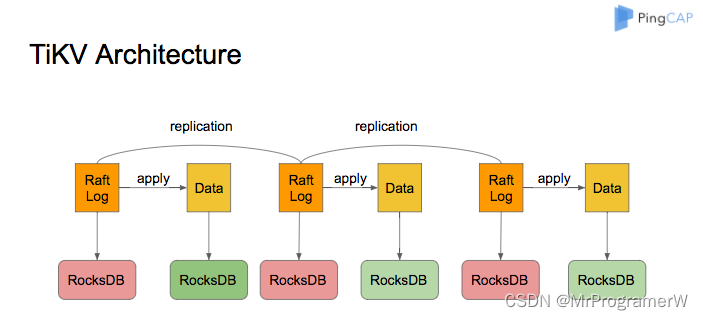
一、微前端
微前端是指存在于浏览器中的微服务,其借鉴了后端微服务的架构理念,将微服务的概念扩展到前端。即将一个大型的前端应用拆分为成多个模块,每个微前端模块可以有不同的团队开发并进行管理,且可以自主选择框架,以及有自己的仓库,可以独立部署上线。
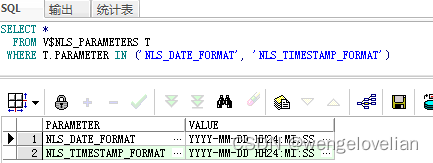
(1)未使用微服务之前的项目架构
(2)使用微服务之前的项目架构
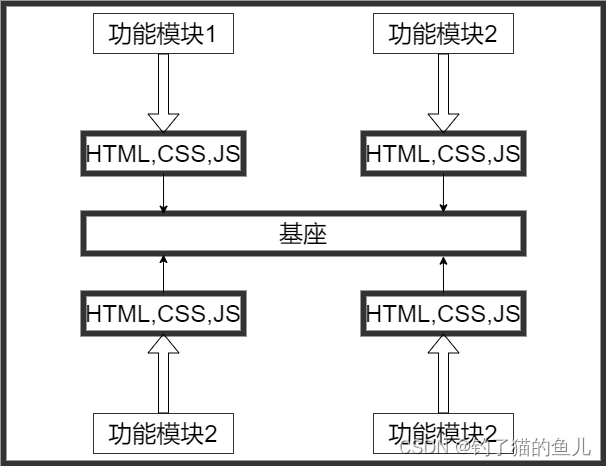
二、微前端的优点
团队自治
在公司里面,一般团队都是按照业务划分的,在没有微前端的时候,如果几个团队维护一个项目肯定会遇到一些冲突,比如合并代码的冲突,上线时间的冲突等。应用了微前端之后,就可以将项目根据业务模块拆分成几个小的模块,每个模块都有不同的团队去维护,单独开发,单独部署上线,这样团队可以实现自治,减少甚至不会出现和其他团队冲突的情况。
兼容老项目
如果公司中存在古老的或者其他巨石项目,但是又不想用旧的技术栈去为维护,选择使用微服务的方式去拆分项目是一个很好的选择。
跨技术栈
如果我们的微前端系统重需要新增一个业务模块时,只需要单独的新建一个项目,至于项目采用技术栈,完全可以有团队自己去定义,即使和其他模块用不同的技术栈也不会有任务问题。

三、微前端示例
需求:做一个vue2的微前端,以vue2为主应用,其他技术栈为子应用。
step1:创建主应用(基座)
vue create main-app
step2:主应用安装qiankun
npm install qiankun
step3:创建main-app.js
// 1.要加载的子应用列表
const microApps = [
{
name: 'test-web', // 子应用名称
entry: 'http://localhost:8081/', //子应用运行地址
activeRule: '/test-web',//匹配的路由
sanbox: true //解决css冲突
},
]
const apps = microApps.map(item => {
return {
...item,
container: '#test-web', // 子应用挂载的div
props: {
routerBase: item.activeRule // 下发基础路由
}
}
})
export default apps
step4:引入main-app.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import router from './router'
import store from './store'
Vue.config.productionTip = false
import { registerMicroApps, start } from 'qiankun';
import mainApp from './main-app'
// 2.注册子应用
registerMicroApps(mainApp, {
beforeLoad: app => {
console.log('before load app.name====>>>>>', app.name)
},
beforeMount: [
app => {
console.log('[LifeCycle] before mount %c%s', 'color: green;', app.name)
}
],
afterMount: [
app => {
console.log('[LifeCycle] after mount %c%s', 'color: green;', app.name)
}
],
afterUnmount: [
app => {
console.log('[LifeCycle] after unmount %c%s', 'color: green;', app.name)
}
]
})
// 3.启动微服务
start()
new Vue({
router,
store,
render: h => h(App)
}).$mount('#app')
step5:配置主应用路由
在main-app/src文件夹下添加qiankun文件夹,并且添加index.vue文件作为入口文件
<template>
<div id="test-web"></div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
mounted() {},
};
</script>
<style>
#test-web {
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
}
</style>
router.js
import Vue from "vue";
import VueRouter from "vue-router";
import HomeView from "../views/HomeView.vue";
import layout from '../views/qiankun/index.vue'
Vue.use(VueRouter);
const routes = [
{
path: "/",
name: "home",
component: HomeView,
},
{
path: "/about",
name: "about",
// route level code-splitting
// this generates a separate chunk (about.[hash].js) for this route
// which is lazy-loaded when the route is visited.
component: () =>
import(/* webpackChunkName: "about" */ "../views/AboutView.vue"),
},
{
path: "/test-web/*",
meta: 'test-web',
component: layout
}
];
const router = new VueRouter({
mode: "history",
base: process.env.BASE_URL,
routes,
});
export default router;
step6:创建子应用
vue create sub-app
step7:修改子应用main.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import router from './router'
import store from './store'
//引入public-path.js
// import "../public-path";
Vue.config.productionTip = false
// new Vue({
// router,
// store,
// render: h => h(App)
// }).$mount('#app')
// 判断是否在qiankun的运行环境下,非qiankun运行环境下单独运行
if (window.__POWERED_BY_QIANKUN__) {
// eslint-disable-next-line no-undef
__webpack_public_path__ = window.__INJECTED_PUBLIC_PATH_BY_QIANKUN__;
}
let instance = null;
function render(props = {}) {
const { container } = props;
console.log(11111111111111, window.__POWERED_BY_QIANKUN__, '字段值')
instance = new Vue({
router,
store,
render: h => h(App),
}).$mount(container ? container.querySelector('#app') : '#app', true); //开启沙箱
}
if (!window.__POWERED_BY_QIANKUN__) {
console.log('独立运行')
render();
}
function storeTest(props) {
props.onGlobalStateChange &&
props.onGlobalStateChange(
(value, prev) => console.log(`[onGlobalStateChange - ${props.name}]:`, value, prev),
true,
);
props.setGlobalState &&
props.setGlobalState({
ignore: props.name,
user: {
name: props.name,
},
});
}
// 各个生命周期,只会在微应用初始化的时候调用一次,下次进入微应用重新进入是会直接调用mount钩子,不会再重复调用bootstrap
export async function bootstrap() {
console.log('111111111111 [vue] vue app bootstraped');
}
// 应用每次进入都会调用mount方法,通常在这里触发应用的渲染方法
export async function mount(props) {
console.log('11111111111 [vue] props from main framework', props);
storeTest(props);
render(props);
}
// 应用每次切除/注销会调用的方法,在这里会注销微应用的应用实例
export async function unmount() {
instance.$destroy();
instance.$el.innerHTML = '';
instance = null;
}
step8:注册子应用路由
<!--子应用页面代码-->
<template>
<div class="sub-app">我是子应用页面11</div>
</template>
<style lang="scss" scoped>
.sub-app {
cursor: pointer;
background-color: aqua;
}
</style>
import Vue from 'vue'
import VueRouter from 'vue-router'
import HomeView from '../views/HomeView.vue'
Vue.use(VueRouter)
const routes = [
{
path: '/',
name: 'home',
component: HomeView
},
{
path: '/about',
name: 'about',
// route level code-splitting
// this generates a separate chunk (about.[hash].js) for this route
// which is lazy-loaded when the route is visited.
component: () => import(/* webpackChunkName: "about" */ '../views/AboutView.vue')
},
{
path: '/test',
name: 'test',
// route level code-splitting
// this generates a separate chunk (about.[hash].js) for this route
// which is lazy-loaded when the route is visited.
component: () => import(/* webpackChunkName: "about" */ '../views/subapp/index.vue')
},
{
path: '/testtwo',
name: 'testtwo',
// route level code-splitting
// this generates a separate chunk (about.[hash].js) for this route
// which is lazy-loaded when the route is visited.
component: () => import(/* webpackChunkName: "about" */ '../views/subapp/two.vue')
},
]
const router = new VueRouter({
mode: 'history',
base: window.__POWERED_BY_QIANKUN__ ? '/test-web/' : '/',
routes
})
export default router
step9:修改vite.config.js
const { name } = require('./package.json')
module.exports = {
publicPath: '/', // 打包相对路径
devServer: {
port: 8081, // 运行端口号
headers: {
'Access-Control-Allow-Origin': '*' // 防止加载时跨域
}
},
chainWebpack: config => config.resolve.symlinks(false),
configureWebpack: {
output: {
library: `${name}-[name]`,
libraryTarget: 'umd', // 把微应用打包成 umd 库格式
// webpack5.0以上版本使用如下字段
chunkLoadingGlobal: `webpackJsonp_${name}`
}
}
}
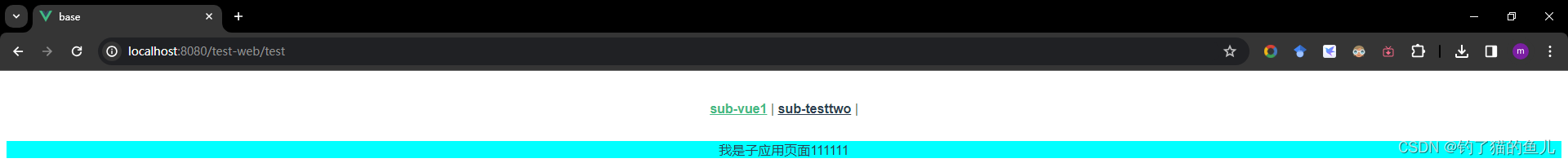
step10:修改引用主应用和子应用
主应用的App.vue添加如下代码
<template>
<div id="app">
<div id="nav">
<router-link to="/test-web/test">sub-vue1</router-link> |
<router-link to="/test-web/testtwo">sub-testtwo</router-link> |
</div>
<router-view />
</div>
</template>
<style lang="scss">
#app {
font-family: Avenir, Helvetica, Arial, sans-serif;
-webkit-font-smoothing: antialiased;
-moz-osx-font-smoothing: grayscale;
text-align: center;
color: #2c3e50;
}
#nav {
padding: 30px;
a {
font-weight: bold;
color: #2c3e50;
&.router-link-exact-active {
color: #42b983;
}
}
}
</style>
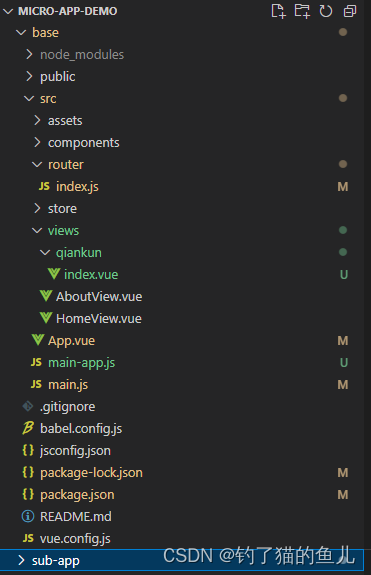
step11:项目目录
四、微前端的问题
样式隔离

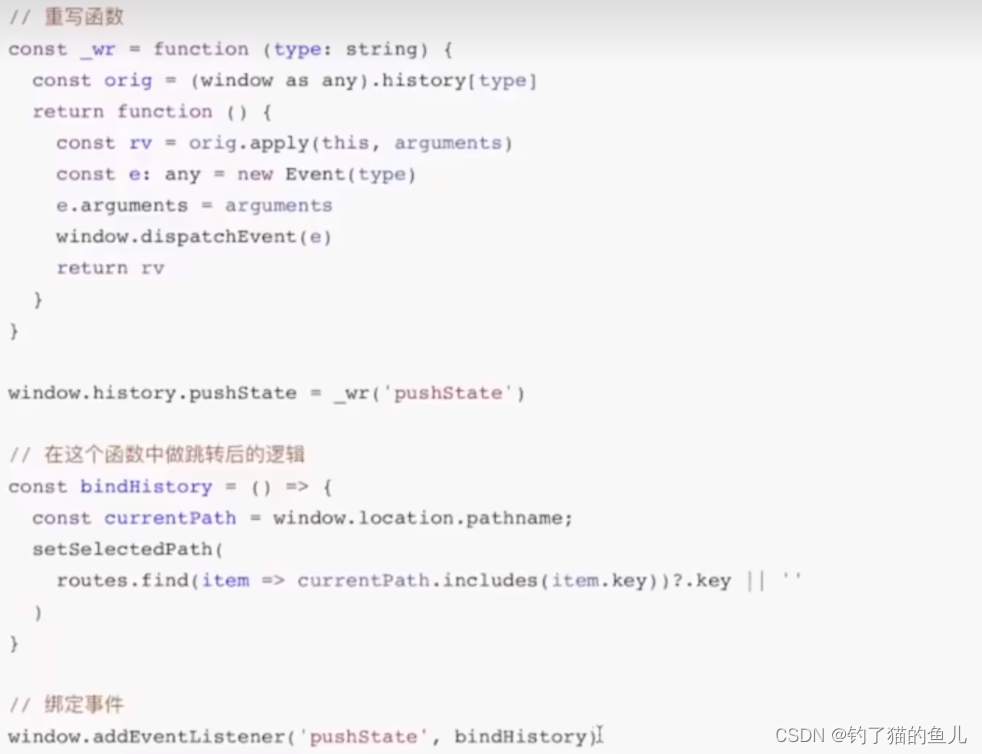
具体方案:在基座中复写并监听history.pushState()方法并做相应的跳转逻辑
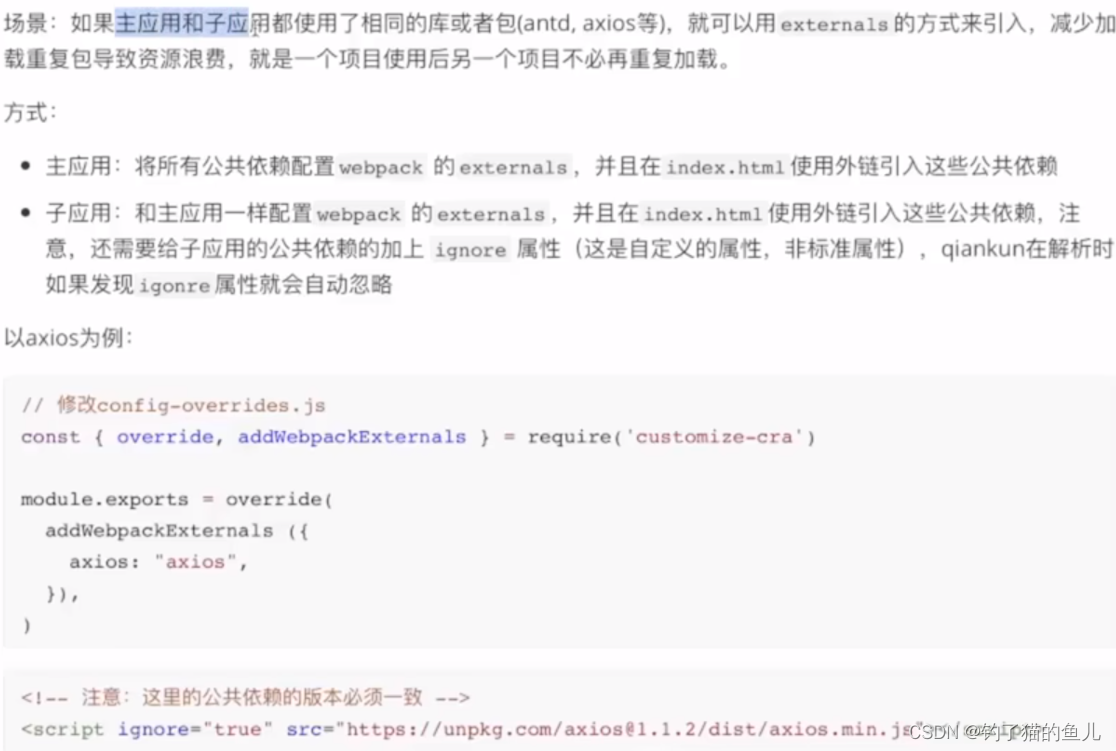
公共依赖加载
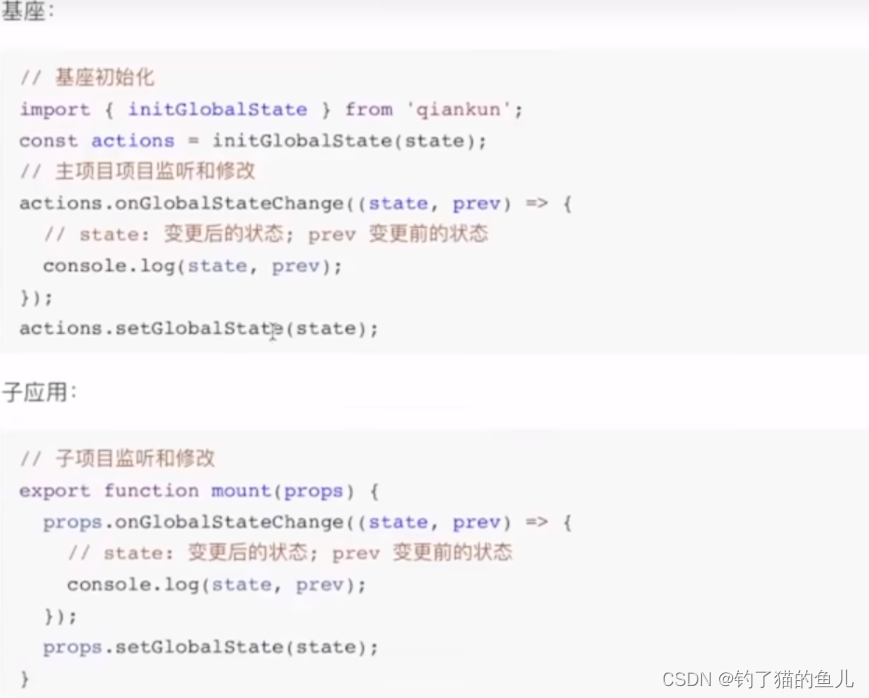
全局状态管理
一般来说,各个子应用是通过业务来划分的,不同业务线应该降低耦合度,尽量去避免通信,但是如果涉及到一些公共的状态或者操作,qinakun也是支持的。
qiankun提供了一个全局的GlobalState来共享数据,基层初始化之后,子应用可以监听到这个数据的变化,也能提交到这个数据。