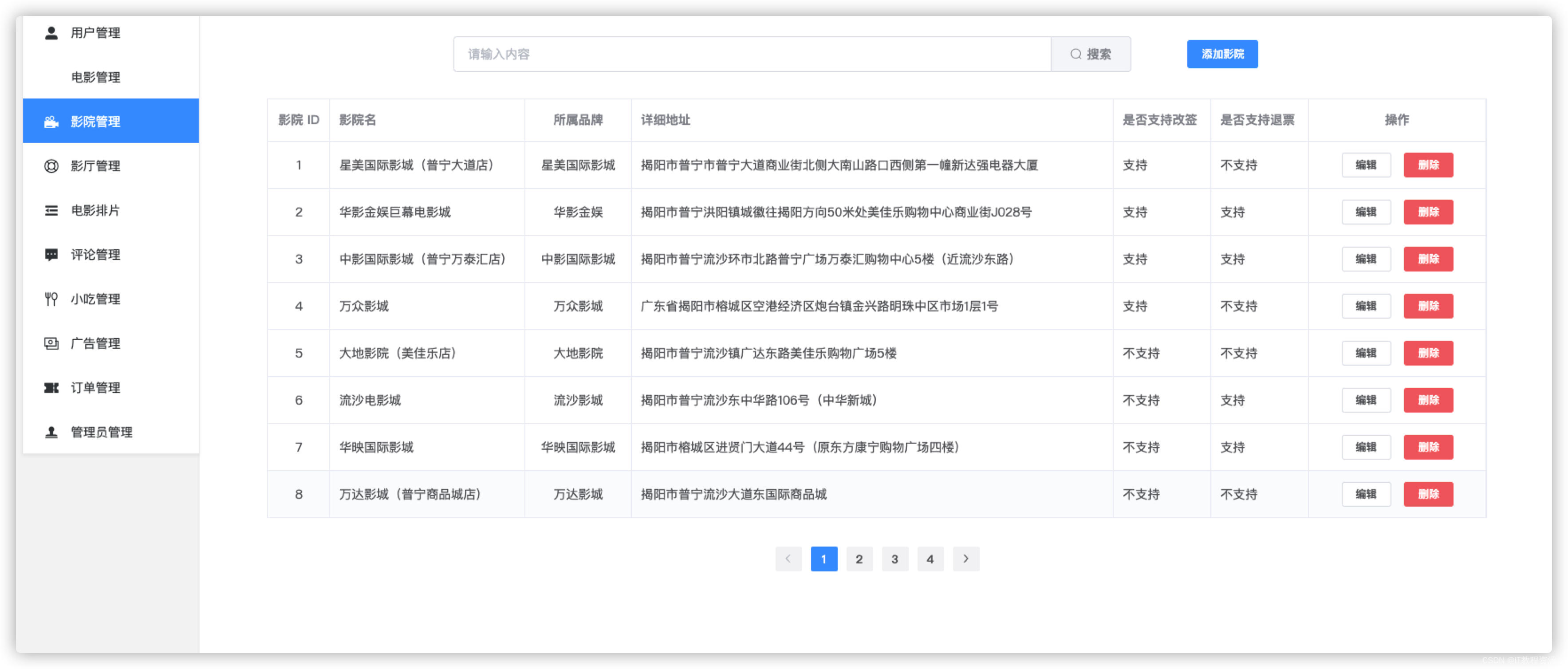
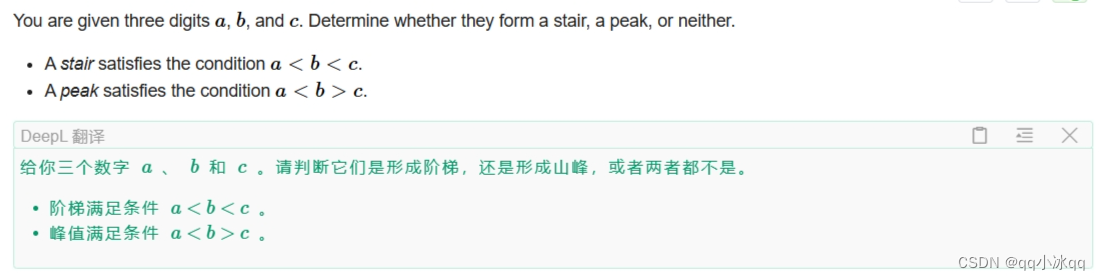
A. Stair, Peak, or Neither?(模拟)
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int t;
scanf("%d", &t);
int a, b, c;
while(t--){
scanf("%d%d%d", &a, &b, &c);
if(a < b && b < c) printf("STAIR\n");
else if(a < b && b > c) printf("PEAK\n");
else printf("NONE\n");
}
return 0;
}
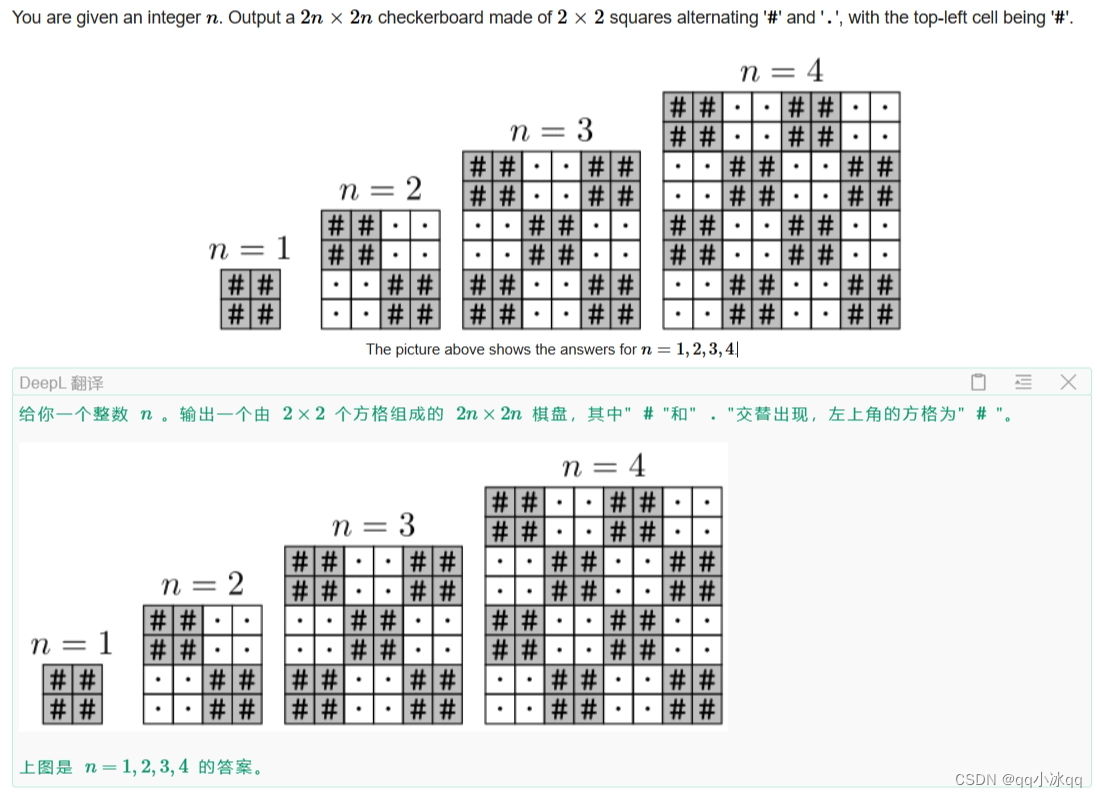
B. Upscaling(模拟)
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
char g[100][100];
int main(){
int t;
scanf("%d", &t);
while(t--){
int n;
scanf("%d", &n);
int f = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= 2 * n; i++){
for(int j = 1; j <= 2 * n; j += 2){
if(i % 2 == 0){
cout << g[i - 1][j] << g[i - 1][j];
} else {
if(f == 0){
if(g[i - 2][j] == '#'){
g[i][j] = '.';
g[i][j + 1] = '.';
cout << "..";
} else {
g[i][j] = '#';
g[i][j + 1] = '#';
cout << "##";
f = 1;
}
} else if(f == 1){
if(g[i - 2][j] == '.'){
g[i][j] = '#';
g[i][j + 1] = '#';
cout << "##";
} else {
g[i][j] = '.';
g[i][j + 1] = '.';
cout << "..";
f = 0;
}
}
}
}
cout << endl;
}
//cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}
C. Clock Conversion(模拟)

#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int t;
cin >> t;
for (int i = 0; i < t; i++) {
string s;
cin >> s;
int hours = stoi(s.substr(0, 2));
int minutes = stoi(s.substr(3, 2));
if (hours >= 12) {
if (hours > 12) {
hours -= 12;
}
cout << (hours < 10 ? "0" : "") << hours << ":" << (minutes < 10 ? "0" : "") << minutes << " PM" << endl;
} else {
if (hours == 0) {
hours = 12;
}
cout << (hours < 10 ? "0" : "") << hours << ":" << (minutes < 10 ? "0" : "") << minutes << " AM" << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
D. Product of Binary Decimals(dfs)

指数型枚举每一位是 0 还剩 1,然后除掉这个数,再继续搜索
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int a[20];
int f;
int check(int x) {
while (x) {
int digit = x % 10;
if (digit > 1) return 0;
x /= 10;
}
return 1;
}
void dfs(int u, int n) {
if (u > 5) {
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
sum = sum * 10 + a[i];
}
if(sum == 0 || sum == 1) return;
if (n % sum == 0){
if(n / sum == 1){
f = 1;
return;
}else{
dfs(1, n / sum);
}
}
return;
}
a[u] = 1;
dfs(u + 1, n);
a[u] = 0;
a[u] = 0;
dfs(u + 1, n);
a[u] = 0;
}
int main() {
int t;
cin >> t;
int n;
while (t--) {
f = 0;
cin >> n;
if(check(n)) f = 1;
else dfs(1, n);
if (f) cout << "YES" << endl;
else cout << "NO" << endl;
}
return 0;
}
E. Nearly Shortest Repeating Substring(思维)

因为最多只能有一个字符不同,那么每个长度的区间只需要枚举连续的两段,判断即可
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int st[50];
int main(){
int t, n;
string s;
cin>>t;
while(t--){
cin>>n>>s;
int res = n;
for(int len = 1; len <= n; len++){
if(n % len != 0) continue;
string m = s.substr(0, len);
int cnt1 = 0, cnt2 = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i+=len){
for(int j = 0; j < len; j++){
if(m[j] != s[i + j]) cnt1++;
}
}
m = s.substr(len, len + len);
for(int i = 0; i < n; i+=len){
for(int j = 0; j < len; j++){
if(m[j] != s[i + j]) cnt2++;
}
}
if(cnt1 <= 1 || cnt2 <= 1){
res = len;
break;
}
}
cout<<res<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
F. 0, 1, 2, Tree!(二叉树)


#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int t;
cin>>t;
int a, b, c;
while(t--){
cin>>a>>b>>c;
if(c != a + 1) cout<<-1<<endl;
else if(a + b + c == 1) cout<<0<<endl;
else{
// 存储当前父节点,子节点,树的高度
int cur = 1, ne = 0, res = 1;
for(int i = 0; i < a + b; i++){
// 如果父节点用完了,子节点就变成父节点
if(!cur){
swap(cur, ne);
res++;
}
cur--, ne++;
// 如果两个节点的还没用完,那就先用它
if(i < a) ne++;
}
cout<<res<<endl;
}
}
return 0;
}