val) * 100, 2)
print(acc_linear_svc)
线性模型
# Perceptron
from sklearn.linear_model import Perceptron
perceptron = Perceptron()
perceptron.fit(x_train, y_train)
y_pred = perceptron.predict(x_val)
acc_perceptron = round(accuracy_score(y_pred, y_val) * 100, 2)
print(acc_perceptron)
决策树模型
#Decision Tree
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
decisiontree = DecisionTreeClassifier()
decisiontree.fit(x_train, y_train)
y_pred = decisiontree.predict(x_val)
acc_decisiontree = round(accuracy_score(y_pred, y_val) * 100, 2)
print(acc_decisiontree)
随机森林
# Random Forest
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
randomforest = RandomForestClassifier()
randomforest.fit(x_train, y_train)
y_pred = randomforest.predict(x_val)
acc_randomforest = round(accuracy_score(y_pred, y_val) * 100, 2)
print(acc_randomforest)
KNN近邻模型
# KNN or k-Nearest Neighbors
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
knn = KNeighborsClassifier()
knn.fit(x_train, y_train)
y_pred = knn.predict(x_val)
acc_knn = round(accuracy_score(y_pred, y_val) * 100, 2)
print(acc_knn)
随机梯度下降
# Stochastic Gradient Descent
from sklearn.linear_model import SGDClassifier
sgd = SGDClassifier()
sgd.fit(x_train, y_train)
y_pred = sgd.predict(x_val)
acc_sgd = round(accuracy_score(y_pred, y_val) * 100, 2)
print(acc_sgd)
梯度提升决策树
# Gradient Boosting Classifier
from sklearn.ensemble import GradientBoostingClassifier
gbk = GradientBoostingClassifier()
gbk.fit(x_train, y_train)
y_pred = gbk.predict(x_val)
acc_gbk = round(accuracy_score(y_pred, y_val) * 100, 2)
print(acc_gbk)
模型评分
models = pd.DataFrame({
'Model': ['Support Vector Machines', 'KNN', 'Logistic Regression',
'Random Forest', 'Naive Bayes', 'Perceptron', 'Linear SVC',
'Decision Tree', 'Stochastic Gradient Descent', 'Gradient Boosting Classifier'],
'Score': [acc_svc, acc_knn, acc_logreg,
acc_randomforest, acc_gaussian, acc_perceptron,acc_linear_svc, acc_decisiontree,
acc_sgd, acc_gbk]})
models.sort_values(by='Score', ascending=False)
算法评分结果如下:

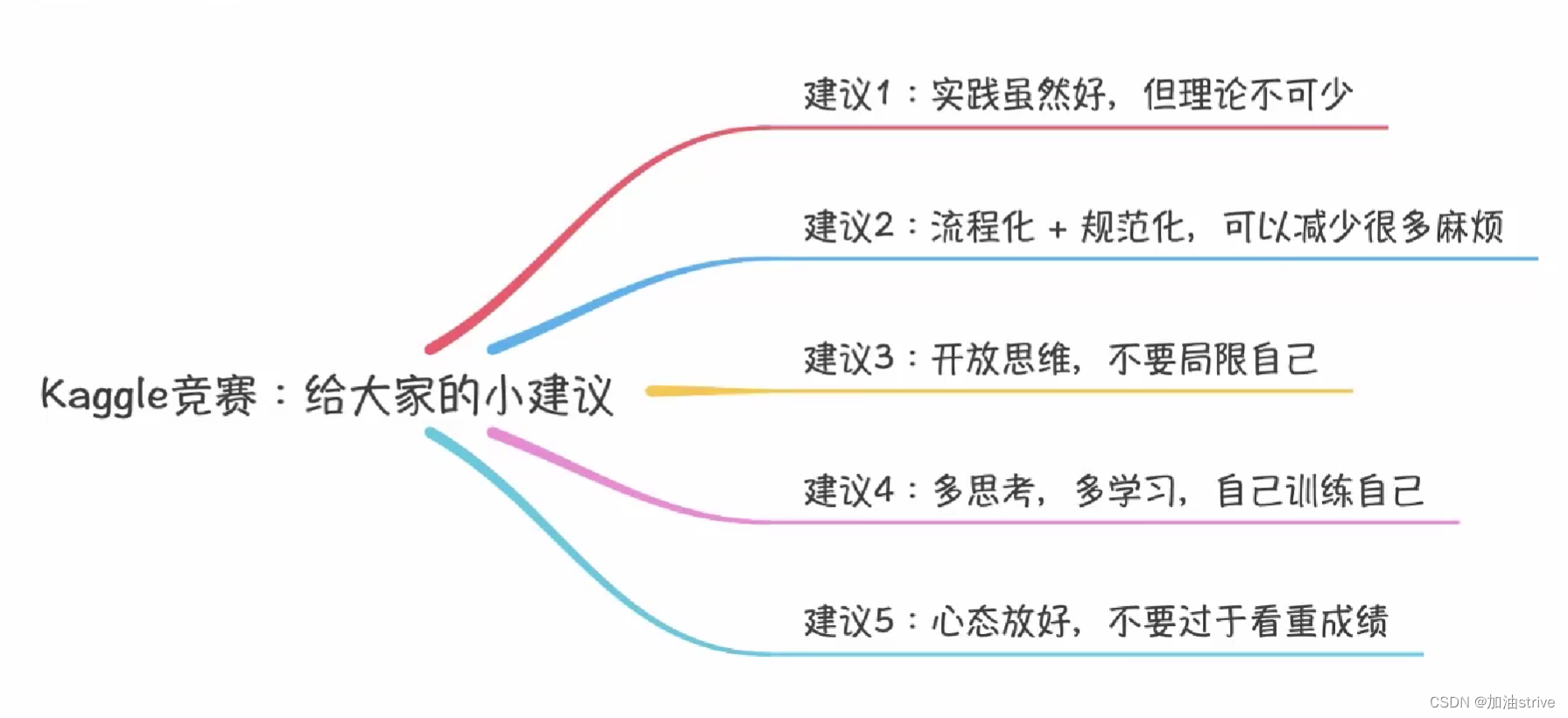
kaggle比赛相关tips