文章目录
- 前言
- 一. pyspark连接hudi
- 二. 创建表
- 三. 插入数据
- 四. 查询数据
- 五. Time Travel查询
- 六. 更新数据
- 七. 增量查询
- 八. 基于时间点查询
- 九. 删除数据
- 9.1 软删除
- 9.2 硬删除
- 十. 插入覆盖
- 十一. Spark其它命令
- 11.1 Alter Table
- 11.2 Partition SQL Command
- 参考:
前言
| 软件 | 版本 |
|---|---|
| Python | 3.8 |
| Hadoop | 3.3.2 |
| Spark | 3.3.1 |
| Hudi | 0.12.0 |
Hudi官网demo提供了3种通过Spark操作Hudi的方法:
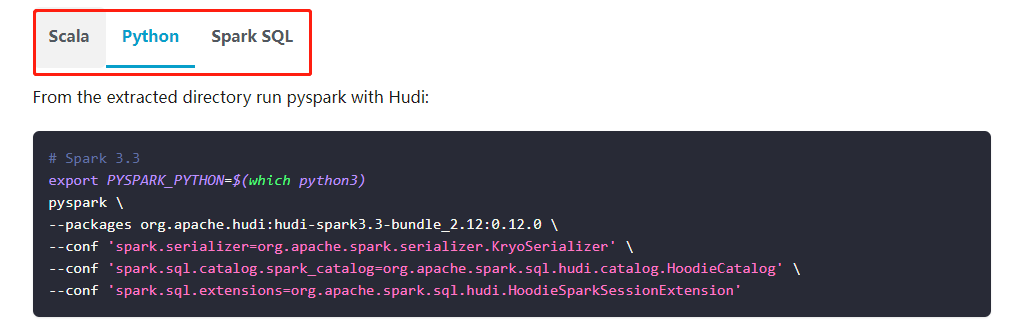
这里我们选择通过pyspark来操作
一. pyspark连接hudi
pyspark连接hudi:
# Spark 3.3
export PYSPARK_PYTHON=$(which python3)
pyspark \
--packages org.apache.hudi:hudi-spark3.3-bundle_2.12:0.12.0 \
--conf 'spark.serializer=org.apache.spark.serializer.KryoSerializer' \
--conf 'spark.sql.catalog.spark_catalog=org.apache.spark.sql.hudi.catalog.HoodieCatalog' \
--conf 'spark.sql.extensions=org.apache.spark.sql.hudi.HoodieSparkSessionExtension'
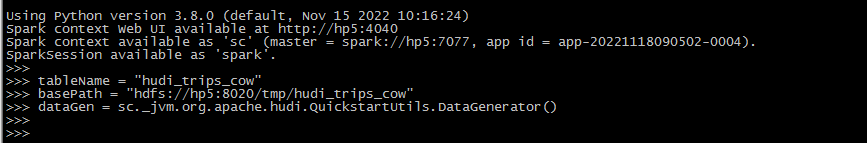
设置表名、基本路径和数据生成器:
# pyspark
tableName = "hudi_trips_cow"
basePath = "hdfs://hp5:8020/tmp/hudi_trips_cow"
dataGen = sc._jvm.org.apache.hudi.QuickstartUtils.DataGenerator()
二. 创建表
spark中不需要单独的create table命令。如果表不存在,第一批写入操作将创建该表。
三. 插入数据
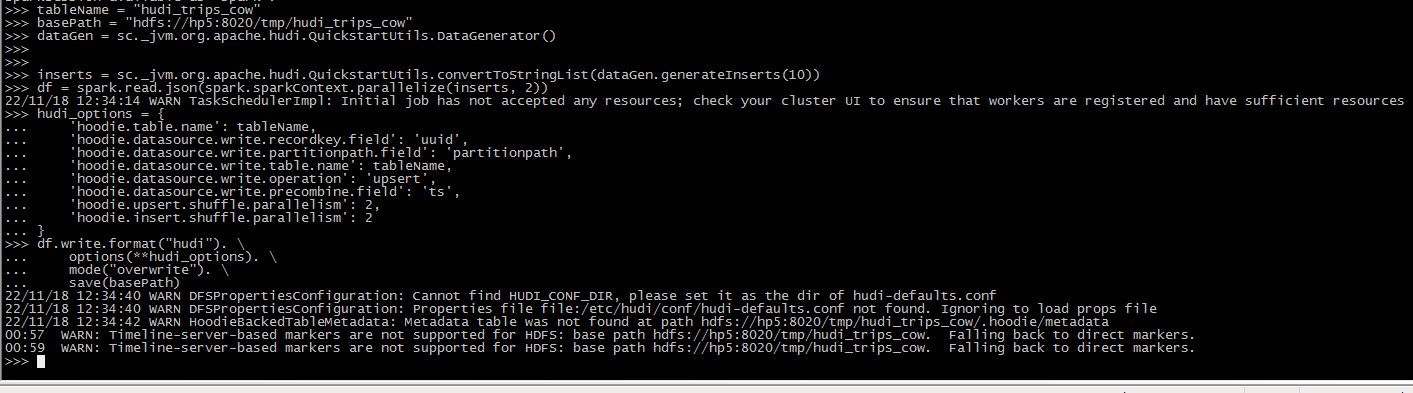
生成一些新的trip,将它们加载到DataFrame中,并将DataFrame写入Hudi表中.
# pyspark
inserts = sc._jvm.org.apache.hudi.QuickstartUtils.convertToStringList(dataGen.generateInserts(10))
df = spark.read.json(spark.sparkContext.parallelize(inserts, 2))
hudi_options = {
'hoodie.table.name': tableName,
'hoodie.datasource.write.recordkey.field': 'uuid',
'hoodie.datasource.write.partitionpath.field': 'partitionpath',
'hoodie.datasource.write.table.name': tableName,
'hoodie.datasource.write.operation': 'upsert',
'hoodie.datasource.write.precombine.field': 'ts',
'hoodie.upsert.shuffle.parallelism': 2,
'hoodie.insert.shuffle.parallelism': 2
}
df.write.format("hudi"). \
options(**hudi_options). \
mode("overwrite"). \
save(basePath)
四. 查询数据
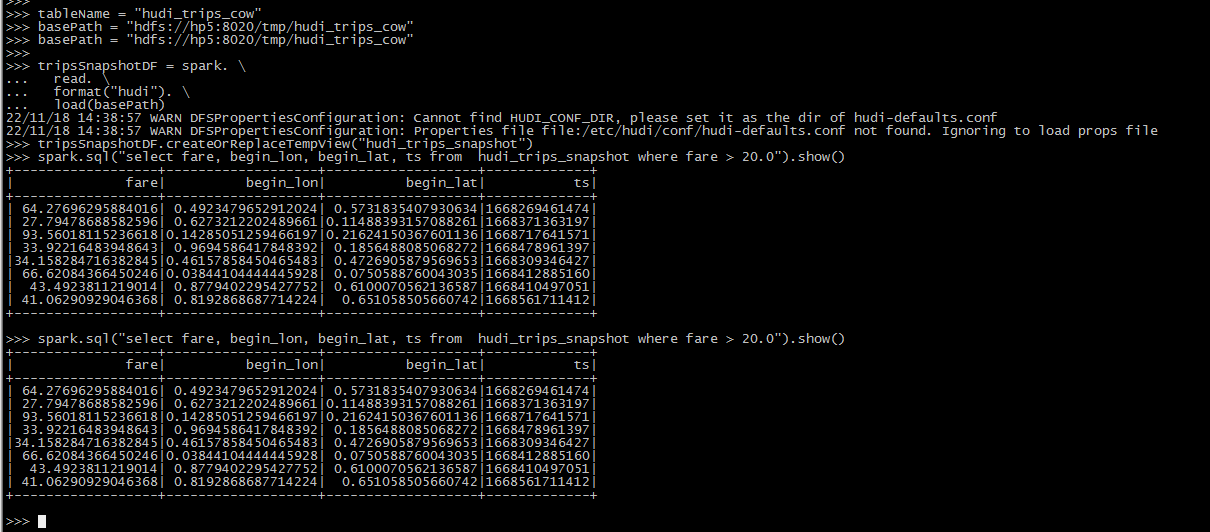
# pyspark
tripsSnapshotDF = spark. \
read. \
format("hudi"). \
load(basePath)
# load(basePath) use "/partitionKey=partitionValue" folder structure for Spark auto partition discovery
tripsSnapshotDF.createOrReplaceTempView("hudi_trips_snapshot")
spark.sql("select fare, begin_lon, begin_lat, ts from hudi_trips_snapshot where fare > 20.0").show()
spark.sql("select _hoodie_commit_time, _hoodie_record_key, _hoodie_partition_path, rider, driver, fare from hudi_trips_snapshot").show()
五. Time Travel查询
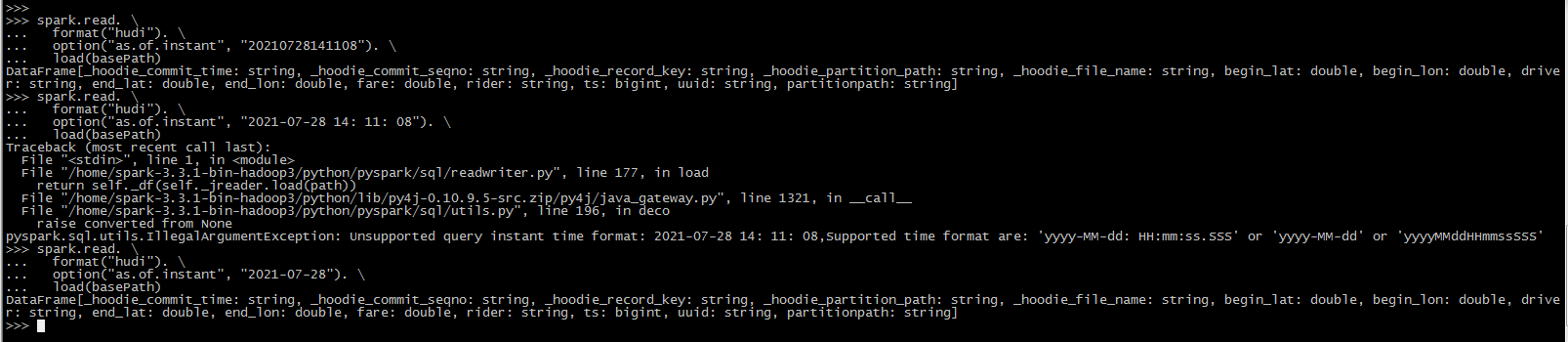
Hudi从0.9.0开始支持Time Travel查询。目前支持三种查询时间格式,如下所示。
#pyspark
spark.read. \
format("hudi"). \
option("as.of.instant", "20210728141108"). \
load(basePath)
# It is equal to "as.of.instant = 2021-07-28 00:00:00"
spark.read. \
format("hudi"). \
option("as.of.instant", "2021-07-28"). \
load(basePath)
六. 更新数据
这类似于插入新数据。使用数据生成器生成现有行程的更新,加载到DataFrame中,并将DataFrame写入hudi表。
# pyspark
updates = sc._jvm.org.apache.hudi.QuickstartUtils.convertToStringList(dataGen.generateUpdates(10))
df = spark.read.json(spark.sparkContext.parallelize(updates, 2))
df.write.format("hudi"). \
options(**hudi_options). \
mode("append"). \
save(basePath)
七. 增量查询
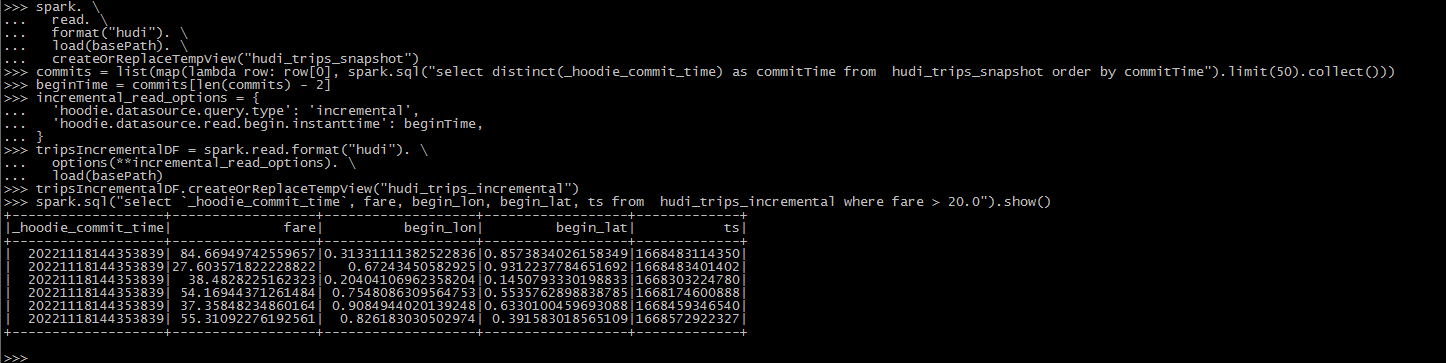
Hudi还提供了获取自给定提交时间戳以来更改的记录流的功能。这可以通过使用Hudi的增量查询来实现,并提供需要流化更改的开始时间。如果我们希望在给定的提交之后进行所有更改(通常是这样),则不需要指定endTime。
# pyspark
# reload data
spark. \
read. \
format("hudi"). \
load(basePath). \
createOrReplaceTempView("hudi_trips_snapshot")
commits = list(map(lambda row: row[0], spark.sql("select distinct(_hoodie_commit_time) as commitTime from hudi_trips_snapshot order by commitTime").limit(50).collect()))
beginTime = commits[len(commits) - 2] # commit time we are interested in
# incrementally query data
incremental_read_options = {
'hoodie.datasource.query.type': 'incremental',
'hoodie.datasource.read.begin.instanttime': beginTime,
}
tripsIncrementalDF = spark.read.format("hudi"). \
options(**incremental_read_options). \
load(basePath)
tripsIncrementalDF.createOrReplaceTempView("hudi_trips_incremental")
spark.sql("select `_hoodie_commit_time`, fare, begin_lon, begin_lat, ts from hudi_trips_incremental where fare > 20.0").show()
八. 基于时间点查询
# pyspark
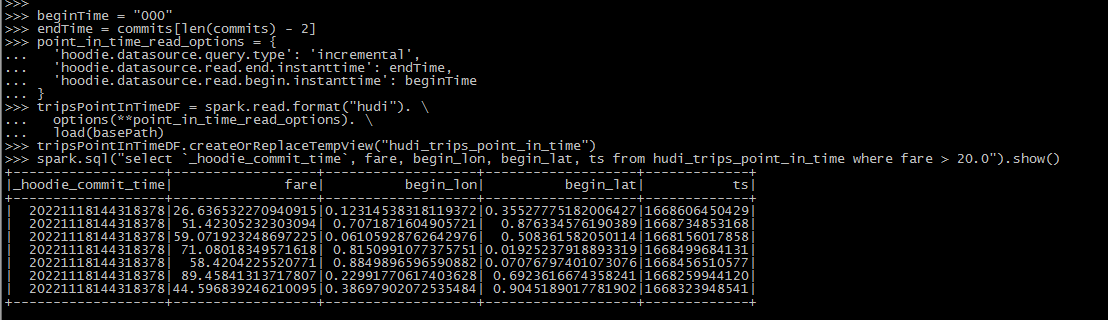
beginTime = "000" # Represents all commits > this time.
endTime = commits[len(commits) - 2]
# query point in time data
point_in_time_read_options = {
'hoodie.datasource.query.type': 'incremental',
'hoodie.datasource.read.end.instanttime': endTime,
'hoodie.datasource.read.begin.instanttime': beginTime
}
tripsPointInTimeDF = spark.read.format("hudi"). \
options(**point_in_time_read_options). \
load(basePath)
tripsPointInTimeDF.createOrReplaceTempView("hudi_trips_point_in_time")
spark.sql("select `_hoodie_commit_time`, fare, begin_lon, begin_lat, ts from hudi_trips_point_in_time where fare > 20.0").show()
九. 删除数据
Apache Hudi支持两种类型的删除:
(1)软删除:保留记录键,只清除所有其他字段的值(软删除中为空的记录始终保存在存储中,而不会删除);
(2)硬删除:从表中物理删除记录的任何痕迹。详细信息请参见写入数据页面的删除部分。
9.1 软删除
# pyspark
from pyspark.sql.functions import lit
from functools import reduce
spark.read.format("hudi"). \
load(basePath). \
createOrReplaceTempView("hudi_trips_snapshot")
# fetch total records count
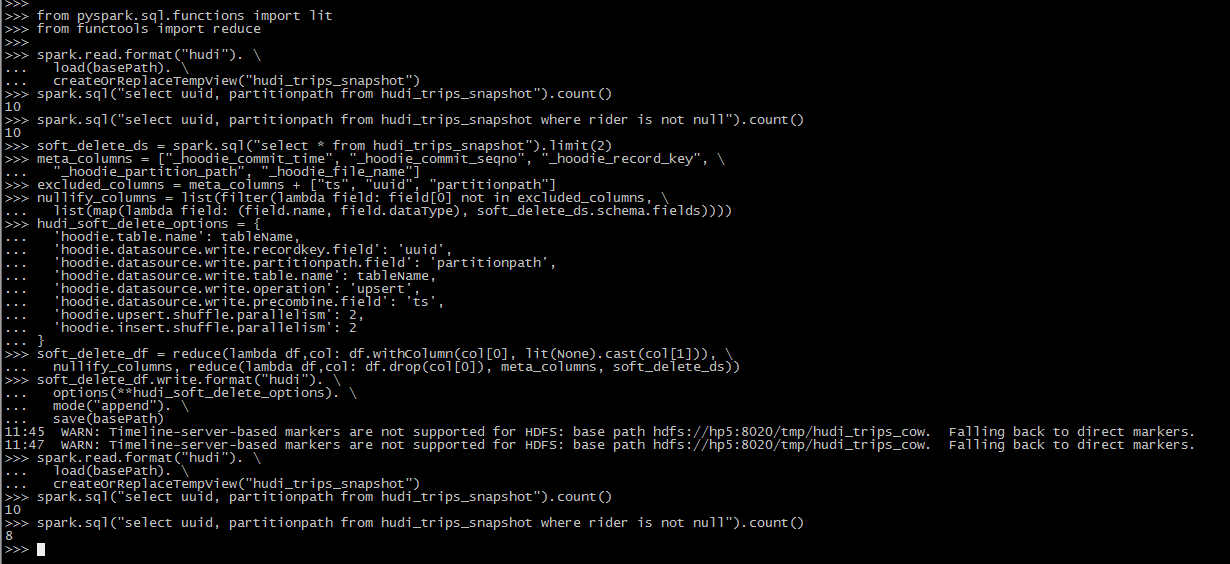
spark.sql("select uuid, partitionpath from hudi_trips_snapshot").count()
spark.sql("select uuid, partitionpath from hudi_trips_snapshot where rider is not null").count()
# fetch two records for soft deletes
soft_delete_ds = spark.sql("select * from hudi_trips_snapshot").limit(2)
# prepare the soft deletes by ensuring the appropriate fields are nullified
meta_columns = ["_hoodie_commit_time", "_hoodie_commit_seqno", "_hoodie_record_key", \
"_hoodie_partition_path", "_hoodie_file_name"]
excluded_columns = meta_columns + ["ts", "uuid", "partitionpath"]
nullify_columns = list(filter(lambda field: field[0] not in excluded_columns, \
list(map(lambda field: (field.name, field.dataType), soft_delete_ds.schema.fields))))
hudi_soft_delete_options = {
'hoodie.table.name': tableName,
'hoodie.datasource.write.recordkey.field': 'uuid',
'hoodie.datasource.write.partitionpath.field': 'partitionpath',
'hoodie.datasource.write.table.name': tableName,
'hoodie.datasource.write.operation': 'upsert',
'hoodie.datasource.write.precombine.field': 'ts',
'hoodie.upsert.shuffle.parallelism': 2,
'hoodie.insert.shuffle.parallelism': 2
}
soft_delete_df = reduce(lambda df,col: df.withColumn(col[0], lit(None).cast(col[1])), \
nullify_columns, reduce(lambda df,col: df.drop(col[0]), meta_columns, soft_delete_ds))
# simply upsert the table after setting these fields to null
soft_delete_df.write.format("hudi"). \
options(**hudi_soft_delete_options). \
mode("append"). \
save(basePath)
# reload data
spark.read.format("hudi"). \
load(basePath). \
createOrReplaceTempView("hudi_trips_snapshot")
# This should return the same total count as before
spark.sql("select uuid, partitionpath from hudi_trips_snapshot").count()
# This should return (total - 2) count as two records are updated with nulls
spark.sql("select uuid, partitionpath from hudi_trips_snapshot where rider is not null").count()
9.2 硬删除
# pyspark
# fetch total records count
spark.sql("select uuid, partitionpath from hudi_trips_snapshot").count()
# fetch two records to be deleted
ds = spark.sql("select uuid, partitionpath from hudi_trips_snapshot").limit(2)
# issue deletes
hudi_hard_delete_options = {
'hoodie.table.name': tableName,
'hoodie.datasource.write.recordkey.field': 'uuid',
'hoodie.datasource.write.partitionpath.field': 'partitionpath',
'hoodie.datasource.write.table.name': tableName,
'hoodie.datasource.write.operation': 'delete',
'hoodie.datasource.write.precombine.field': 'ts',
'hoodie.upsert.shuffle.parallelism': 2,
'hoodie.insert.shuffle.parallelism': 2
}
from pyspark.sql.functions import lit
deletes = list(map(lambda row: (row[0], row[1]), ds.collect()))
hard_delete_df = spark.sparkContext.parallelize(deletes).toDF(['uuid', 'partitionpath']).withColumn('ts', lit(0.0))
hard_delete_df.write.format("hudi"). \
options(**hudi_hard_delete_options). \
mode("append"). \
save(basePath)
# run the same read query as above.
roAfterDeleteViewDF = spark. \
read. \
format("hudi"). \
load(basePath)
roAfterDeleteViewDF.createOrReplaceTempView("hudi_trips_snapshot")
# fetch should return (total - 2) records
spark.sql("select uuid, partitionpath from hudi_trips_snapshot").count()
十. 插入覆盖
生成一些新的trip,覆盖输入中出现的所有分区。对于批处理ETL作业,此操作比upsert快,批处理ETL作业一次重新计算整个目标分区(与增量更新目标表相反)。这是因为,我们能够完全绕过索引、预合并和upsert写路径中的其他重分区步骤。
# pyspark
self.spark.read.format("hudi"). \
load(basePath). \
select(["uuid", "partitionpath"]). \
sort(["partitionpath", "uuid"]). \
show(n=100, truncate=False)
inserts = sc._jvm.org.apache.hudi.QuickstartUtils.convertToStringList(dataGen.generateInserts(10))
df = spark.read.json(spark.sparkContext.parallelize(inserts, 2)). \
filter("partitionpath = 'americas/united_states/san_francisco'")
hudi_insert_overwrite_options = {
'hoodie.table.name': tableName,
'hoodie.datasource.write.recordkey.field': 'uuid',
'hoodie.datasource.write.partitionpath.field': 'partitionpath',
'hoodie.datasource.write.table.name': tableName,
'hoodie.datasource.write.operation': 'insert_overwrite',
'hoodie.datasource.write.precombine.field': 'ts',
'hoodie.upsert.shuffle.parallelism': 2,
'hoodie.insert.shuffle.parallelism': 2
}
df.write.format("hudi").options(**hudi_insert_overwrite_options).mode("append").save(basePath)
spark.read.format("hudi"). \
load(basePath). \
select(["uuid", "partitionpath"]). \
sort(["partitionpath", "uuid"]). \
show(n=100, truncate=False)
十一. Spark其它命令
11.1 Alter Table
语法:
-- Alter table name
ALTER TABLE oldTableName RENAME TO newTableName
-- Alter table add columns
ALTER TABLE tableIdentifier ADD COLUMNS(colAndType (,colAndType)*)
-- Alter table column type
ALTER TABLE tableIdentifier CHANGE COLUMN colName colName colType
-- Alter table properties
ALTER TABLE tableIdentifier SET TBLPROPERTIES (key = 'value')
案例:
--rename to:
ALTER TABLE hudi_cow_nonpcf_tbl RENAME TO hudi_cow_nonpcf_tbl2;
--add column:
ALTER TABLE hudi_cow_nonpcf_tbl2 add columns(remark string);
--change column:
ALTER TABLE hudi_cow_nonpcf_tbl2 change column uuid uuid bigint;
--set properties;
alter table hudi_cow_nonpcf_tbl2 set tblproperties (hoodie.keep.max.commits = '10');
11.2 Partition SQL Command
语法:
-- Drop Partition
ALTER TABLE tableIdentifier DROP PARTITION ( partition_col_name = partition_col_val [ , ... ] )
-- Show Partitions
SHOW PARTITIONS tableIdentifier
案例:
--show partition:
show partitions hudi_cow_pt_tbl;
--drop partition:
alter table hudi_cow_pt_tbl drop partition (dt='2021-12-09', hh='10');
参考:
- https://hudi.apache.org/docs/0.12.0/quick-start-guide