概述
● 一个int成员变量 state 表示同步状态
● 通过内置的FIFO队列来完成资源获取线程的排队工作
属性
AbstractQueuedSynchronizer属性
/**
* 同步队列的头节点
*/
private transient volatile Node head;
/**
* 同步队列尾节点,enq 加入
*/
private transient volatile Node tail;
/**
* 同步状态
*/
private volatile int state;
/**
* 获取状态
*/
protected final int getState() {
return state;
}
/**
* 设置状态
*/
protected final void setState(int newState) {
state = newState;
}
/**
* CAS 设置状态
*/
protected final boolean compareAndSetState(int expect, int update) {
// See below for intrinsics setup to support this
return unsafe.compareAndSwapInt(this, stateOffset, expect, update);
}
/**
* The number of nanoseconds for which it is faster to spin
* rather than to use timed park. A rough estimate suffices
* to improve responsiveness with very short timeouts.
*/
static final long spinForTimeoutThreshold = 1000L;
Node 节点属性
static final class Node {
/** 共享节点 */
static final Node SHARED = new Node();
/** 独占节点 */
static final Node EXCLUSIVE = null;
// 在同步队列中等待的线程等待超时或被中断, 需要从同步队列中取消等待, 状态不会变化 |
static final int CANCELLED = 1;
// 后继节点处于等待状态, 当前节点释放了同步状态或者被取消, 通知后续节点, 使后续节点得以运行
static final int SIGNAL = -1;
// 值为-2, 节点在等待队列, 当其他线程 signal(),从等待队列中移除到同步队列中 |
static final int CONDITION = -2;
// 值为-3, 下一次共享获取同步状态将会无条件传播下去
static final int PROPAGATE = -3;
/**
* 节点初始状态,初始化为0
*/
volatile int waitStatus;
/**
* 前一个节点
*/
volatile Node prev;
/**
* 后一个节点
*/
volatile Node next;
/*
* 节点的线程
*/
volatile Thread thread;
/**
* 下一个等待者
*/
Node nextWaiter;
/**
* 是否是共享节点
*/
final boolean isShared() {
return nextWaiter == SHARED;
}
/**
* 前一个节点
*/
final Node predecessor() throws NullPointerException {
Node p = prev;
if (p == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
else
return p;
}
Node() { // Used to establish initial head or SHARED marker
}
Node(Thread thread, Node mode) { // Used by addWaiter
this.nextWaiter = mode;
this.thread = thread;
}
Node(Thread thread, int waitStatus) { // Used by Condition
this.waitStatus = waitStatus;
this.thread = thread;
}
}
常用方法
同步状态的三个方法:
● getState() 获取同步状态
● setState(int newState) 设置当前同步状态
● compareAndSetState(int expect, int update) CAS设置同步状态,原子操作
AbstractQueuedSynchronizer可重写的方法:
| 方法名称 | 方法描述 |
|---|---|
| boolean tryAcquire(int arg) | 独占式获取同步状态,查询当前状态是否符合预期,并且CAS设置 |
| boolean tryRelease(int arg) | 独占式释放同步状态,释放后,等待获取同步状态的线程有机会获取同步状态 |
| int tryAcquireShared(int arg) | 共享式获取同步状态,如果大于等于0,表示获取成功 |
| boolean tryReleaseShared(int arg) | 共享式释放同步状态 |
| boolean isHeldExclusively() | 在独占模式下被线程占用,表示是否被当前线程独占 |
AbstractQueuedSynchronizer提供的模版方法
| 方法名称 | 方法描述 |
|---|---|
| boolean acquire(int arg) | 独占式获取同步状态, 成功返回, 失败队列等待, 调用tryAcquire() |
| boolean acquireInterruptibly(int arg) | acquire 相同, 但是可以中断 |
| int tryAcquireNanos(int arg, long nanos) | acquireInterruptibly 基础上增加了超时限制, 超时返回false, 返回true |
| acquireShared(int arg) | 共享式获取同步状态, 和acquire差不多, 区别是同一时刻可以有多个线程获取同步状态 |
| acquireSharedInterruptibly(int arg) | acquireShared 相同, 但是可以中断 |
| int tryAcquireSharedInterruptibly(int arg, long nanos) | acquireSharedInterrup |
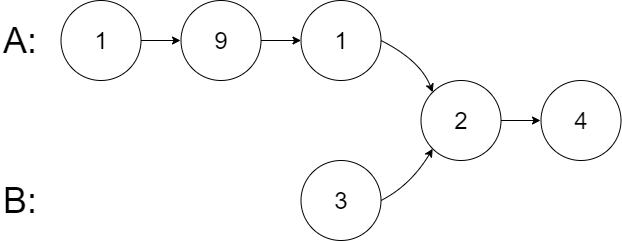
流程图
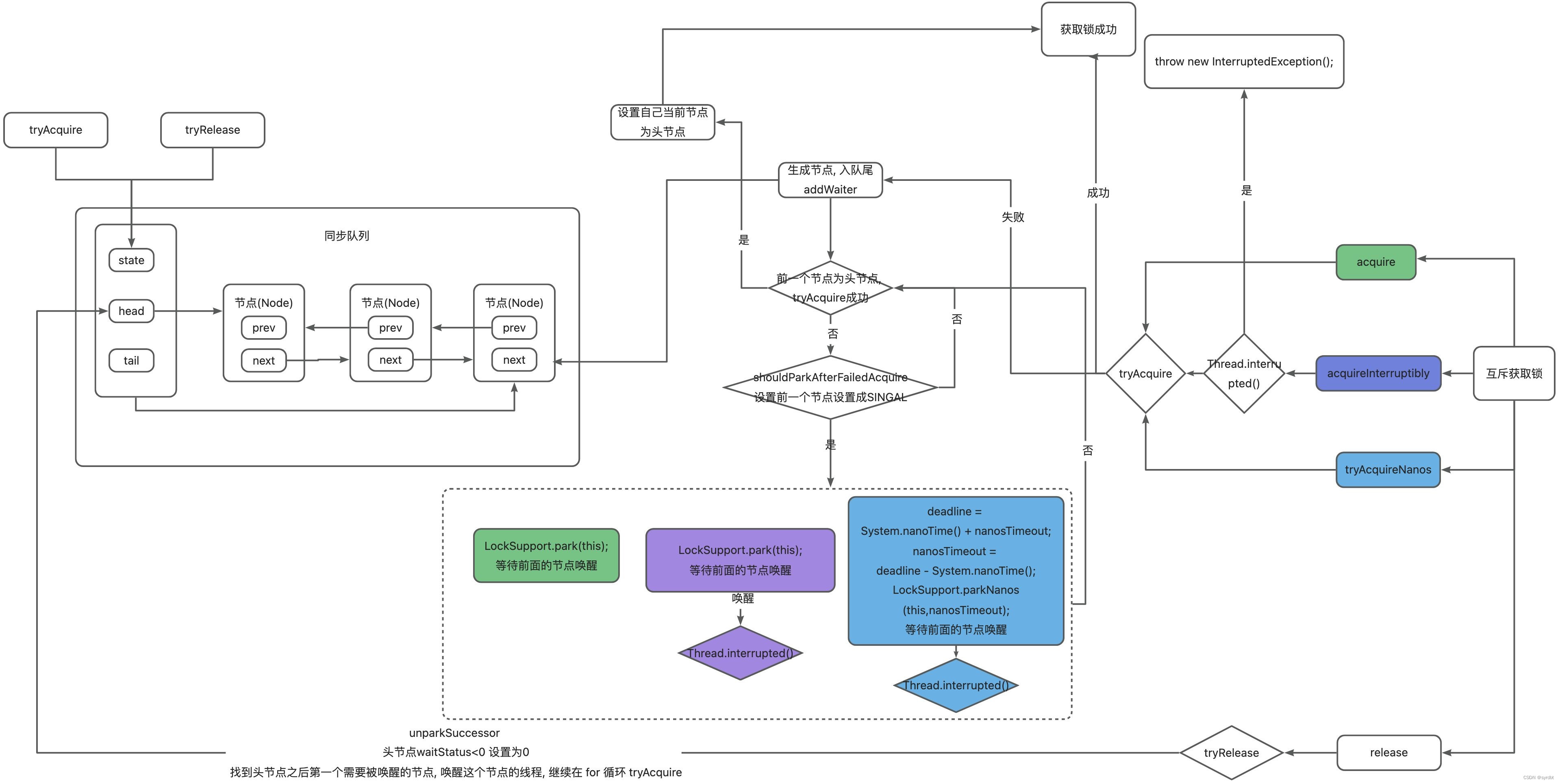
流程图主要方法源码阅读
acquire
独占式获取同步状态, 成功返回, 失败队列等待
public final void acquire(int arg) {
// tryAcquire获取信号量
// 如果失败 tryAcquire(arg)=false addWaiter入队列、acquireQueued 排队获取锁
if (!tryAcquire(arg) &&
acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg))
selfInterrupt();
}
final boolean acquireQueued(final Node node, int arg) {
boolean failed = true;
try {
boolean interrupted = false;
for (;;) {
// 前一个节点是头节点 尝试获取锁 获取锁成功 设置自己为头节点
final Node p = node.predecessor();
if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) {
setHead(node);
p.next = null; // help GC
failed = false;
return interrupted;
}
// 前面节点设置为 singal,自己就可以睡眠了
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
parkAndCheckInterrupt())
// 被中断 尝试获取信号量
interrupted = true;
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
addWaiter
节点进入同步队列
private Node addWaiter(Node mode) {
// 创建节点
Node node = new Node(Thread.currentThread(), mode);
// Try the fast path of enq; backup to full enq on failure
Node pred = tail;
// 尾节点不为空
if (pred != null) {
// 设置当前节点的前一个节点为尾节点
node.prev = pred;
// cas 设置自己为尾节点
if (compareAndSetTail(pred, node)) {
pred.next = node;
return node;
}
}
// 尾节点为空 或 cas 设置自己为尾节点失败了
enq(node);
return node;
}
/**
* 入队
*/
private Node enq(final Node node) {
for (;;) {
Node t = tail;
// 尾节点为空,设置新的头节点
if (t == null) { // Must initialize
if (compareAndSetHead(new Node()))
tail = head;
} else {
// 设置当前节点的前一个节点为尾节点
node.prev = t;
// cas 设置自己为尾节点
if (compareAndSetTail(t, node)) {
t.next = node;
return t;
}
}
}
}
shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire
前面节点设置为 singal,设置成功返回true,失败false
private static boolean shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(Node pred, Node node) {
int ws = pred.waitStatus;
// 前面的节点SIGNAL自己就可以park了
if (ws == Node.SIGNAL)
return true;
if (ws > 0) {
// 找到第一个不是取消状态的节点
do {
node.prev = pred = pred.prev;
} while (pred.waitStatus > 0);
pred.next = node;
} else {
/*
* 设置 WaitStatus SIGNAL
*/
compareAndSetWaitStatus(pred, ws, Node.SIGNAL);
}
return false;
}
parkAndCheckInterrupt
private final boolean parkAndCheckInterrupt() {
LockSupport.park(this);
return Thread.interrupted();
}
acquireInterruptibly
acquire 相同, 但是可以中断
public final void acquireInterruptibly(int arg)
throws InterruptedException {
// 被中断抛出InterruptedException
if (Thread.interrupted())
throw new InterruptedException();
if (!tryAcquire(arg))
doAcquireInterruptibly(arg);
}
private void doAcquireInterruptibly(int arg)
throws InterruptedException {
final Node node = addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE);
boolean failed = true;
try {
for (;;) {
final Node p = node.predecessor();
if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) {
setHead(node);
p.next = null; // help GC
failed = false;
return;
}
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
parkAndCheckInterrupt())
// 被中断抛出InterruptedException
throw new InterruptedException();
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
tryAcquireNanos
acquireInterruptibly 基础上增加了超时限制, 超时返回false, 返回true
public final boolean tryAcquireNanos(int arg, long nanosTimeout)
throws InterruptedException {
if (Thread.interrupted())
throw new InterruptedException();
return tryAcquire(arg) ||
doAcquireNanos(arg, nanosTimeout);
}
private boolean doAcquireNanos(int arg, long nanosTimeout)
throws InterruptedException {
if (nanosTimeout <= 0L)
return false;
final long deadline = System.nanoTime() + nanosTimeout;
final Node node = addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE);
boolean failed = true;
try {
for (;;) {
final Node p = node.predecessor();
if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) {
setHead(node);
p.next = null; // help GC
failed = false;
return true;
}
nanosTimeout = deadline - System.nanoTime();
// 超时返回false
if (nanosTimeout <= 0L)
return false;
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
nanosTimeout > spinForTimeoutThreshold)
// park指定时间
LockSupport.parkNanos(this, nanosTimeout);
// 中断抛出异常
if (Thread.interrupted())
throw new InterruptedException();
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
release
释放信号量, 如果头节点不为空 状态为SINGAL, 唤醒头节点的下一个节点
public final boolean release(int arg) {
if (tryRelease(arg)) {
// 释放arg信号量成功
Node h = head;
// 如果头节点不为空 状态为SINGAL, 唤醒头节点的下一个节点
if (h != null && h.waitStatus != 0)
unparkSuccessor(h);
return true;
}
return false;
}
private void unparkSuccessor(Node node) {
int ws = node.waitStatus;
// 唤醒先修改waitStatus从SINGAL->0初始化
if (ws < 0)
compareAndSetWaitStatus(node, ws, 0);
// 找到node之后第一个不被取消的节点, LockSupport.unpark唤醒该节点
Node s = node.next;
if (s == null || s.waitStatus > 0) {
s = null;
for (Node t = tail; t != null && t != node; t = t.prev)
if (t.waitStatus <= 0)
s = t;
}
if (s != null)
LockSupport.unpark(s.thread);
}
参考文献
- Java并发编程的艺术第二版 方腾飞、魏鹏、程晓明