1.方法
RGB转灰度有很多种方式
1.将RGB中任意分量拿出来当做灰度值。
2.取RGB三通道的均值来当灰度值。
3.将RGB转YUV(YCbCr)然后取Y分量作为灰度值。
其余的几种实现方式较为简单,这里不做介绍。重点实现RGB转YCbCr。
1.1 YUV(YCbCr)格式
Y表示亮度,U和V表示色度,用于描述影像的饱和度和色调。RGB转YUV的转换一般是色彩空间的转换。YUV主要用在模拟系统中,而YCbCr是通过YUV信号的发展,并通过校正
的主要应用在数字视频中的一种编码方法。YUV适用于PAL和SECAM彩色电视制式,而YCrCb适用于计算机用的显示器。 一般意义上 YCbCr 即为 YUV 信号,没有严格的划分。 CbCr 分别为蓝色色度分量、红色色度分量。
RGB注重人色彩的感知,YUV则注重亮度的敏感程度。
使用YUV描述图像的好处在于:
(1)亮度(Y)与色度(U、V)是独立的;
(2)人眼能够识别数千种不同的色彩,但只能识别20多种灰阶值,采用YUV标准可以降低数字彩色图像所需的储存容量。
1.1.1 YUV4:4:4
YUV三个通道采样率相同,因此每个分量相互独立。通常一个分量占8bit,一个像素占3byte。
1.1.2 YUV4:2:2
YUV三个通道采样率不同,UV分量只有Y的一半,两个UV共占用一个Y。
1.2 RGB转YCbCr公式

但是由于Verilog HDL无法进行浮点运算,因此使用扩大256倍,再向右移8Bit的方式来转换公式,(0.083 = 00010101)

2.算法验证平台搭建
2.1 图片转txt文本
首先将图片转化为txt文本格式方便其他模块读取。
clear ;
clc ;
close;
RGB = imread('../img/1920x1080.bmp');
imshow(RGB);
[row,col,chn] = size(RGB);
fid = fopen('../data//pre.txt','w+');
for i = 1:row
for j = 1:col
for k = 1:chn
fprintf(fid,'%02x',RGB(i,j,k));
end
fprintf(fid,'\n');
end
end
fclose(fid);
2.2 txt文本数据仿真回传
2.2.1 文本读取
这里首先读取MATLAB生成的pre.txt文本,读取txt文本的模块为img_gen3,表示读取的RGB888的数据。
`timescale 1ns / 1ps
module img_gen3
#(
parameter ACTIVE_IW = 1920 ,
parameter ACTIVE_IH = 1080 ,
parameter TOTAL_IW = 2200 ,
parameter TOTAL_IH = 1100 ,
parameter H_START = 100 ,
parameter V_START = 4
)(
input wire clk ,
input wire rst_n ,
output reg vs ,
output reg de ,
output reg [23:0] data
);
reg [23:0] raw_array [ACTIVE_IW*ACTIVE_IH-1:0];
integer i;
initial begin
for(i=0;i<ACTIVE_IW*ACTIVE_IH;i=i+1)
raw_array[i] = 0;
end
initial begin
$readmemh("H:/picture/Z7/lesson6/data/pre.txt",raw_array);
end
reg [15:0] hcnt ;
reg [15:0] vcnt ;
reg h_de ;
reg v_de ;
reg index_de ;
reg [31:0] index ;
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n)
if(!rst_n)
hcnt <= 'd0;
else if(hcnt == TOTAL_IW - 1)
hcnt <= 'd0;
else
hcnt <= hcnt + 1'b1;
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n)
if(!rst_n)
vcnt <= 'd0;
else if(hcnt == TOTAL_IW - 1 && vcnt == TOTAL_IH - 1)
vcnt <= 'd0;
else if(hcnt == TOTAL_IW - 1)
vcnt <= vcnt + 1'b1;
else
vcnt <= vcnt;
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n)
if(!rst_n)
vs <= 'd0;
else if(vcnt>=2)
vs <= 1'b1;
else
vs <= 1'b0;
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n)
if(!rst_n)
h_de <= 'd0;
else if(hcnt >= H_START && hcnt < H_START + ACTIVE_IW)
h_de <= 1'b1;
else
h_de <= 1'b0;
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n)
if(!rst_n)
v_de <= 'd0;
else if(vcnt >= V_START && vcnt < V_START + ACTIVE_IH)
v_de <= 1'b1;
else
v_de <= 1'b0;
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n)
if(!rst_n)
index_de <= 'd0;
else if(index == ACTIVE_IW * ACTIVE_IH-1)
index_de <= 1'b0;
else if(h_de == 1'b1 && v_de == 1'b1)
index_de <= 1'b1;
else
index_de <= 1'b0;
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n)
if(!rst_n)
index_de <= 'd0;
else if(h_de == 1'b1 && v_de == 1'b1)
index_de <= 1'b1;
else
index_de <= 1'b0;
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n)
if(!rst_n)
index <= 'd0;
else if(index == ACTIVE_IW * ACTIVE_IH-1)
index <= 1'b0;
else if(index_de == 1'b1)
index <= index + 1;
else
index <= index;
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n)
if(!rst_n)
de <= 'd0;
else
de <= index_de;
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n)
if(index_de == 1'b1)
data <= raw_array[index];
else
data <= 0;
endmodule
2.2.1 读取写入
读取的数据在顶层写入为post.txt。
`timescale 1ns / 1ps
module tb_top(
);
reg clk ;
reg rst_n ;
integer outfile;
initial begin
clk = 0;
rst_n = 0;
#20
rst_n = 1;
outfile = $fopen("H:/picture/Z7/lesson6/data/post.txt","w");
end
always #5 clk = ~clk;
wire vs ;
wire de ;
wire [23:0] data;
img_gen3 #(
.ACTIVE_IW (1920 ),
.ACTIVE_IH (1080 ),
.TOTAL_IW (2200 ),
.TOTAL_IH (1100 ),
.H_START (100 ),
.V_START (4 )
)u_img_gen3(
.clk (clk ),
.rst_n (rst_n ),
.vs (vs ),
.de (de ),
.data (data )
);
reg vs_r ;
always @(posedge clk)
if(rst_n == 0)
vs_r <= 1'b0;
else
vs_r <= vs;
always @(posedge clk)
if(~vs&&vs_r)
$stop;
else if(de == 1)
$fdisplay(outfile,"%h\t%h\t%h",data[23:16],data[15:8],data[7:0]);
endmodule
2.2.3 MATLAB数据读取
这里对比pre.txt和post.txt是否相等的方式有很多中,可以直接用文本对比工具,也可以用MATLAB做对比。这里只做一个txt转bmp。
clear ;
clc ;
close;
RGB = imread('../img/1920x1080.bmp');
imshow(RGB);
[row,col,chn] = size(RGB);
fid = fopen('../data//pre.txt','w+');
for i = 1:row
for j = 1:col
for k = 1:chn
fprintf(fid,'%02x',RGB(i,j,k));
end
fprintf(fid,'\n');
end
end
fclose(fid);
搭建后对比pre.txt与post.txt的数据一致。可以开始验证算法了。
3 rgb2ycbcr算法实现与仿真
3.1 rgb2ycbcr算法实现
本算法实现包括三个时钟周期,第一个时钟周期算乘法,第二个时钟周期算加减,第三个时钟周期算触发(截位)。
module rgb2ycbcr(
input wire clk , //系统时钟
input wire rst_n , //复位信号
input wire pre_hsync , //输入的场同步
input wire pre_vsync , //输入行同步
input wire pre_de , //数据有效信号
input wire [ 7:0] pre_r , //输入像素数据
input wire [ 7:0] pre_g ,
input wire [ 7:0] pre_b ,
output reg post_hsync , //输出行同步
output reg post_vsync , //输出场同步
output reg post_de , //输出数据有效信号
output reg [7:0] post_y , //输出y(亮度)分量
output reg [7:0] post_cb , //输出蓝色色度分量
output reg [7:0] post_cr //输出红色色度分量
);
reg [15:0] pre_r0 ;
reg [15:0] pre_r1 ;
reg [15:0] pre_r2 ;
reg [15:0] pre_g0 ;
reg [15:0] pre_g1 ;
reg [15:0] pre_g2 ;
reg [15:0] pre_b0 ;
reg [15:0] pre_b1 ;
reg [15:0] pre_b2 ;
reg [15:0] post_y0 ;
reg [15:0] post_cb0;
reg [15:0] post_cr0;
reg pre_hsync_d0;
reg pre_vsync_d0;
reg pre_de_d0 ;
reg pre_hsync_d1;
reg pre_vsync_d1;
reg pre_de_d1 ;
/*********************************************************
RGB888 to YCbCr
Y = 0.299R +0.587G + 0.114B
Cb = 0.568(B-Y) + 128 = -0.172R-0.339G + 0.511B + 128
CR = 0.713(R-Y) + 128 = 0.511R-0.428G -0.083B + 128
Y = (77 *R + 150*G + 29 *B)>>8
Cb = (-43*R - 85 *G + 128*B)>>8 + 128
Cr = (128*R - 107*G - 21 *B)>>8 + 128
Y = (77 *R + 150*G + 29 *B )>>8
Cb = (-43*R - 85 *G + 128*B + 32768)>>8
Cr = (128*R - 107*G - 21 *B + 32768)>>8
*********************************************************/
//计算乘法项
always @(posedge clk)begin
if(rst_n == 0)begin
pre_r0 <= 'd0;
pre_r1 <= 'd0;
pre_r2 <= 'd0;
end
else begin
pre_r0 <= pre_r *77;
pre_r1 <= pre_r *43;
pre_r2 <= pre_r *128;
end
end
always @(posedge clk)begin
if(rst_n == 0)begin
pre_g0 <= 'd0;
pre_g1 <= 'd0;
pre_g2 <= 'd0;
end
else begin
pre_g0 <= pre_g *150;
pre_g1 <= pre_g *85 ;
pre_g2 <= pre_g *107;
end
end
always @(posedge clk)begin
if(rst_n == 0)begin
pre_b0 <= 'd0;
pre_b1 <= 'd0;
pre_b2 <= 'd0;
end
else begin
pre_b0 <= pre_b *29;
pre_b1 <= pre_b *128 ;
pre_b2 <= pre_b *21;
end
end
//计算加减法
always @(posedge clk)begin
if(rst_n == 0)begin
post_y0 <= 0;
post_cb0 <= 0;
post_cr0 <= 0;
end
else begin
post_y0 <= pre_r0 + pre_g0 + pre_b0;
post_cb0 <= 32768 - pre_r1 - pre_g1 + pre_b1;
post_cr0 <= 32768 + pre_r2 - pre_g2 - pre_b2;
end
end
//移位赋值
always @(posedge clk)begin
if(rst_n == 0)begin
post_y <= 0;
post_cb <= 0;
post_cr <= 0;
end
else begin
post_y <= post_y0 /256;
post_cb <= post_cb0/256;
post_cr <= post_cr0/256;
end
end
//本次计算一共用了三个时钟周期 所以其余的信号需要打三拍出来
always @(posedge clk)begin
if(rst_n == 0)begin
pre_hsync_d0 <= 'd0;
pre_vsync_d0 <= 'd0;
pre_de_d0 <= 'd0;
pre_hsync_d1 <= 'd0;
pre_vsync_d1 <= 'd0;
pre_de_d1 <= 'd0;
post_hsync <= 'd0;
post_vsync <= 'd0;
post_de <= 'd0;
end
else begin
pre_hsync_d0 <= pre_hsync ;
pre_vsync_d0 <= pre_vsync ;
pre_de_d0 <= pre_de ;
pre_hsync_d1 <= pre_hsync_d0 ;
pre_vsync_d1 <= pre_vsync_d0 ;
pre_de_d1 <= pre_de_d0 ;
post_hsync <= pre_hsync_d1 ;
post_vsync <= pre_vsync_d1 ;
post_de <= pre_de_d1 ;
end
end
endmodule
3.2 算法仿真与验证
3.2.1 算法仿真模块
`timescale 1ns / 1ps
module tb_rgb2ycbcr();
reg clk ;
reg rst_n ;
reg pre_hsync ;
wire pre_vsync ;
wire pre_de ;
wire [7:0] pre_r ;
wire [7:0] pre_g ;
wire [7:0] pre_b ;
wire post_hsync ;
wire post_vsync ;
wire post_de ;
wire [7:0] post_y ;
wire [7:0] post_cb ;
wire [7:0] post_cr ;
integer outfile;
always #10 clk = ~clk;
initial begin
clk = 0;
rst_n = 0;
pre_hsync = 1;
#200
rst_n = 1;
outfile = $fopen("H:/picture/Z7/lesson6/data/post.txt","w");
end
img_gen3#(
.ACTIVE_IW (1920 ),
.ACTIVE_IH (1080 ),
.TOTAL_IW (2200 ),
.TOTAL_IH (1100 ),
.H_START (100 ),
.V_START (4 )
)u_img_gen3(
.clk (clk ),
.rst_n (rst_n ),
.vs (pre_vsync ),
.de (pre_de ),
.data ({pre_r,pre_g,pre_b})
);
rgb2ycbcr u1_rgb2ycbcr(
.clk (clk ), //系统时钟
.rst_n (rst_n ), //复位信号
.pre_hsync (pre_hsync ), //输入的场同步
.pre_vsync (pre_vsync ), //输入行同步
.pre_de (pre_de ), //数据有效信号
.pre_r (pre_r ), //输入像素数据
.pre_g (pre_g ),
.pre_b (pre_b ),
.post_hsync (post_hsync ), //输出行同步
.post_vsync (post_vsync ), //输出场同步
.post_de (post_de ), //输出数据有效信号
.post_y (post_y ), //输出y(亮度)分量
.post_cb (post_cb ), //输出蓝色色度分量
.post_cr (post_cr ) //输出红色色度分量
);
reg vs_r ;
always @(posedge clk)
if(rst_n == 0)
vs_r <= 1'b0;
else
vs_r <= post_vsync;
always @(posedge clk)
if(~post_vsync&&vs_r)
$stop;
else if(post_de == 1)
$fdisplay(outfile,"%h",post_y);
endmodule
3.2.2 算法的MATLAB验证
clc;
clear all;
RGB = imread('../img/1920x1080.bmp');
[row,col,chn] = size(RGB);
RGB = double(RGB);
for i = 1:row
for j = 1:col
for k = 1:chn
Y(i,j) = (77*RGB(i,j,1) + 150*RGB(i,j,2) + 29*RGB(i,j,3) )/256;
Cb(i,j) = (-43*RGB(i,j,1) - 85*RGB(i,j,2) + 128*RGB(i,j,3) +32768 )/256;
Cr(i,j) = (128*RGB(i,j,1) - 107*RGB(i,j,2) - 21*RGB(i,j,3) +32768 )/256;
end
end
end
matlab_Y = uint8(floor(Y));
a = textread('../data/post.txt','%s');
IMdec = hex2dec(a);
col = 1920;
row = 1080;
IM = reshape(IMdec,col,row);
fpga_Y = uint8(IM)';
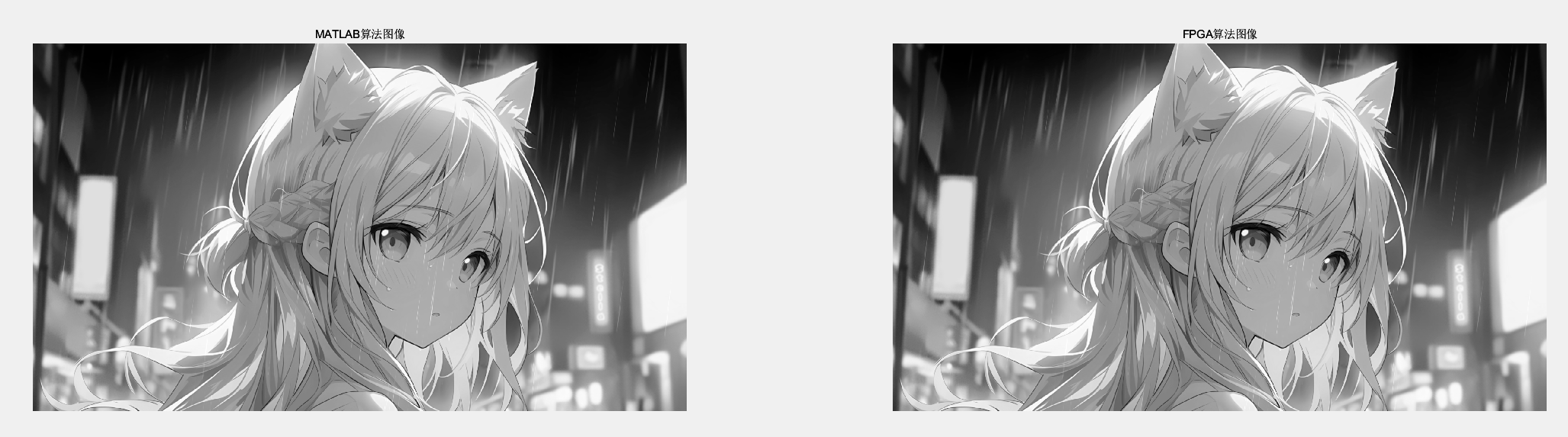
subplot(1,2,1)
imshow(matlab_Y),title('MATLAB算法图像');
subplot(1,2,2)
imshow(fpga_Y),title('FPGA算法图像');
sub = matlab_Y - fpga_Y;
min_sub = min(min(sub));
max_sub = max(max(sub));
最终MATLAB读取MolelSim的仿真数据以及MATLAN本身实现的rgb2ycbcr算法模块做对比。两者数据完全一样。

3.2.3 TXT转bmp
clear;
clc;
close all;
a = textread('../data/post.txt','%s');
IMdec = hex2dec(a);
col = 1920;
row = 1080;
IM = reshape(IMdec,col,row);
b = uint8(IM)';
imwrite(b,'../img/post.bmp');
imshow('../img/post.bmp');