0.死锁的由来
假设有两个线程T1和T2,它们需要对两个互斥量mtx1和mtx2进行访问。而且需要按照以下顺序获取互斥量的所有权:
-T1先获取mte1的所有权,再获取mt2的所有权。
-T2先获取 mtx2的所有权。再铁取 mtx1的所有权。
如果两个线程同时执行,就会出现死锁问题。因为T1获取了mtx1的所有权,但是无法获取mtx2的所有权,而T2获取了mtx2的所有权,但是无法获取 mtx1的所有权,两个线程互相等待对方释放互斥量,导致死锁。
1.不同锁类型
| 类型 | 类名 | 作用 |
|---|---|---|
| 超时锁 | timed_mutex | 避免长时间死锁 |
| 递归锁 | recursive_mutex | 同一线程的同一锁可以锁多次避免死锁 |
| 共享锁 | shared_mutex | 可以充分利用cpu资源 |
2.各种锁
2.1超时锁
①作用:避免长时间死锁
②性质:可以记录锁获取情况,多次超时,可以记录日志,获取错误情况。
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
#include <mutex>
std::timed_mutex tmux;
void ThreadMainTime(int i)
{
for (;;)
{
if (tmux.try_lock_for(std::chrono::microseconds(500)))
{
std::cout << i << ":[try_lock_for timeout]" << std::endl;
continue;
}
std::cout << "[in]"<< i << std::endl;
tmux.unlock();
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::microseconds(1));
}
}
int main()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
std::thread th(ThreadMainTime, i + 1);
th.detach();
}
getchar();
return 0;
}
2.2递归锁
①作用:同一线程的同一锁可以锁多次,避免不必要的死锁。
②性质:组合业务用到同一个锁
注:recursive_timed_mutex为递归超时锁!
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
#include <mutex>
std::recursive_mutex rmux;
void Task1()
{
rmux.lock();
std::cout << "task1 [in] " << std::endl;
rmux.unlock();
}
void Task2()
{
rmux.lock();
std::cout << "task2 [in] " << std::endl;
rmux.unlock();
}
void ThreadMainRec(int i)
{
for (;;)
{
rmux.lock();
Task1();
std::cout << i << "[in]" << std::endl;
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::microseconds(2000));
Task2();
rmux.unlock();
}
}
int main()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
std::thread th(ThreadMainRec, i + 1);
th.detach();
}
getchar();
return 0;
}
2.3共享锁
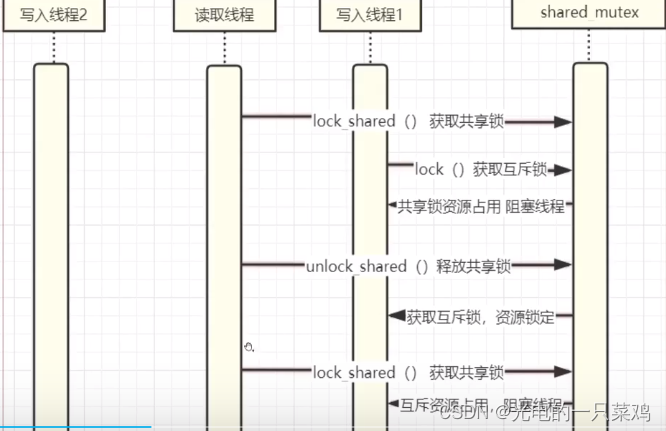
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
#include <mutex>
#include <shared_mutex>
std::shared_timed_mutex stmux;
void ThreadRead(int i)
{
for (;;)
{
stmux.lock_shared();
std::cout << "Read:" << i << std::endl;
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::microseconds(3000));
stmux.unlock_shared();
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::microseconds(1));
}
}
void ThreadWrite(int i)
{
for (;;)
{
stmux.lock_shared();
stmux.unlock_shared();
stmux.lock();
std::cout << "Write:" << i << std::endl;
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::microseconds(3000));
stmux.unlock();
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::microseconds(1));
}
}
int main()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
std::thread th(ThreadWrite, i + 1);
th.detach();
}
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
std::thread th(ThreadRead, i + 1);
th.detach();
}
getchar();
return 0;
}