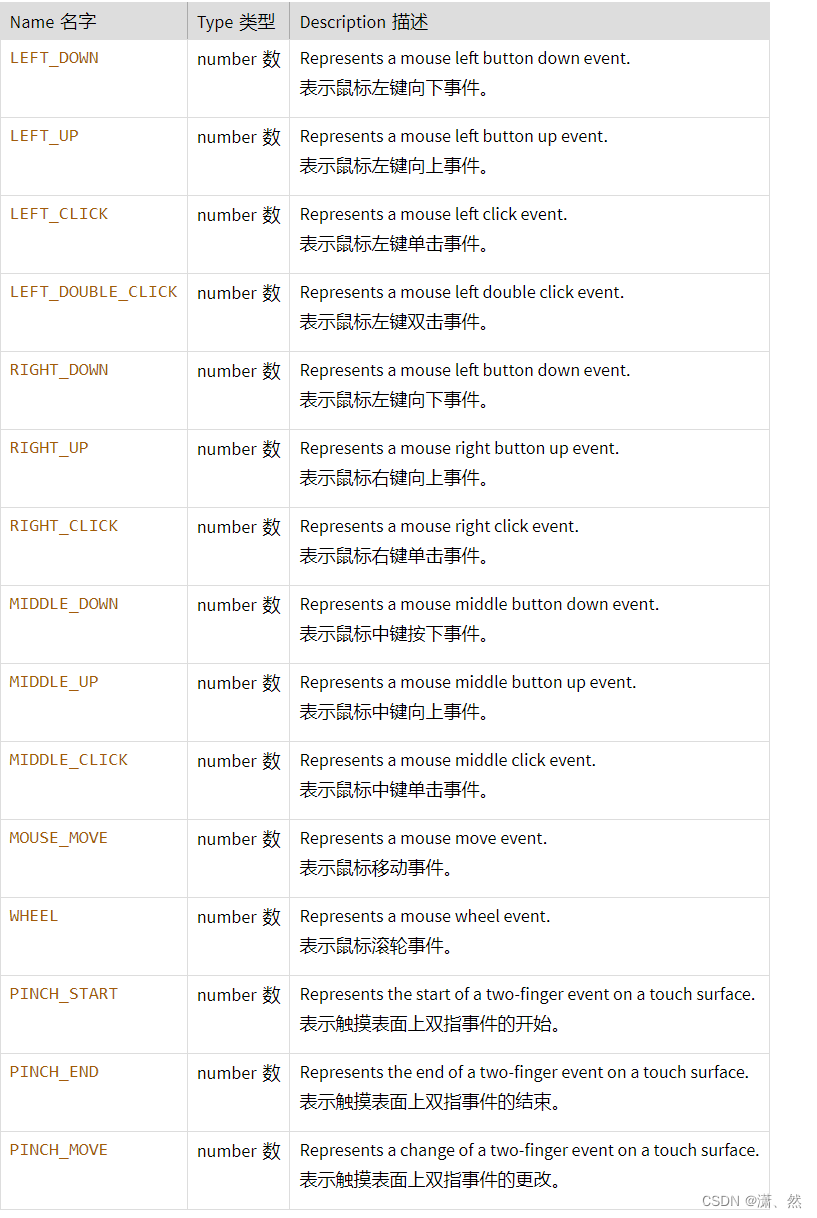
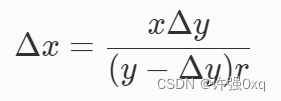解题思路:
快速幂 + 欧拉函数
快速幂比较常见于数据较大的取模场景,欧拉函数感觉还是有点抽象
注意:
取模的时候就不要简写了,例如:res = res * a % mod;不要写成res *= a % mod;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
static int mod = 998244353;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
long a = sc.nextLong();
long b = sc.nextLong();
// 如果a等于1,则直接输出0,因为任何数的0次方都是1
if (a == 1) System.out.println(0);
// 初始化结果res为a
long res = a, x = a;
// 循环,从2开始到x的平方根,检查x的因子
for (int i = 2; i <= Math.sqrt(x); i++) {
// 如果i是x的因子
if (x % i == 0) {
// 不断除以i,直到x不能被i整除
while (x % i == 0) x /= i;
// 根据欧拉定理,将res中所有i的因子替换为i-1
res = res / i * (i - 1);
}
}
// 如果x还有大于1的因子,重复上述操作
if (x > 1) res = res / x * (x - 1);
// 输出结果,为res乘以a的b-1次方,并对mod取模
System.out.println(res * qmi(a, b - 1) % mod);
}
// 快速幂运算方法,用于计算a的b次方模mod的值
private static long qmi(long a, long b) {
long res = 1;
while (b > 0) {
if ((b % 2) == 1) res = res * a % mod;
a = a * a % mod;
b /= 2;
}
return res % mod;
}
}