104.二叉树的最大深度
力扣题目链接(opens new window)
题目
给定一个二叉树,找出其最大深度。
二叉树的深度为根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点数。
说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
示例: 给定二叉树 [3,9,20,null,null,15,7],

返回它的最大深度 3 。
解答
- 二叉树节点的深度:指从根节点到该节点的最长简单路径边的条数或者节点数(取决于深度从0开始还是从1开始)(求深度用前序遍历,将根结点的深度依次向下返回)
- 二叉树节点的高度:指从该节点到叶子节点的最长简单路径边的条数或者节点数(取决于高度从0开始还是从1开始)(求高度用后续遍历,将叶子结点的高度依次向上返回)
- 根节点的高度就是二叉树的最大深度
//正常递归三部曲
class Solution {
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null)
return 0;
int leftLen = maxDepth(root.left);
int rightLen = maxDepth(root.right);
return Math.max(leftLen,rightLen) + 1;
}
}
111.二叉树的最小深度
力扣题目链接(opens new window)
题目
给定一个二叉树,找出其最小深度。
最小深度是从根节点到最近叶子节点的最短路径上的节点数量。
说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
示例:
给定二叉树 [3,9,20,null,null,15,7],

返回它的最小深度 2
解答
陷入的误区:没有左孩子的分支会算为最短深度(没到叶子就停止了)(不能直接与求最大深度相提并论)
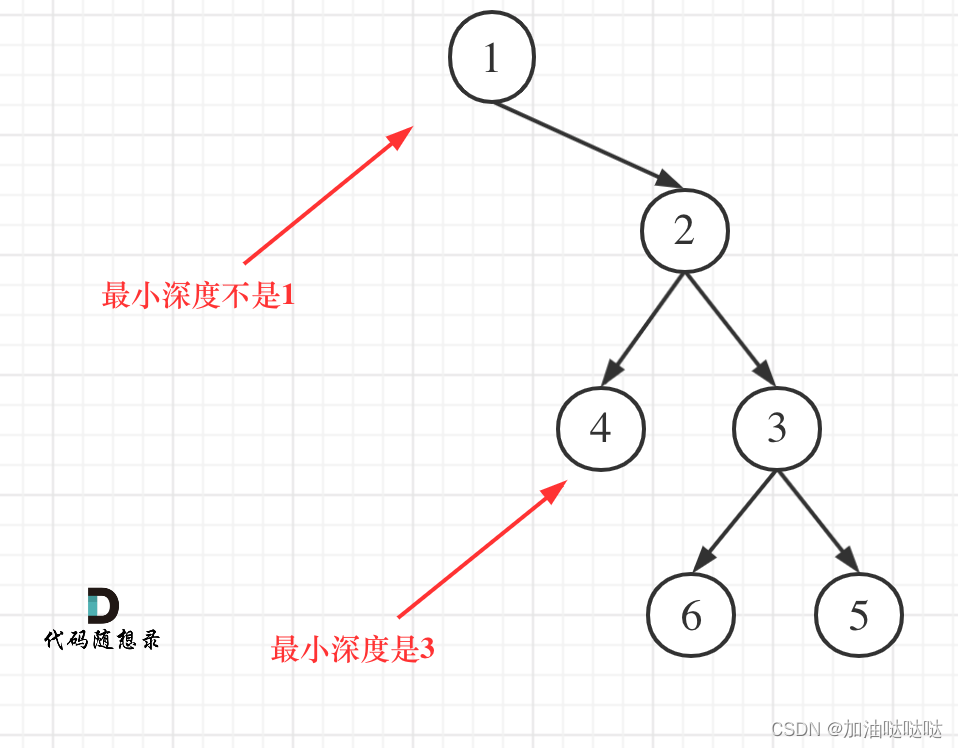
-
如果左子树为空,右子树不为空,说明最小深度是 1 + 右子树的深度。
-
如果右子树为空,左子树不为空,最小深度是 1 + 左子树的深度。 最后如果左右子树都不为空,返回左右子树深度最小值 + 1 。
class Solution {
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null)
return 0;
if (root.left == null && root.right != null)
return minDepth(root.right) + 1;
if (root.left != null && root.right == null)
return minDepth(root.left) + 1;
int leftHeight = minDepth(root.left);
int rightHeight = minDepth(root.right);
return Math.min(leftHeight,rightHeight) + 1;
}
}
222.完全二叉树的节点个数
力扣题目链接(opens new window)
题目
给出一个完全二叉树,求出该树的节点个数。
示例 1:
- 输入:root = [1,2,3,4,5,6]
- 输出:6
示例 2:
- 输入:root = []
- 输出:0
示例 3:
- 输入:root = [1]
- 输出:1
提示:
- 树中节点的数目范围是[0, 5 * 10^4]
- 0 <= Node.val <= 5 * 10^4
- 题目数据保证输入的树是完全二叉树
解答
1. 常规的递归,没用到完全二叉树的性质
class Solution {
public int countNodes(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null)
return 0;
//后序遍历
int leftNum = countNodes(root.left);//左
int rightNum = countNodes(root.right);//右
return leftNum + rightNum + 1;//中
}
}
2. 使用层次遍历依次计数
class Solution {
public int countNodes(TreeNode root) {
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
if (root != null)
queue.offer(root);
int sum = 0;//出队就计数
while (!queue.isEmpty()){
TreeNode temp = queue.poll();
sum++;
if (temp.left != null)
queue.offer(temp.left);
if (temp.right != null)
queue.offer(temp.right);
}
return sum;
}
}
3. 利用完全二叉树的性质
在完全二叉树中,除了最底层节点可能没填满外,其余每层节点数都达到最大值,并且最下面一层的节点都集中在该层最左边的若干位置。若最底层为第 h 层,则该层包含 1~ 2^(h-1) 个节点。
完全二叉树只有两种情况,情况一:就是满二叉树,情况二:最后一层叶子节点没有满。
对于情况一,可以直接用 2^树深度 - 1 来计算,注意这里根节点深度为1。
对于情况二,分别递归左孩子,和右孩子,递归到某一深度一定会有左孩子或者右孩子为满二叉树**(叶子节点也属于是满二叉树)**,然后依然可以按照情况1来计算。
class Solution {
public int countNodes(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null)
return 0;
//看当前结点是不是满二叉树,按照完全二叉树的定义
//如果左子树和右子树的高度相等,当前结点对应的树一定为满二叉树,可以使用公式计算结点
TreeNode left = root.left;
TreeNode right = root.right;
int leftHeight = 0;
int rightHeight = 0;
while (left != null){
left = left.left;
leftHeight++;
}
while (right != null){
right = right.right;
rightHeight++;
}
if (rightHeight == leftHeight){//此时为满二叉树,使用定义
int height = leftHeight + 1;//因为leftHeight的高度并不是当前子树的根节点的高度
return (int) Math.pow(2,height) - 1;
// return (2 << leftHeight) - 1;
//这行代码可以代替上面两行,但是使用的hight不一样,下面一定要是leftHeight或rightHeight
//<< 是位运算符,表示左移操作。
// 对于整数,左移操作是将其二进制表示向左移动指定的位数,并在右侧用0填充。
//2<<1 表示将整数2的二进制表示向左移动1位。
//2的二进制表示为 10
//将其向左移动1位,右侧用0填充,得到100
//转换为十进制,结果为4
}
//不是满二叉树,就单独计算
return countNodes(root.left) + countNodes(root.right) + 1;
}
}