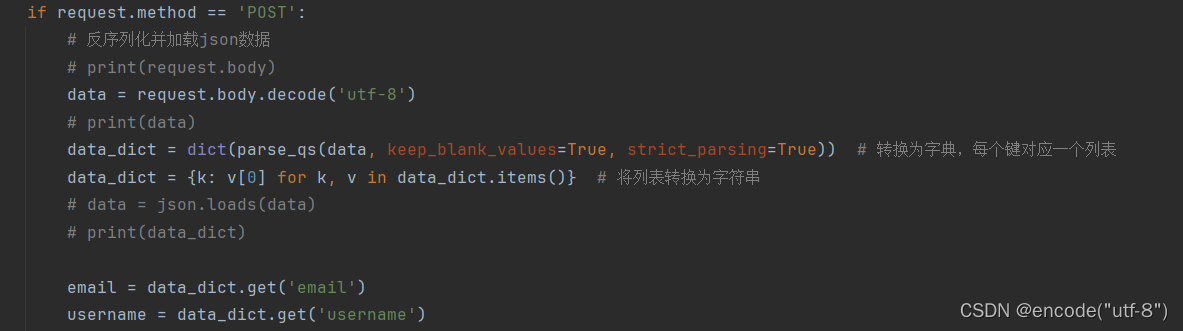
Here

解题思路
- 两个序列,保持顺序
- 对于代价的产生进行考虑
- 当添入一个大于当前序列最后值的数,代价加1,但下次判断标准变大
- 当添入一个小于当前序列最后值的数,代价不增,但下次判断标准变小
- 考虑形象化描述
- 将两个序列看作两个箱子,箱子有容积的限制
- 只能放入比它小的箱子,且下一次只能在新放入的箱子内再放
- 即只允许箱子套箱子,不允许箱子叠放
- 所以添入一个小于当前序列最后值的数,看作大箱子内放小箱子,容积变小
- 考虑贪心决策
- 对于两个箱子,进行比较,定义
为容积较大的,
较小
- 则能往
中放的,放
中,减少容积损失
- 不能放
能往
中放的,放
中
- 均不能放的,则将较小的箱子
删去,换为当前
大小的箱子,代价加1,减少容积损失
import java.io.*;
import java.math.BigInteger;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Objects;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.Stack;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
import java.util.TreeMap;
import java.util.TreeSet;
import java.util.Vector;
//implements Runnable
public class Main {
static long md=(long)998244353;
static long Linf=Long.MAX_VALUE/2;
static int inf=Integer.MAX_VALUE/2;
static int N=2000010;
static int n=0;
static int m=0;
static void solve() throws Exception{
AReader input=new AReader();
// Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in);
PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
String al="abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz";
char[] ac=al.toCharArray();
int T=input.nextInt();
while(T>0) {
T--;
n=input.nextInt();
int[] a=new int[n+1];
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i)a[i]=input.nextInt();
int num=0;
int b=inf;
int c=inf;
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i) {
if(a[i]<=c) {
c=a[i];
}else if(a[i]<=b) {
b=a[i];
}else {
num++;
c=a[i];
}
if(c>b) {
int t=c;
c=b;
b=t;
}
}
out.println(num);
}
out.flush();
out.close();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
solve();
}
// public static final void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// new Thread(null, new Tx2(), "线程名字", 1 << 27).start();
// }
// @Override
// public void run() {
// try {
// //原本main函数的内容
// solve();
//
// } catch (Exception e) {
// }
// }
static
class AReader{
BufferedReader bf;
StringTokenizer st;
BufferedWriter bw;
public AReader(){
bf=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
st=new StringTokenizer("");
bw=new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
}
public String nextLine() throws IOException{
return bf.readLine();
}
public String next() throws IOException{
while(!st.hasMoreTokens()){
st=new StringTokenizer(bf.readLine());
}
return st.nextToken();
}
public char nextChar() throws IOException{
//确定下一个token只有一个字符的时候再用
return next().charAt(0);
}
public int nextInt() throws IOException{
return Integer.parseInt(next());
}
public long nextLong() throws IOException{
return Long.parseLong(next());
}
public double nextDouble() throws IOException{
return Double.parseDouble(next());
}
public float nextFloat() throws IOException{
return Float.parseFloat(next());
}
public byte nextByte() throws IOException{
return Byte.parseByte(next());
}
public short nextShort() throws IOException{
return Short.parseShort(next());
}
public BigInteger nextBigInteger() throws IOException{
return new BigInteger(next());
}
public void println() throws IOException {
bw.newLine();
}
public void println(int[] arr) throws IOException{
for (int value : arr) {
bw.write(value + " ");
}
println();
}
public void println(int l, int r, int[] arr) throws IOException{
for (int i = l; i <= r; i ++) {
bw.write(arr[i] + " ");
}
println();
}
public void println(int a) throws IOException{
bw.write(String.valueOf(a));
bw.newLine();
}
public void print(int a) throws IOException{
bw.write(String.valueOf(a));
}
public void println(String a) throws IOException{
bw.write(a);
bw.newLine();
}
public void print(String a) throws IOException{
bw.write(a);
}
public void println(long a) throws IOException{
bw.write(String.valueOf(a));
bw.newLine();
}
public void print(long a) throws IOException{
bw.write(String.valueOf(a));
}
public void println(double a) throws IOException{
bw.write(String.valueOf(a));
bw.newLine();
}
public void print(double a) throws IOException{
bw.write(String.valueOf(a));
}
public void print(char a) throws IOException{
bw.write(String.valueOf(a));
}
public void println(char a) throws IOException{
bw.write(String.valueOf(a));
bw.newLine();
}
}
}