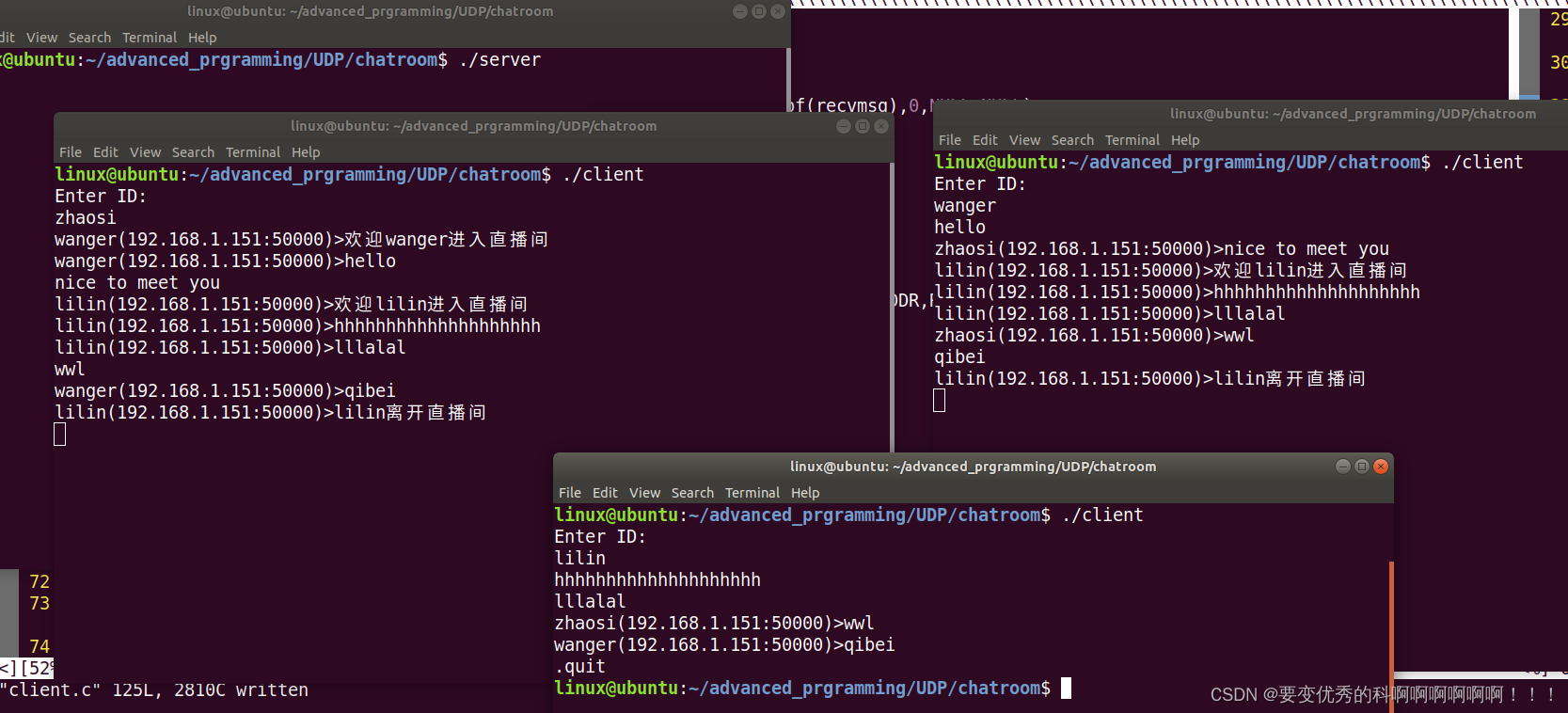
解题思路:
经典dfs题目,需要重点掌握。
养成好习惯,静态方法都要用到的变量提前想到定义为静态常量。
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
//注意加static,经常忘记导致编译错误
static int N, M, x1, x2, y1, y2, min = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
static int[][] a, v;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
N = scan.nextInt();
M = scan.nextInt();
// 初始化网格,注意题目条件,出发点和终点的坐标都是从1开始,所以我们的下标不能像往常一样从0开始
a = new int[N + 1][M + 1];
//初始化记录最少步数的访问数组
v = new int[N + 1][M + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= M; j++) {
a[i][j] = scan.nextInt();
//赋最大值,代表没有被访问过
v[i][j] = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
}
x1 = scan.nextInt();
y1 = scan.nextInt();
x2 = scan.nextInt();
y2 = scan.nextInt();
dfs(0, x1, y1);
// 如果找不到路径,则输出-1,否则输出最短路径长度
if (min == Integer.MAX_VALUE) {
min = -1;
}
System.out.println(min);
}
public static void dfs(int step, int x, int y) {
v[x][y] = step;
if (x == x2 && y == y2) {
min = Math.min(min, step);
return;
}
// 方向数组
int[] dx = { 1, -1, 0, 0 };
int[] dy = { 0, 0, 1, -1 };
// 尝试向四个方向搜索
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int xx = x + dx[i];
int yy = y + dy[i];
//注意v[x][y] + 1 < v[xx][yy],我们继续dfs的前提是v[xx][yy]没有被访问,
//或当前路径长度加1到达v[xx][yy]后比v[xx][yy]本身的路径更短
if (xx > 0 && yy > 0 && xx <= N && yy <= M && v[x][y] + 1 < v[xx][yy] && a[xx][yy] == 1) {
dfs(step + 1, xx, yy);
}
}
}
}





![练习 17 Web [极客大挑战 2019]PHP](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/2ca1741a82434f4a994791762229bea2.png)