一、排序
sort简介
- sort函数包含在头文件<algorithm>中。
- 在使用前需要#include <algorithm>或使用万能头文件。
- sort是C++标准库中的一个函数模板,用于对指定范围内的元素进行排序。
- sort算法使用的是快速排序(QuickSort)或者类似快速排序的改进算法,具有较好的平均时间复杂度, 一般为O(nlogn)。
sort用法
sort(起始地址,结束地址的下一位,*比较函数);
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
//#include <bits /stdc++.h>
using namespace std ;
int main()
{
int a[1000];
int n;
cin >> n;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++ )cin>>a[i];
sort(a + 1,a + n + 1);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)cout<<a[i]<<' ';
}
sort(起始地址,结束地址的下一位,*比较函数);
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
//#include <bits /stdc++.h>
using namespace std ;
int main()
{
vector<int> v = {5, 1, 3, 9, 11};
sort(v.begin(),v.end());
for(int i = 0; i < v.size(); ++i)cout<<v[i]<<" ";
}
自定义比较函数
- sort默认使用小于号进行排序,如果想要自定义比较规则,
- 可以传入第三个参数,可以是函数或lambda表达式。
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
//#include <bits /stdc++.h>
using namespace std ;
bool cmp(const int &u, const int &v)
{
return u > v;
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(0),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);
vector<int> v = {5, 1, 3, 9, 11};
sort(v.begin(),v.end(),cmp);
for(int i = 0; i < v.size(); ++i)cout<<v[i]<<" ";
}#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
//#include <bits /stdc++.h>
using namespace std ;
bool cmp(const int &u, const int &v)
{
return u > v;
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(0),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);
vector<int> v = {5, 1, 3, 9, 11};
sort(v.begin(),v.end(),[](const int &u,const int &v){return u > v;});
for(int i = 0; i < v.size(); ++i)cout<<v[i]<<" ";
}
二、最值查找函数
min 和 max函数
min(a, b)返回a和b中较小的那个值,只能传入两个值,或传入一个列表。
例如:
min(3, 5)= 3
min({1,2,3, 4})= 1
max(a, b)返回a和b中较大的那个值,只能传入两个值,或传入一个列表。
例如:
max(7, 5)= 7
min({1,2,3, 4})= 4
时间复杂度为O(1),传入参数为数组时时间复杂度为O(n), n为数组大小。
min,max函数是在取最值操作时最常用的操作。
min_ element和max_ element
min_ element(st, ed)返回地址[st, ed)中最小的那个值的地址(迭代器) ,传入参数为两个地址或迭代器。
max_ element(st, ed)返回地址[st, ed)中最大的那个值的地址(迭代器),传入参数为两个地址或迭代器。
时间复杂度均为O(n), n为数组大小(由传入的参数决定)。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(void) {
vector<int> v = {5,1,3,9,11}
cout<< *max_element(v.begin(),v.end())<<endl;
return 0;
}
nth_ element函数
nth_ element(st, k, ed)
进行部分排序,返回值为void()
传入参数为三个地址或迭代器。其中第二个参数位置的元素将处于正确位置,其他位置元素的顺序可能是任意的,但前面的都比它小,后面的都比它大。
时间复杂度O(n)。
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
int main(void) {
vector<int> v = {5,1,3,9,11};
nth_element(v.begin(),v.begin()+3, v.end());
for (auto &i : v)cout<<i<<" ";
return 0;
}三、二分查找
二分查找的前提
库函数只能对数组进行二分查找。
对一个数组进行二分查找的前提是这个数组中的元素是单调的,一般为单调不减,当然如果是单调不增也可以(需要修改比较函数)。例如:
[1, 5,5,9,18]是单调的[1,9,9,7,15]不是单调的[9,8,8,7,7,1]是单调的
binary_search 函数
binary_search是C++标准库中的一个算法函数,用于在已排序的序列(例如数组或容器)中查找特定元素。
它通过二分查找算法来确定序列中是否存在目标元素。
函数返回一个bool值,表示目标元素是否存在于序列中。如果需要获取找到的元素的位置,可以使用
std:lower_bound函数或std:upper_bound函数。
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
int main(void) {
vector<int> v = {1,2,3,4,5};
int target = 5;
bool found = binary_search(v.begin(), v.end(), target);
if (found) cout<< "yes";
else cout<<"not exist";
return 0;
}lower_bound 和 upper_bound
前提:数组必须为非降序。
如果要在非升序的数组中使用,可以通过修改比较函数实现(方法与sort自定义比较函数类似)。lower_bound(st, ed,x)返回地址[st, ed)中第一个小于等于x的元素的地址。
upper_bound(st, ed,x)返回地址[st, ed)中第一个大于x的元素的地址。如果不存在则返回最后一个元素的下一个位置,在vector中即end()。
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
int main(void) {
vector<int> v = {1,5,7,3,11,8,9};
sort(v.begin(), v.end()) ;
cout<< *lower_bound(v.begin(), v.end(), 8) <<endl;
return 0;
}四、大小写转换
islowerlisupper 函数
slower和isupper是C++标准库中的字符分类函数,用于检查一个字符是否为小写字母或大写字母。islower和isupper函数需要包含头文件<cctype>,也可用万能头包含。
函数返回值为bool类型。
tolowerl/toupper函数
tolower(char ch)可以将ch转换为小写字母,如果ch不是大写字母则不进行操作。toupper()同理。
ascll 码
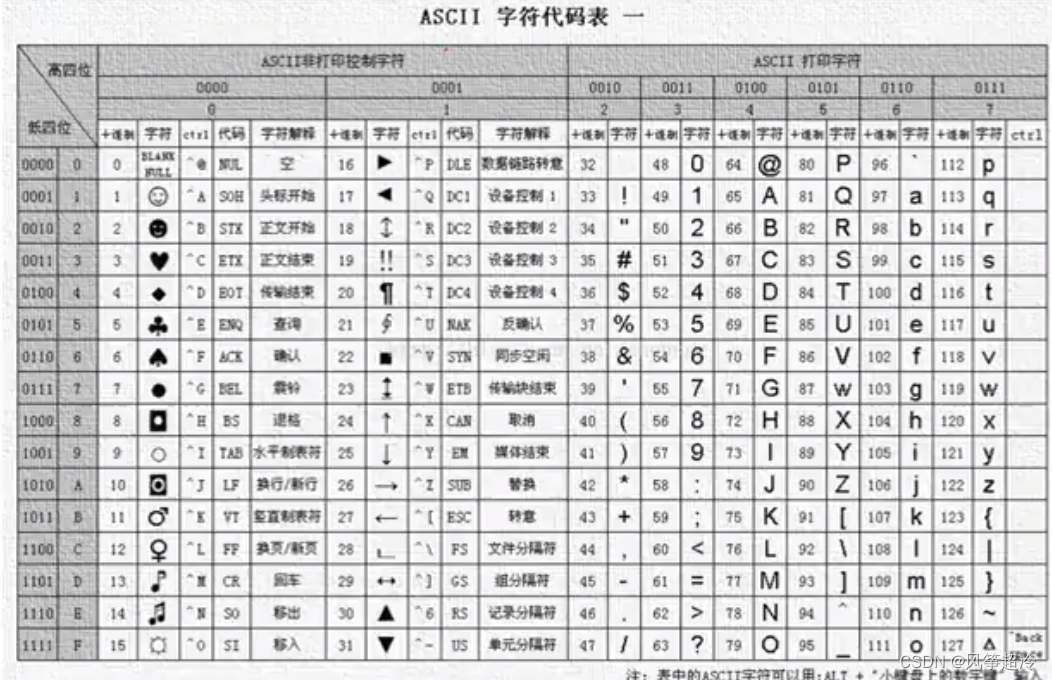
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
void ConvertCh(char &i){
if('a' < i && i < 'z') i = i - 'a' + 'A';
else if ('A' <= i && i > 'Z') i = i - 'A' + 'a';
}
int main(void) {
string s;
cin>>s;
for (auto &i : s) ConvertCh(i);
cout<< s;
return 0;
}五、next_permutation() 函数
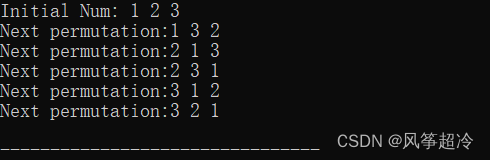
next_permutation函数用于生成当前序列的下一个排列。它按照字典序对序列进行重新排列,如果存在下一个排列,则将当前序列更改为下一个排列,开返回true;如来刖序列一经是最后一个排列,则将序列更改为第一个排列,并返回false。
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
int main(void) {
vector<int> nums = {1, 2, 3};
cout<<"Initial Num:"<<" ";
for(int num : nums){
cout<< num <<" ";
}
cout<< endl;
while (next_permutation(nums.begin(),nums.end())){
cout << "Next permutation:";
for(int num: nums){
cout << num <<" ";
}
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}
preu_permutation()函数
preu_permutation函数与next_permutation函数相反,它用于生成当前序列的上一个排列。它
按照字典序对序列进行重新排列,如果存在上一个排列,则将当前序列更改为上一个序列,并返回true;如果当前序列已经是第一个排列,则将序列更改为最后一个排列,并返回false。
六、memset() 函数
memset()是一个用于设置内仔块值的函数。
它的原型定义在<cstring>头文件中,函数的声明如下:
void*memset(void* ptr,int value,size_t num);
memset()函数接受三个参数:
1.ptr:指向要设置值的内存块的指针。2.value:要设置的值,通常是一个整数(8位二进制数)。3.num:要设置的字节数。
memset()函数将ptr指向的内存块的前num个字节设置为value的值。它返回
一个指向ptr的指针。
memset()函数通常用于初始化内存块,将其设置为特定的值。
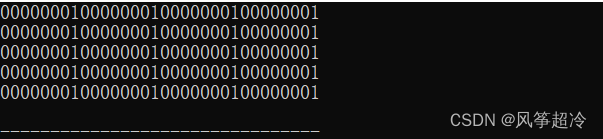
例如,如果要将一个整型数组的所有元素设置为0,可以使用memset()函数如下
int arr[10j;
memset(arr,0,sizeof(arr));#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
#include<cstring>
#include<bitset>
using namespace std;
int main(void) {
int a[5];
memset(a, 1, sizeof(a));
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++) cout<<bitset<32>(a[i])<<endl;
return 0;
}
七、swap() 函数
swap(T &a,T &b)函数接受两个参数:
1.a:要交换值的第一个变量的引用。2.b:要交换值的第二个变量的引用。
swap()函数通过将第一个变量的值存储到临时变量中,然后将第二个变量的值赋给第一个变量,最后将临时变量的值赋给第二个变量,实现两个变量值的交换。
swap()函数可以用于交换任意类型的变量,包括基本类型(如整数、浮点数等)和自定义类型(如结构体、类对象等))。
八、reverse() 函数
reverse()是一个用于反转容器中元素顺序的函数。
它的原型定义在<algorithm>头文件中,函数的声明如下:
template<class BidirIt>
void reverse(BidirIt first,Bidirit last);
reverse()函数接受两个参数:
1.first:指向容器中要反转的第一个元素的迭代器。
2.last:指向容器中要反转的最后一个元素的下一个位置的迭代器。reverse()函数将[first, last)范围内的元素顺序进行反转。
也就是说,它会将[first, last)范围内的元素按相反的顺序重新排列。reverse()函数可用于反转各种类型的容器,包括数组、向量、链表等。
以下是一个示例,展示如何使用reverse()函数反转一个整型向量的元素顺序:
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
#include<cstring>
#include<bitset>
using namespace std;
int main(void) {
vector<int> v = {1,2,3};
reverse(v.begin(), v.end());
for(int num : v){
cout<< num <<" ";
}
cout<< endl;
return 0;
}在上述示例中,std:reverse(vec.begin().
vec.end())将整型向量vec中的元素顺序进行反转。最终输出的结果是54321。
需要注意的是,reverse()函数只能用于支持双向迭代器的容器,因为它需要能够向前和向后遍历容器中的元素。对于只支持单向迭代器的容器(如前向链表),无法使用reverse()函数进行反转。
九、unique() 函数
unique()是一个用于去除容器中相邻重复元素的函数。它的原型定义在<algorithm>头文件中,函数的声明如下:
unique(first, last) 函数接受两个参数:
1.first:指向容器中要去重的第一个元素的迭代器。
2.last:指向容器中要去重的最后一个元素的下一个位置的迭代器。
unique()函数将[first, last)范围内的组邻重复元素去除,并返回一个指向去重后范围的尾后迭代器去重后的范围中只保留了第一个出现的元素,后续重复的元素都被移除。
unique()函数可用于去除各种类型的容器中的相邻重复元素,包括数组、向量、链表等。





![ElasticSearch文档批量操作[ES系列] - 第503篇](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/4872bc1ecd01a0d1df4022cb7a9ef9ac.png)