Java常用函数接口
Java 8 中引入的常用函数式接口,也就是 java.util.function 包中的接口。这些接口提供了一种简洁的方式来定义函数,常用于 Lambda 表达式和方法引用。下面是一些常用的接口:
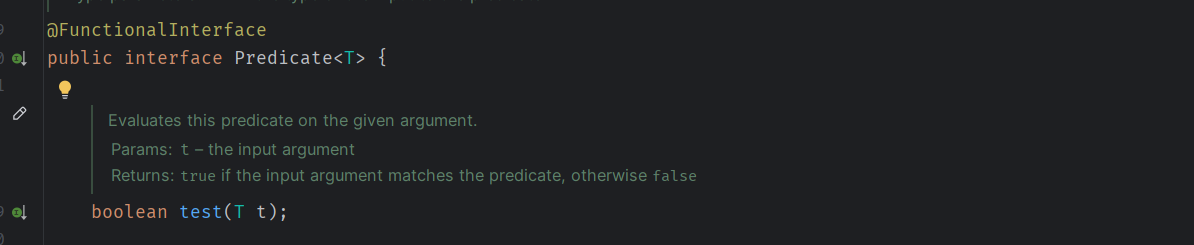
一、Predicate(断言)
- 方法:
test(T t),接受一个参数并返回一个 boolean 值。 - 用途:用于检查给定的输入是否满足某些条件。常见的用法是过滤集合中的元素。
示例一:
Predicate<Integer> isPositive = num -> num > 0;
System.out.println(isPositive.test(5)); // 输出 true
System.out.println(isPositive.test(-3)); // 输出 false
示例二:
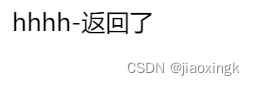
public static void main(String[] args) {
doPredicate(s -> s.contains("h"));
}
public static void doPredicate(Predicate<String> predicate){
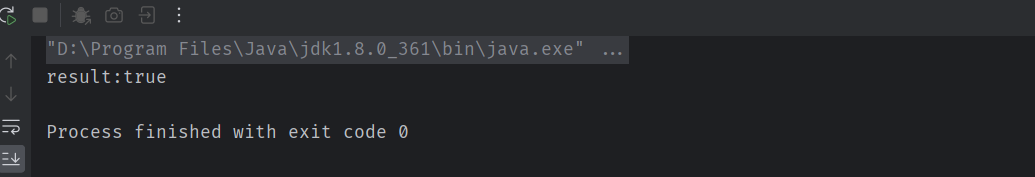
System.out.println("result:"+predicate.test("hello"));
}
输出结果:
二、Consumer(消费者)
- 方法:
accept(T t),接受一个参数并且不返回结果。 - 用途:对给定的输入执行某些操作,但没有返回值。

示例一:
Consumer<String> printUpperCase = str -> System.out.println(str.toUpperCase());
printUpperCase.accept("hello"); // 输出 HELLO
示例二:
public static void main(String[] args) {
doConsumer(s -> System.out.println(s.toUpperCase()));
}
public static void doConsumer(Consumer<String> consumer){
consumer.accept("hello");
}
结果:

三、Supplier(供应商)
- 方法:
get(),不接受任何参数,但返回一个结果。 - 用途:生成或提供值,常用于延迟计算或工厂方法。
示例一:
Supplier<Double> randomNumber = () -> Math.random();
System.out.println(randomNumber.get()); // 输出一个随机数
示例二:
public static void main(String[] args) {
doSupplier(()->"hello");
}
public static void doSupplier(Supplier<String> supplier){
System.out.println(supplier.get());
}
结果:

四、Function(函数)
- 方法:
apply(T t),接受一个参数并返回一个结果。 - 用途:将输入映射为输出,是最常用的函数式接口之一。
- 说明,传入两个泛型,也可以理解为将第二个类型转为第一个类型,第二个泛型类型也就是要入参的类型,返回值为第一个泛型类型
示例一:
Function<Integer, String> convertToString = num -> "The number is: " + num;
System.out.println(convertToString.apply(10)); // 输出 The number is: 10
示例二:
public static void main(String[] args) {
int result = doFunction(str ->{
int integer = Integer.parseInt(str);
return integer*100;
});
System.out.println(result);
}
public static Integer doFunction(Function<String,Integer> function){
return function.apply("10");
}
结果:

五、Comparator(比较)
- 方法:
int compare(T obj1, T obj2):接受两个参数并比较它们的顺序。如果第一个参数应该排在第二个参数之前,则返回负整数;如果第一个参数应该排在第二个参数之后,则返回正整数;如果两个参数相等,则返回零。 - 用途:排序:最常见的用途是对集合中的元素进行排序。通过传递一个
Comparator对象给排序算法(如Collections.sort()或Arrays.sort()),可以自定义对象的比较方式。
示例:
实现从短到长排序
String[] strings = {"apple", "banana", "orange", "grape"};
Arrays.sort(strings,(s1,s2)-> s1.length() -s2.length());
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(strings));
结果: