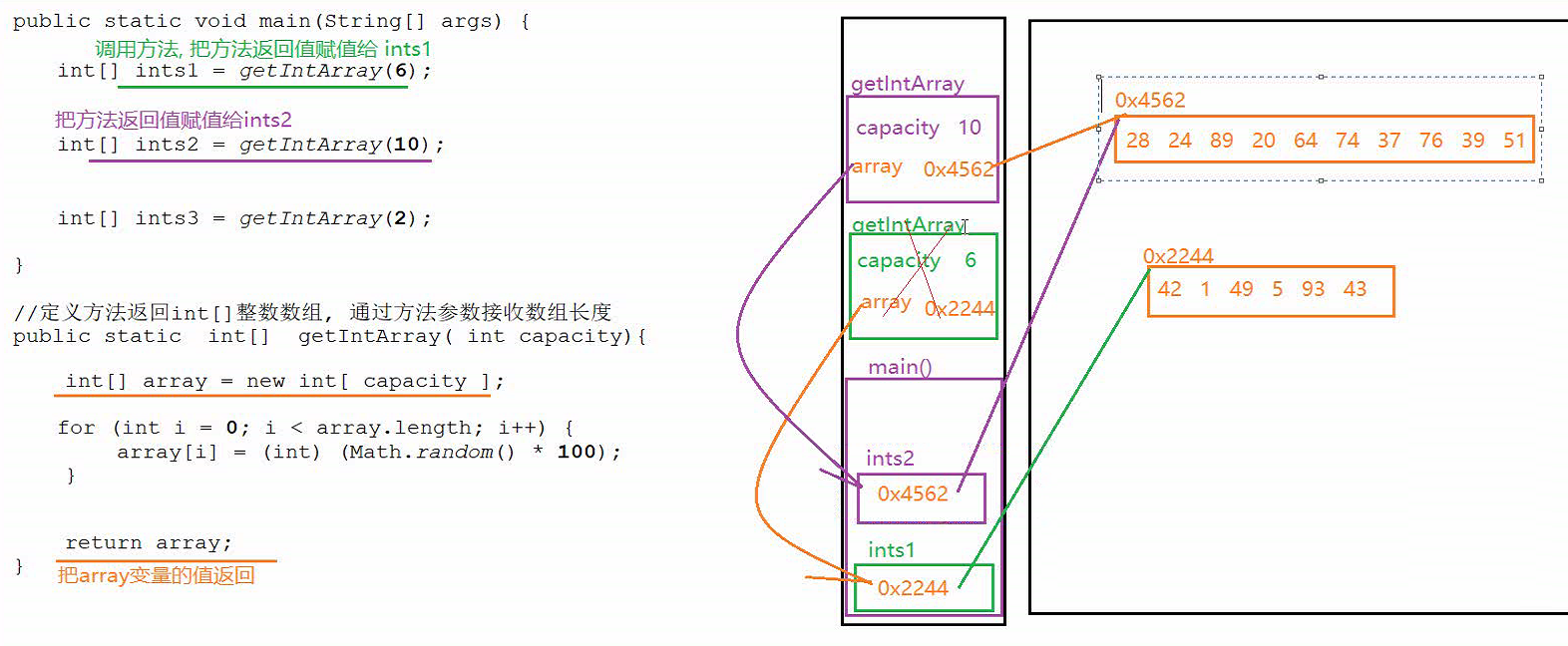
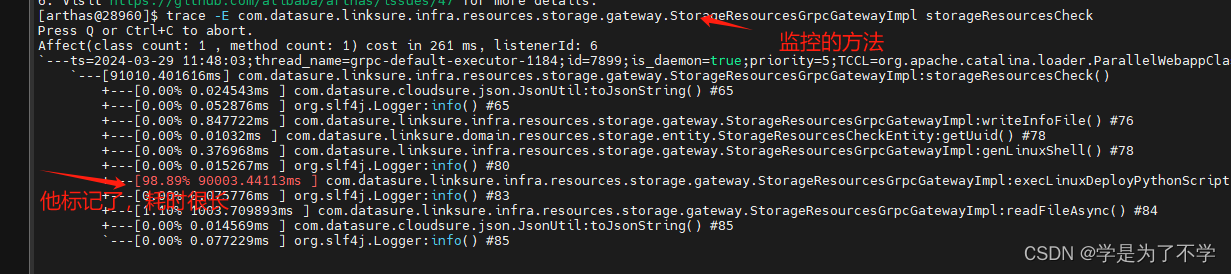
分析task装饰器原理
from celery.task import periodic_task
task源码如下
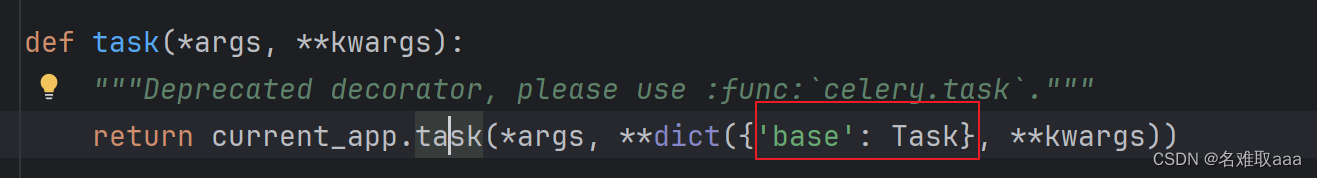
def task(*args, **kwargs):
"""Deprecated decorator, please use :func:`celery.task`."""
return current_app.task(*args, **dict({'base': Task}, **kwargs))
这里回调用celery.app.base.Celery.task
附上源码
def task(self, *args, **opts):
"""Decorator to create a task class out of any callable.
See :ref:`Task options<task-options>` for a list of the
arguments that can be passed to this decorator.
Examples:
.. code-block:: python
@app.task
def refresh_feed(url):
store_feed(feedparser.parse(url))
with setting extra options:
.. code-block:: python
@app.task(exchange='feeds')
def refresh_feed(url):
return store_feed(feedparser.parse(url))
Note:
App Binding: For custom apps the task decorator will return
a proxy object, so that the act of creating the task is not
performed until the task is used or the task registry is accessed.
If you're depending on binding to be deferred, then you must
not access any attributes on the returned object until the
application is fully set up (finalized).
"""
if USING_EXECV and opts.get('lazy', True):
# When using execv the task in the original module will point to a
# different app, so doing things like 'add.request' will point to
# a different task instance. This makes sure it will always use
# the task instance from the current app.
# Really need a better solution for this :(
from . import shared_task
return shared_task(*args, lazy=False, **opts)
def inner_create_task_cls(shared=True, filter=None, lazy=True, **opts):
_filt = filter
def _create_task_cls(fun):
if shared:
def cons(app):
return app._task_from_fun(fun, **opts)
cons.__name__ = fun.__name__
connect_on_app_finalize(cons)
if not lazy or self.finalized:
ret = self._task_from_fun(fun, **opts)
else:
# return a proxy object that evaluates on first use
ret = PromiseProxy(self._task_from_fun, (fun,), opts,
__doc__=fun.__doc__)
self._pending.append(ret)
if _filt:
return _filt(ret)
return ret
return _create_task_cls
if len(args) == 1:
if callable(args[0]):
return inner_create_task_cls(**opts)(*args)
raise TypeError('argument 1 to @task() must be a callable')
if args:
raise TypeError(
'@task() takes exactly 1 argument ({0} given)'.format(
sum([len(args), len(opts)])))
return inner_create_task_cls(**opts)
不用管上面的废话,重点是返回这个对象
ret = PromiseProxy(self._task_from_fun, (fun,), opts,
__doc__=fun.__doc__)
他是调用父类的实例化
class Proxy(object):
"""Proxy to another object."""
# Code stolen from werkzeug.local.Proxy.
__slots__ = ('__local', '__args', '__kwargs', '__dict__')
def __init__(self, local,
args=None, kwargs=None, name=None, __doc__=None):
object.__setattr__(self, '_Proxy__local', local)
object.__setattr__(self, '_Proxy__args', args or ())
object.__setattr__(self, '_Proxy__kwargs', kwargs or {})
if name is not None:
object.__setattr__(self, '__custom_name__', name)
if __doc__ is not None:
object.__setattr__(self, '__doc__', __doc__)
这个时候设置了三个属性_Proxy__local就是传递进来的self._task_from_fun,_Proxy__args设置为args,_Proxy__kwargs设置为kwargs,回到一开始代码看args和kwargs,kwargs里面有一个base=Task而这个Task就是celery的Task类,他里面有delay方法,Task类位置在这celery.app.task.Task源码太多就不附上了
当调用delay属性因为不存在,使用调用了魔术方法,他重写了对应的魔术方法如下
def __getattr__(self, name):
if name == '__members__':
return dir(self._get_current_object())
return getattr(self._get_current_object(), name)
这里从self._get_current_object()中获取name属性返回,这里的name就是delay
接下来分析self._get_current_object()
def _get_current_object(self):
"""Get current object.
This is useful if you want the real
object behind the proxy at a time for performance reasons or because
you want to pass the object into a different context.
"""
loc = object.__getattribute__(self, '_Proxy__local')
if not hasattr(loc, '__release_local__'):
return loc(*self.__args, **self.__kwargs)
try: # pragma: no cover
# not sure what this is about
return getattr(loc, self.__name__)
except AttributeError: # pragma: no cover
raise RuntimeError('no object bound to {0.__name__}'.format(self))
重点就是获取loc,loc = object.__getattribute__(self, '_Proxy__local')这里获取到这个属性就是上面在初始化设置的_task_from_fun方法,接下来return loc(*self.__args, **self.__kwargs),他使用type创建一个task类并返回,所以现在那个task方法变成了一个task类他就有delay方法,附上_task_from_fun方法源码
def _task_from_fun(self, fun, name=None, base=None, bind=False, **options):
if not self.finalized and not self.autofinalize:
raise RuntimeError('Contract breach: app not finalized')
name = name or self.gen_task_name(fun.__name__, fun.__module__)
base = base or self.Task
if name not in self._tasks:
run = fun if bind else staticmethod(fun)
task = type(fun.__name__, (base,), dict({
'app': self,
'name': name,
'run': run,
'_decorated': True,
'__doc__': fun.__doc__,
'__module__': fun.__module__,
'__header__': staticmethod(head_from_fun(fun, bound=bind)),
'__wrapped__': run}, **options))()
# for some reason __qualname__ cannot be set in type()
# so we have to set it here.
try:
task.__qualname__ = fun.__qualname__
except AttributeError:
pass
self._tasks[task.name] = task
task.bind(self) # connects task to this app
add_autoretry_behaviour(task, **options)
else:
task = self._tasks[name]
return task