hibernate session接口
Session接口是hibernate向应用程序提供的操纵数据库的最主要的接口,提供了保存、更新、删除和加载Java对象的方法。
session具有一个缓存,位于缓存中的对象成为持久化对象,和数据库中的相关记录对应。session能够在某些时间点,按照缓存中对象的变化来执行相关的SQL语句,来同步更新数据库,这一过程称为刷新缓存(flush)。
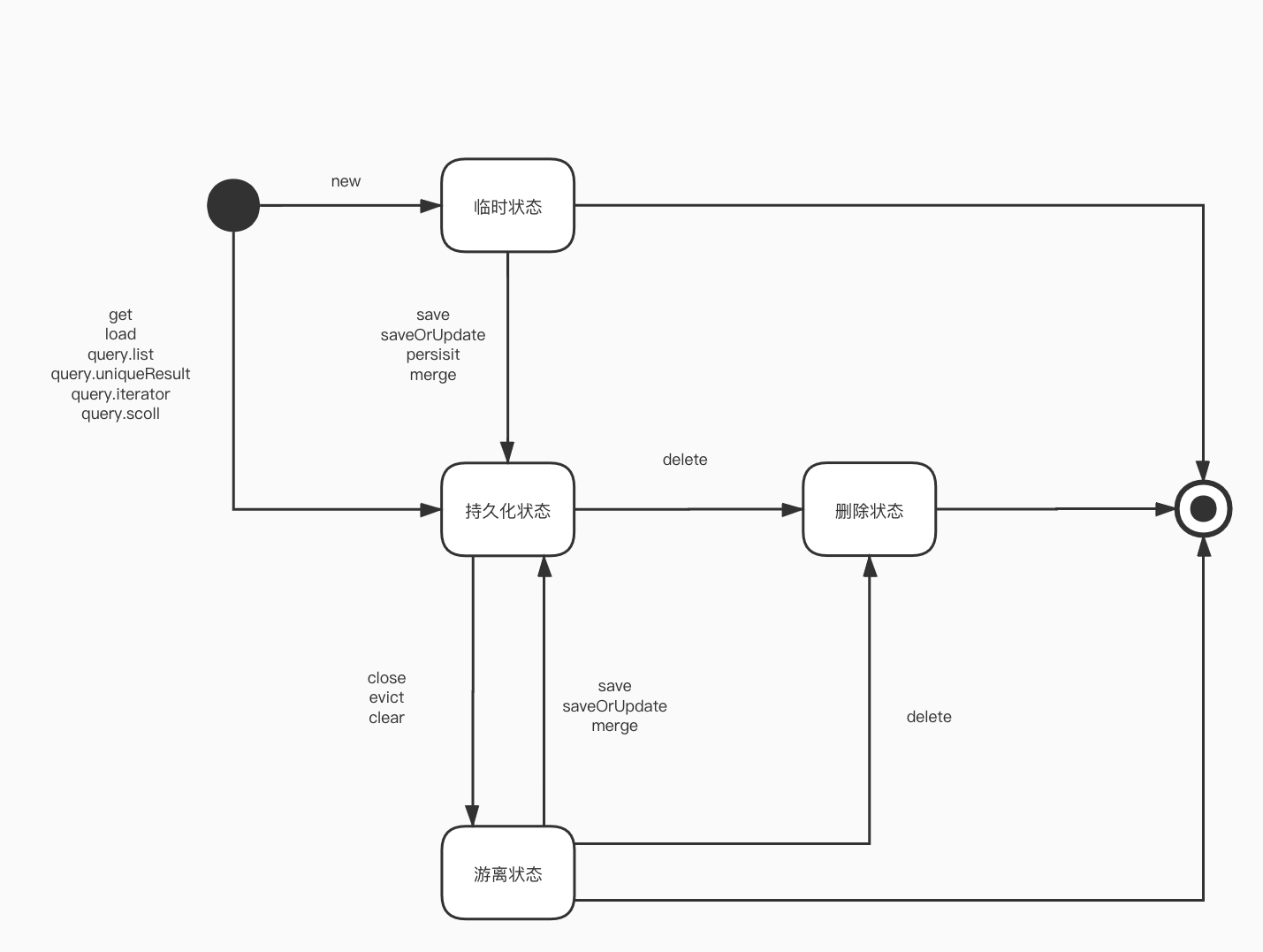
hibernate把对象分为4种状态,持久化状态,临时状态,游离状态,删除状态。session的特定方法可以使对象进行状态转换
session缓存
session实例没有结束生命周期,且没有清理缓存,则存放在session缓存中的对象也不会结束生命周期,session缓存可以减少访问数据库的频率。
操作session缓存
flush方法
缓存中对象同步到数据库(会插入或更新数据库),使数据库中的状态与缓存中一致
注意:
session在以下情况下会刷新缓存
-
hibernate在事务提交之前会执行flush()方法,然后再向数据库提交事务
-
显示调用session.flush()方法
-
在执行HQL或者QBC查询,会先进行flush()操作,以得到数据表最新的记录
refresh方法
将数据库同步到缓存中(会查询数据库),使缓存中的状态与数据库一致
session.refresh();
clear方法
清理缓存,可以将session中的缓存清除
session.clear();
四种状态的转换
临时状态(Transient)
-
在使用代理主键的情况下,OID通常为null -
不处于session缓存中 -
在数据库中也没有对应的记录,此时刚new了一个实体对象,还存在于保存临时数据的内存区域中
持久化状态(Persist)
-
OID不为null -
位于session缓存中 -
若在数据库中已经有和其对应的记录,持久化对象和数据库中的相关记录对应 -
session在flush缓存时,会根据持久化对象的属性变化,来同步数据库 -
在同一个session实例的缓存中,数据库表中每条记录只对应唯一的持久化对象 -
持久化对象的id不可以被修改,因为hibernate是根据id去进行比较的
删除状态(Removed)
-
在数据库中没有和其OID对应的记录 -
不再处于session缓存中
游离状态(Detached)
-
OID不为null -
不再处于session缓存中 -
一般情况下,游离对象是由持久化对象转变过来的(session进行close、clear、evict等情况),数据库中可能还存在它对应的记录,但是因为会话已经消失,对象不在持久化管理之内,所以处于游离状态
save方法和persist方法的区别
在调用persist()方法时如果存在id,则会抛出异常,而save方法则可以正常执行
org.hibernate.PersistentObjectException: detached entity passed to persist
get方法和load方法的区别
-
执行get方法会立即加载对象,执行load方法若不使用该对象,则不会立即查询,而是返回一个代理对象(延时加载)
-
若数据表中没有对应的记录,get方法返回null,load方法抛出异常
org.hibernate.ObjectNotFoundException: No row with the given identifier exists -
load方法可能会抛出懒加载异常
org.hibernate.LazyInitializationException: could not initialize proxy - no Session
注意:在session缓存中不能够有两个相同OID的对象,否则会报异常
public static void testOid(Session session){
User user = (User) session.get(User.class,1);
System.out.println(user);
User user1 = new User();
user1.setId(1);
user1.setName("王五");
session.saveOrUpdate(user1);
}
org.hibernate.NonUniqueObjectException: A different object with the same identifier value was already associated with the session
evict方法
从session缓存中将指定的持久化对象移除
hibernate获取原生JDBC连接进行操作
可以使用doWork或者doReturnWork来使用原生JDBC操作数据
session.doWork(new Work() {
@Override
public void execute(Connection connection) throws SQLException {
}
});
session.doReturningWork(new ReturningWork<Object>() {
@Override
public Object execute(Connection connection) throws SQLException {
return null;
}
});
session方法说明
public interface Session extends SharedSessionContract {
/**
* Obtain a {@link Session} builder with the ability to grab certain information from this session.
*
* @return The session builder
*/
public SharedSessionBuilder sessionWithOptions();
/**
* Force this session to flush. Must be called at the end of a
* unit of work, before committing the transaction and closing the
* session (depending on {@link #setFlushMode(FlushMode)},
* {@link Transaction#commit()} calls this method).
* <p/>
* <i>Flushing</i> is the process of synchronizing the underlying persistent
* store with persistable state held in memory.
*
* @throws HibernateException Indicates problems flushing the session or
* talking to the database.
*/
public void flush() throws HibernateException;
/**
* Set the flush mode for this session.
* <p/>
* The flush mode determines the points at which the session is flushed.
* <i>Flushing</i> is the process of synchronizing the underlying persistent
* store with persistable state held in memory.
* <p/>
* For a logically "read only" session, it is reasonable to set the session's
* flush mode to {@link FlushMode#MANUAL} at the start of the session (in
* order to achieve some extra performance).
*
* @param flushMode the new flush mode
* @see FlushMode
*/
public void setFlushMode(FlushMode flushMode);
/**
* Get the current flush mode for this session.
*
* @return The flush mode
*/
public FlushMode getFlushMode();
/**
* Set the cache mode.
* <p/>
* Cache mode determines the manner in which this session can interact with
* the second level cache.
*
* @param cacheMode The new cache mode.
*/
public void setCacheMode(CacheMode cacheMode);
/**
* Get the current cache mode.
*
* @return The current cache mode.
*/
public CacheMode getCacheMode();
// 获取创建该会话的sessionFactory
public SessionFactory getSessionFactory();
// 关闭数据库连接
public Connection close() throws HibernateException;
// 取消当前查询的执行
public void cancelQuery() throws HibernateException;
// 当前session是否开启
public boolean isOpen();
// 当前session是否连接
public boolean isConnected();
// 该session中是否包含必须与数据库痛的变化
public boolean isDirty() throws HibernateException;
/**
* Will entities and proxies that are loaded into this session be made
* read-only by default?
*
* To determine the read-only/modifiable setting for a particular entity
* or proxy:
* @see Session#isReadOnly(Object)
*
* @return true, loaded entities/proxies will be made read-only by default;
* false, loaded entities/proxies will be made modifiable by default.
*/
public boolean isDefaultReadOnly();
/**
* Change the default for entities and proxies loaded into this session
* from modifiable to read-only mode, or from modifiable to read-only mode.
*
* Read-only entities are not dirty-checked and snapshots of persistent
* state are not maintained. Read-only entities can be modified, but
* changes are not persisted.
*
* When a proxy is initialized, the loaded entity will have the same
* read-only/modifiable setting as the uninitialized
* proxy has, regardless of the session's current setting.
*
* To change the read-only/modifiable setting for a particular entity
* or proxy that is already in this session:
* @see Session#setReadOnly(Object,boolean)
*
* To override this session's read-only/modifiable setting for entities
* and proxies loaded by a Query:
* @see Query#setReadOnly(boolean)
*
* @param readOnly true, the default for loaded entities/proxies is read-only;
* false, the default for loaded entities/proxies is modifiable
*/
public void setDefaultReadOnly(boolean readOnly);
// 返回与当前实体关联的会话标识符
public Serializable getIdentifier(Object object);
/**
* Check if this instance is associated with this <tt>Session</tt>.
*
* @param object an instance of a persistent class
* @return true if the given instance is associated with this <tt>Session</tt>
*/
public boolean contains(Object object);
/**
* Remove this instance from the session cache. Changes to the instance will
* not be synchronized with the database. This operation cascades to associated
* instances if the association is mapped with <tt>cascade="evict"</tt>.
*
* @param object The entity to evict
*
* @throws NullPointerException if the passed object is {@code null}
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the passed object is not defined as an entity
*/
public void evict(Object object);
/**
* Return the persistent instance of the given entity class with the given identifier,
* obtaining the specified lock mode, assuming the instance exists.
*
* @param theClass a persistent class
* @param id a valid identifier of an existing persistent instance of the class
* @param lockMode the lock level
*
* @return the persistent instance or proxy
*
* @deprecated LockMode parameter should be replaced with LockOptions
*/
@Deprecated
public Object load(Class theClass, Serializable id, LockMode lockMode);
/**
* Return the persistent instance of the given entity class with the given identifier,
* obtaining the specified lock mode, assuming the instance exists.
*
* @param theClass a persistent class
* @param id a valid identifier of an existing persistent instance of the class
* @param lockOptions contains the lock level
* @return the persistent instance or proxy
*/
public Object load(Class theClass, Serializable id, LockOptions lockOptions);
/**
* Return the persistent instance of the given entity class with the given identifier,
* obtaining the specified lock mode, assuming the instance exists.
*
* @param entityName a persistent class
* @param id a valid identifier of an existing persistent instance of the class
* @param lockMode the lock level
*
* @return the persistent instance or proxy
*
* @deprecated LockMode parameter should be replaced with LockOptions
*/
@Deprecated
public Object load(String entityName, Serializable id, LockMode lockMode);
/**
* Return the persistent instance of the given entity class with the given identifier,
* obtaining the specified lock mode, assuming the instance exists.
*
* @param entityName a persistent class
* @param id a valid identifier of an existing persistent instance of the class
* @param lockOptions contains the lock level
*
* @return the persistent instance or proxy
*/
public Object load(String entityName, Serializable id, LockOptions lockOptions);
/**
* Return the persistent instance of the given entity class with the given identifier,
* assuming that the instance exists. This method might return a proxied instance that
* is initialized on-demand, when a non-identifier method is accessed.
* <br><br>
* You should not use this method to determine if an instance exists (use <tt>get()</tt>
* instead). Use this only to retrieve an instance that you assume exists, where non-existence
* would be an actual error.
*
* @param theClass a persistent class
* @param id a valid identifier of an existing persistent instance of the class
*
* @return the persistent instance or proxy
*/
public Object load(Class theClass, Serializable id);
/**
* Return the persistent instance of the given entity class with the given identifier,
* assuming that the instance exists. This method might return a proxied instance that
* is initialized on-demand, when a non-identifier method is accessed.
* <br><br>
* You should not use this method to determine if an instance exists (use <tt>get()</tt>
* instead). Use this only to retrieve an instance that you assume exists, where non-existence
* would be an actual error.
*
* @param entityName a persistent class
* @param id a valid identifier of an existing persistent instance of the class
*
* @return the persistent instance or proxy
*/
public Object load(String entityName, Serializable id);
/**
* Read the persistent state associated with the given identifier into the given transient
* instance.
*
* @param object an "empty" instance of the persistent class
* @param id a valid identifier of an existing persistent instance of the class
*/
public void load(Object object, Serializable id);
/**
* Persist the state of the given detached instance, reusing the current
* identifier value. This operation cascades to associated instances if
* the association is mapped with {@code cascade="replicate"}
*
* @param object a detached instance of a persistent class
* @param replicationMode The replication mode to use
*/
public void replicate(Object object, ReplicationMode replicationMode);
/**
* Persist the state of the given detached instance, reusing the current
* identifier value. This operation cascades to associated instances if
* the association is mapped with {@code cascade="replicate"}
*
* @param entityName The entity name
* @param object a detached instance of a persistent class
* @param replicationMode The replication mode to use
*/
public void replicate(String entityName, Object object, ReplicationMode replicationMode) ;
// 保存对象,生成标识,变为持久化状态
public Serializable save(Object object);
// 保存对象,生成标识,变为持久化状态
public Serializable save(String entityName, Object object);
// 保存或更新对象
public void saveOrUpdate(Object object);
// 保存或更新对象
public void saveOrUpdate(String entityName, Object object);
// 更新该标识符所对应的对象
public void update(Object object);
// 更新该标识符所对应的对象
public void update(String entityName, Object object);
/**
* Copy the state of the given object onto the persistent object with the same
* identifier. If there is no persistent instance currently associated with
* the session, it will be loaded. Return the persistent instance. If the
* given instance is unsaved, save a copy of and return it as a newly persistent
* instance. The given instance does not become associated with the session.
* This operation cascades to associated instances if the association is mapped
* with {@code cascade="merge"}
* <p/>
* The semantics of this method are defined by JSR-220.
*
* @param object a detached instance with state to be copied
*
* @return an updated persistent instance
*/
public Object merge(Object object);
/**
* Copy the state of the given object onto the persistent object with the same
* identifier. If there is no persistent instance currently associated with
* the session, it will be loaded. Return the persistent instance. If the
* given instance is unsaved, save a copy of and return it as a newly persistent
* instance. The given instance does not become associated with the session.
* This operation cascades to associated instances if the association is mapped
* with {@code cascade="merge"}
* <p/>
* The semantics of this method are defined by JSR-220.
*
* @param entityName The entity name
* @param object a detached instance with state to be copied
*
* @return an updated persistent instance
*/
public Object merge(String entityName, Object object);
/**
* Make a transient instance persistent. This operation cascades to associated
* instances if the association is mapped with {@code cascade="persist"}
* <p/>
* The semantics of this method are defined by JSR-220.
*
* @param object a transient instance to be made persistent
*/
public void persist(Object object);
/**
* Make a transient instance persistent. This operation cascades to associated
* instances if the association is mapped with {@code cascade="persist"}
* <p/>
* The semantics of this method are defined by JSR-220.
*
* @param entityName The entity name
* @param object a transient instance to be made persistent
*/
public void persist(String entityName, Object object);
// 删除该持久化对象
public void delete(Object object);
// 删除该持久化对象
public void delete(String entityName, Object object);
/**
* Obtain the specified lock level upon the given object. This may be used to
* perform a version check (<tt>LockMode.READ</tt>), to upgrade to a pessimistic
* lock (<tt>LockMode.PESSIMISTIC_WRITE</tt>), or to simply reassociate a transient instance
* with a session (<tt>LockMode.NONE</tt>). This operation cascades to associated
* instances if the association is mapped with <tt>cascade="lock"</tt>.
*
* @param object a persistent or transient instance
* @param lockMode the lock level
*
* @deprecated instead call buildLockRequest(LockMode).lock(object)
*/
@Deprecated
public void lock(Object object, LockMode lockMode);
/**
* Obtain the specified lock level upon the given object. This may be used to
* perform a version check (<tt>LockMode.OPTIMISTIC</tt>), to upgrade to a pessimistic
* lock (<tt>LockMode.PESSIMISTIC_WRITE</tt>), or to simply reassociate a transient instance
* with a session (<tt>LockMode.NONE</tt>). This operation cascades to associated
* instances if the association is mapped with <tt>cascade="lock"</tt>.
*
* @param entityName The name of the entity
* @param object a persistent or transient instance
* @param lockMode the lock level
*
* @deprecated instead call buildLockRequest(LockMode).lock(entityName, object)
*/
@SuppressWarnings( {"JavaDoc"})
@Deprecated
public void lock(String entityName, Object object, LockMode lockMode);
/**
* Build a LockRequest that specifies the LockMode, pessimistic lock timeout and lock scope.
* timeout and scope is ignored for optimistic locking. After building the LockRequest,
* call LockRequest.lock to perform the requested locking.
* <p/>
* Example usage:
* {@code session.buildLockRequest().setLockMode(LockMode.PESSIMISTIC_WRITE).setTimeOut(60000).lock(entity);}
*
* @param lockOptions contains the lock level
*
* @return a lockRequest that can be used to lock the passed object.
*/
public LockRequest buildLockRequest(LockOptions lockOptions);
// 从数据库中重新读取该对象
public void refresh(Object object);
/**
* Re-read the state of the given instance from the underlying database. It is
* inadvisable to use this to implement long-running sessions that span many
* business tasks. This method is, however, useful in certain special circumstances.
* For example
* <ul>
* <li>where a database trigger alters the object state upon insert or update
* <li>after executing direct SQL (eg. a mass update) in the same session
* <li>after inserting a <tt>Blob</tt> or <tt>Clob</tt>
* </ul>
*
* @param entityName a persistent class
* @param object a persistent or detached instance
*/
public void refresh(String entityName, Object object);
/**
* Re-read the state of the given instance from the underlying database, with
* the given <tt>LockMode</tt>. It is inadvisable to use this to implement
* long-running sessions that span many business tasks. This method is, however,
* useful in certain special circumstances.
*
* @param object a persistent or detached instance
* @param lockMode the lock mode to use
*
* @deprecated LockMode parameter should be replaced with LockOptions
*/
@Deprecated
public void refresh(Object object, LockMode lockMode);
/**
* Re-read the state of the given instance from the underlying database, with
* the given <tt>LockMode</tt>. It is inadvisable to use this to implement
* long-running sessions that span many business tasks. This method is, however,
* useful in certain special circumstances.
*
* @param object a persistent or detached instance
* @param lockOptions contains the lock mode to use
*/
public void refresh(Object object, LockOptions lockOptions);
/**
* Re-read the state of the given instance from the underlying database, with
* the given <tt>LockMode</tt>. It is inadvisable to use this to implement
* long-running sessions that span many business tasks. This method is, however,
* useful in certain special circumstances.
*
* @param entityName a persistent class
* @param object a persistent or detached instance
* @param lockOptions contains the lock mode to use
*/
public void refresh(String entityName, Object object, LockOptions lockOptions);
/**
* Determine the current lock mode of the given object.
*
* @param object a persistent instance
*
* @return the current lock mode
*/
public LockMode getCurrentLockMode(Object object);
// 为给定集合和查询条件创建查询实例
public Query createFilter(Object collection, String queryString);
// 清除该会话
public void clear();
// 返回给定命名和标识符的持久化对象实例
public Object get(Class clazz, Serializable id);
/**
* Return the persistent instance of the given entity class with the given identifier,
* or null if there is no such persistent instance. (If the instance is already associated
* with the session, return that instance. This method never returns an uninitialized instance.)
* Obtain the specified lock mode if the instance exists.
*
* @param clazz a persistent class
* @param id an identifier
* @param lockOptions the lock mode
*
* @return a persistent instance or null
*/
public Object get(Class clazz, Serializable id, LockOptions lockOptions);
// 返回给定命名和标识符的持久化对象实例
public Object get(String entityName, Serializable id);
/**
* Return the persistent instance of the given entity class with the given identifier,
* or null if there is no such persistent instance. (If the instance is already associated
* with the session, return that instance. This method never returns an uninitialized instance.)
* Obtain the specified lock mode if the instance exists.
*
* @param entityName the entity name
* @param id an identifier
* @param lockOptions contains the lock mode
*
* @return a persistent instance or null
*/
public Object get(String entityName, Serializable id, LockOptions lockOptions);
/**
* Return the entity name for a persistent entity.
*
* @param object a persistent entity
*
* @return the entity name
*/
public String getEntityName(Object object);
/**
* Create an {@link IdentifierLoadAccess} instance to retrieve the specified entity type by
* primary key.
*
* @param entityName The entity name of the entity type to be retrieved
*
* @return load delegate for loading the specified entity type by primary key
*
* @throws HibernateException If the specified entity name cannot be resolved as an entity name
*/
public IdentifierLoadAccess byId(String entityName);
/**
* Create an {@link IdentifierLoadAccess} instance to retrieve the specified entity by
* primary key.
*
* @param entityClass The entity type to be retrieved
*
* @return load delegate for loading the specified entity type by primary key
*
* @throws HibernateException If the specified Class cannot be resolved as a mapped entity
*/
public IdentifierLoadAccess byId(Class entityClass);
/**
* Create an {@link NaturalIdLoadAccess} instance to retrieve the specified entity by
* its natural id.
*
* @param entityName The entity name of the entity type to be retrieved
*
* @return load delegate for loading the specified entity type by natural id
*
* @throws HibernateException If the specified entity name cannot be resolved as an entity name
*/
public NaturalIdLoadAccess byNaturalId(String entityName);
/**
* Create an {@link NaturalIdLoadAccess} instance to retrieve the specified entity by
* its natural id.
*
* @param entityClass The entity type to be retrieved
*
* @return load delegate for loading the specified entity type by natural id
*
* @throws HibernateException If the specified Class cannot be resolved as a mapped entity
*/
public NaturalIdLoadAccess byNaturalId(Class entityClass);
/**
* Create an {@link SimpleNaturalIdLoadAccess} instance to retrieve the specified entity by
* its natural id.
*
* @param entityName The entity name of the entity type to be retrieved
*
* @return load delegate for loading the specified entity type by natural id
*
* @throws HibernateException If the specified entityClass cannot be resolved as a mapped entity, or if the
* entity does not define a natural-id or if its natural-id is made up of multiple attributes.
*/
public SimpleNaturalIdLoadAccess bySimpleNaturalId(String entityName);
/**
* Create an {@link SimpleNaturalIdLoadAccess} instance to retrieve the specified entity by
* its simple (single attribute) natural id.
*
* @param entityClass The entity type to be retrieved
*
* @return load delegate for loading the specified entity type by natural id
*
* @throws HibernateException If the specified entityClass cannot be resolved as a mapped entity, or if the
* entity does not define a natural-id or if its natural-id is made up of multiple attributes.
*/
public SimpleNaturalIdLoadAccess bySimpleNaturalId(Class entityClass);
/**
* Enable the named filter for this current session.
*
* @param filterName The name of the filter to be enabled.
*
* @return The Filter instance representing the enabled filter.
*/
public Filter enableFilter(String filterName);
/**
* Retrieve a currently enabled filter by name.
*
* @param filterName The name of the filter to be retrieved.
*
* @return The Filter instance representing the enabled filter.
*/
public Filter getEnabledFilter(String filterName);
/**
* Disable the named filter for the current session.
*
* @param filterName The name of the filter to be disabled.
*/
public void disableFilter(String filterName);
/**
* Get the statistics for this session.
*
* @return The session statistics being collected for this session
*/
public SessionStatistics getStatistics();
/**
* Is the specified entity or proxy read-only?
*
* To get the default read-only/modifiable setting used for
* entities and proxies that are loaded into the session:
* @see org.hibernate.Session#isDefaultReadOnly()
*
* @param entityOrProxy an entity or HibernateProxy
* @return {@code true} if the entity or proxy is read-only, {@code false} if the entity or proxy is modifiable.
*/
public boolean isReadOnly(Object entityOrProxy);
/**
* Set an unmodified persistent object to read-only mode, or a read-only
* object to modifiable mode. In read-only mode, no snapshot is maintained,
* the instance is never dirty checked, and changes are not persisted.
*
* If the entity or proxy already has the specified read-only/modifiable
* setting, then this method does nothing.
*
* To set the default read-only/modifiable setting used for
* entities and proxies that are loaded into the session:
* @see org.hibernate.Session#setDefaultReadOnly(boolean)
*
* To override this session's read-only/modifiable setting for entities
* and proxies loaded by a Query:
* @see Query#setReadOnly(boolean)
*
* @param entityOrProxy an entity or HibernateProxy
* @param readOnly {@code true} if the entity or proxy should be made read-only; {@code false} if the entity or
* proxy should be made modifiable
*/
public void setReadOnly(Object entityOrProxy, boolean readOnly);
/**
* Controller for allowing users to perform JDBC related work using the Connection managed by this Session.
*
* @param work The work to be performed.
* @throws HibernateException Generally indicates wrapped {@link java.sql.SQLException}
*/
public void doWork(Work work) throws HibernateException;
/**
* Controller for allowing users to perform JDBC related work using the Connection managed by this Session. After
* execution returns the result of the {@link ReturningWork#execute} call.
*
* @param work The work to be performed.
* @param <T> The type of the result returned from the work
*
* @return the result from calling {@link ReturningWork#execute}.
*
* @throws HibernateException Generally indicates wrapped {@link java.sql.SQLException}
*/
public <T> T doReturningWork(ReturningWork<T> work) throws HibernateException;
/**
* Disconnect the session from its underlying JDBC connection. This is intended for use in cases where the
* application has supplied the JDBC connection to the session and which require long-sessions (aka, conversations).
* <p/>
* It is considered an error to call this method on a session which was not opened by supplying the JDBC connection
* and an exception will be thrown.
* <p/>
* For non-user-supplied scenarios, normal transaction management already handles disconnection and reconnection
* automatically.
*
* @return the application-supplied connection or {@code null}
*
* @see #reconnect(Connection)
*/
Connection disconnect();
/**
* Reconnect to the given JDBC connection.
*
* @param connection a JDBC connection
*
* @see #disconnect()
*/
void reconnect(Connection connection);
/**
* Is a particular fetch profile enabled on this session?
*
* @param name The name of the profile to be checked.
* @return True if fetch profile is enabled; false if not.
* @throws UnknownProfileException Indicates that the given name does not
* match any known profile names
*
* @see org.hibernate.engine.profile.FetchProfile for discussion of this feature
*/
public boolean isFetchProfileEnabled(String name) throws UnknownProfileException;
/**
* Enable a particular fetch profile on this session. No-op if requested
* profile is already enabled.
*
* @param name The name of the fetch profile to be enabled.
* @throws UnknownProfileException Indicates that the given name does not
* match any known profile names
*
* @see org.hibernate.engine.profile.FetchProfile for discussion of this feature
*/
public void enableFetchProfile(String name) throws UnknownProfileException;
/**
* Disable a particular fetch profile on this session. No-op if requested
* profile is already disabled.
*
* @param name The name of the fetch profile to be disabled.
* @throws UnknownProfileException Indicates that the given name does not
* match any known profile names
*
* @see org.hibernate.engine.profile.FetchProfile for discussion of this feature
*/
public void disableFetchProfile(String name) throws UnknownProfileException;
/**
* Convenience access to the {@link TypeHelper} associated with this session's {@link SessionFactory}.
* <p/>
* Equivalent to calling {@link #getSessionFactory()}.{@link SessionFactory#getTypeHelper getTypeHelper()}
*
* @return The {@link TypeHelper} associated with this session's {@link SessionFactory}
*/
public TypeHelper getTypeHelper();
/**
* Retrieve this session's helper/delegate for creating LOB instances.
*
* @return This session's LOB helper
*/
public LobHelper getLobHelper();
/**
* Contains locking details (LockMode, Timeout and Scope).
*/
public interface LockRequest {
/**
* Constant usable as a time out value that indicates no wait semantics should be used in
* attempting to acquire locks.
*/
static final int PESSIMISTIC_NO_WAIT = 0;
/**
* Constant usable as a time out value that indicates that attempting to acquire locks should be allowed to
* wait forever (apply no timeout).
*/
static final int PESSIMISTIC_WAIT_FOREVER = -1;
/**
* Get the lock mode.
*
* @return the lock mode.
*/
LockMode getLockMode();
/**
* Specify the LockMode to be used. The default is LockMode.none.
*
* @param lockMode The lock mode to use for this request
*
* @return this LockRequest instance for operation chaining.
*/
LockRequest setLockMode(LockMode lockMode);
/**
* Get the timeout setting.
*
* @return timeout in milliseconds, -1 for indefinite wait and 0 for no wait.
*/
int getTimeOut();
/**
* Specify the pessimistic lock timeout (check if your dialect supports this option).
* The default pessimistic lock behavior is to wait forever for the lock.
*
* @param timeout is time in milliseconds to wait for lock. -1 means wait forever and 0 means no wait.
*
* @return this LockRequest instance for operation chaining.
*/
LockRequest setTimeOut(int timeout);
/**
* Check if locking is cascaded to owned collections and relationships.
*
* @return true if locking will be extended to owned collections and relationships.
*/
boolean getScope();
/**
* Specify if LockMode should be cascaded to owned collections and relationships.
* The association must be mapped with {@code cascade="lock"} for scope=true to work.
*
* @param scope {@code true} to cascade locks; {@code false} to not.
*
* @return {@code this}, for method chaining
*/
LockRequest setScope(boolean scope);
/**
* Perform the requested locking.
*
* @param entityName The name of the entity to lock
* @param object The instance of the entity to lock
*/
void lock(String entityName, Object object);
/**
* Perform the requested locking.
*
* @param object The instance of the entity to lock
*/
void lock(Object object);
}
/**
* Add one or more listeners to the Session
*
* @param listeners The listener(s) to add
*/
public void addEventListeners(SessionEventListener... listeners);
}
[https://zhhll.icu/2020/框架/hibernate/基础/6.hibernate session接口/](https://zhhll.icu/2020/框架/hibernate/基础/6.hibernate session接口/)
本文由 mdnice 多平台发布