YOLOv8成功添加ShuffleAttention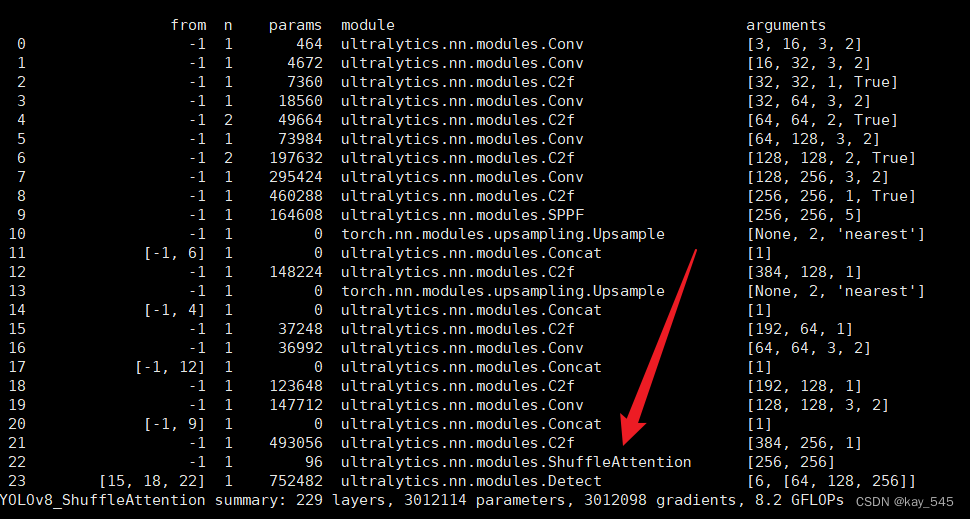
⭐欢迎大家订阅我的专栏一起学习⭐
🚀🚀🚀订阅专栏,更新及时查看不迷路🚀🚀🚀
YOLOv5涨点专栏:http://t.csdnimg.cn/1Aqzu
YOLOv8涨点专栏:http://t.csdnimg.cn/jMjHb
YOLOv7专栏:http://t.csdnimg.cn/yhXBl
💡魔改网络、复现论文、优化创新💡

目录
原理
代码实现
yaml文件实现
完整代码分享
启动命令
注意事项
注意力机制使神经网络能够准确地关注输入的所有相关元素,已成为提高深度神经网络性能的重要组成部分。计算机视觉研究中广泛使用的注意力机制主要有两种:空间注意力和通道注意力,其目的分别是捕获像素级的成对关系和通道依赖性。虽然将它们融合在一起可能会比它们单独的实现获得更好的性能,但它不可避免地会增加计算开销。高效的ShuffleAttention(SA)模块可以解决这个问题,它采用ShuffleAttention单元来有效地结合两种类型的注意机制。具体来说,SA 首先将通道维度分组为多个子特征,然后并行处理它们。然后,对于每个子特征,SA 利用洗牌单元来描述空间和通道维度上的特征依赖性。之后,所有子特征被聚合,并采用“通道洗牌”算子来实现不同子特征之间的信息通信。 SA 模块高效且有效,例如,SA 针对主干 ResNet50 的参数和计算量分别为 300 vs. 25.56M 和 2.76e-3 GFLOPs vs. 4.12 GFLOPs,并且性能提升超过 1.34% Top-1 准确度方面。
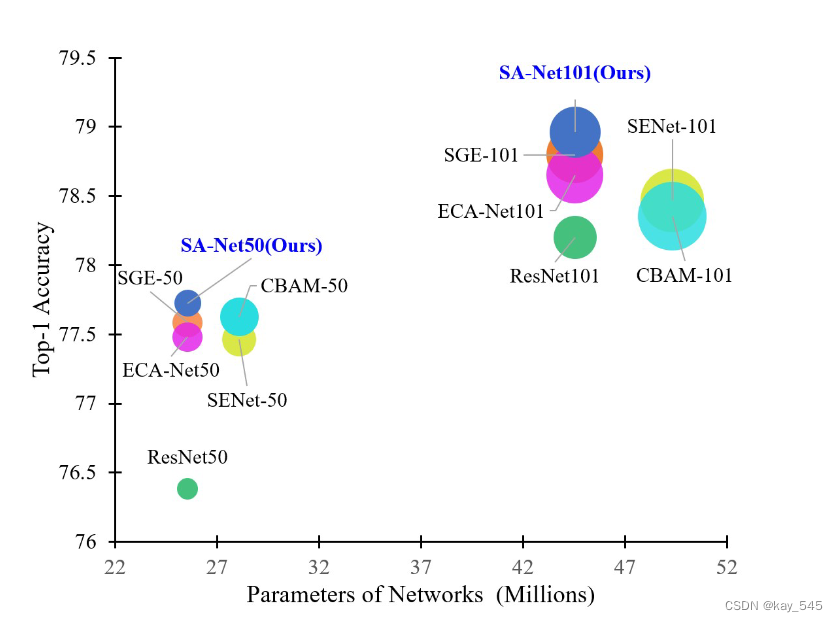
使用 ResNets 作为主干的 ImageNet-1k 上最近的 SOTA 注意力模型(包括 SENet、CBAM、ECA-Net、SGE-Net 和 SA-Net)在准确性、网络参数和 GFLOP 方面的比较。圆圈的大小表示 GFLOP。显然,所提出的 SA-Net 实现了更高的精度,同时模型复杂度更低
原理
首先介绍构建SA模块的过程,该模块将输入特征图分组,并使用Shuffle Unit将通道注意力和空间注意力整合到每个组的一个块中。之后,所有子特征被聚合,并利用“通道洗牌”算子来实现不同子特征之间的信息通信。然后,我们展示如何在深度 CNN 中采用 SA。最后,我们可视化效果并验证所提出的 SA 的可靠性。 SA模块整体架构如图所示
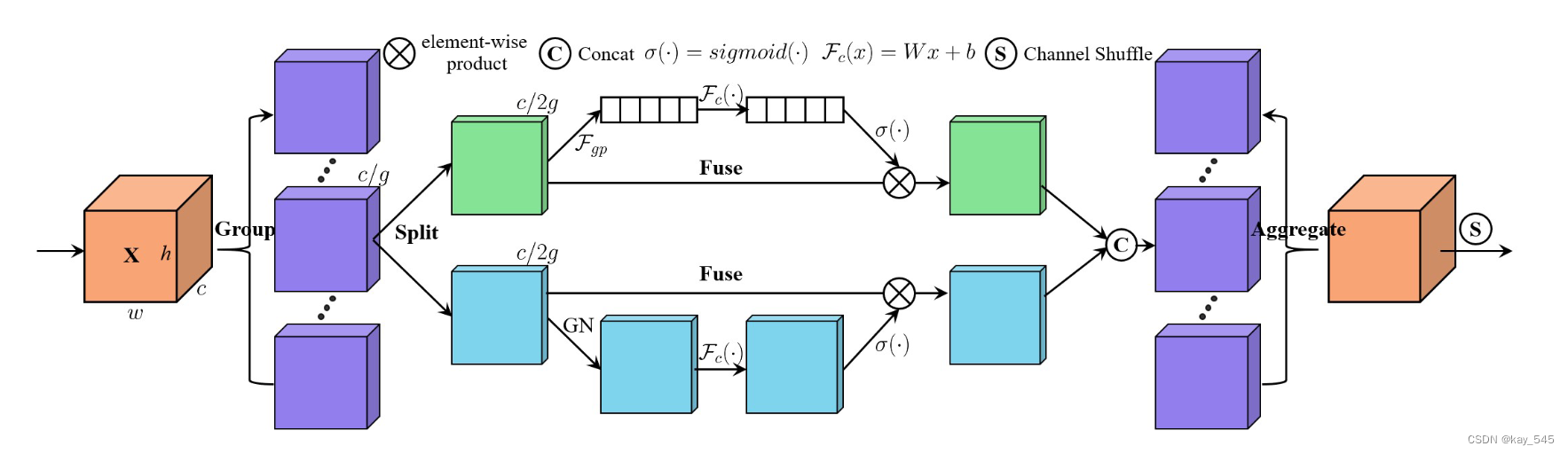
它采用“通道分割”并行处理各组的子特征。对于通道注意力分支,使用 GAP 生成通道统计量,然后使用一对参数来缩放和移动通道向量。对于空间注意力分支,采用群范数生成空间统计量,然后创建类似于通道分支的紧凑特征。然后将两个分支连接起来。之后,所有子特征被聚合,最后我们利用“通道洗牌”运算符来实现不同子特征之间的信息通信。
完全捕获通道依赖性的一个选项是利用SE块。然而,它会带来太多的参数,这不利于在速度和准确性之间进行权衡,设计更轻量级的注意力模块。此外,像 ECA 一样,不适合通过执行大小为 k 的更快一维卷积来生成通道权重,因为 k 往往会更大。为了改进,我们提供了一种替代方案,首先通过简单地使用全局平均池化(GAP)来嵌入全局信息,生成通道统计量 s ∈ RC/2G×1×1,可以通过空间维度缩小Xk1 来计算高×宽此外,还创建了一个紧凑的功能来指导精确和自适应的选择。这是通过带有 sigmoid 激活的简单门控机制来实现的。
与通道注意力不同,空间注意力关注的是“哪里”,是信息性的部分,与通道注意力是互补的。首先,我们在 Xk2 上使用群范数 (GN)来获得空间统计数据。然后,采用Fc(·)来增强^ Xk2的表示。
之后,所有子特征都被聚合。最后,与ShuffleNet v2 类似,我们采用“channel shuffle”算子来实现沿通道维度的跨组信息流。 SA模块的最终输出与X的大小相同,使得SA非常容易与现代架构集成
代码实现
class ShuffleAttention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, channel=512, reduction=16, G=8):
super().__init__()
self.G = G
self.channel = channel
self.avg_pool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1)
self.gn = nn.GroupNorm(channel // (2 * G), channel // (2 * G))
self.cweight = Parameter(torch.zeros(1, channel // (2 * G), 1, 1))
self.cbias = Parameter(torch.ones(1, channel // (2 * G), 1, 1))
self.sweight = Parameter(torch.zeros(1, channel // (2 * G), 1, 1))
self.sbias = Parameter(torch.ones(1, channel // (2 * G), 1, 1))
self.sigmoid = nn.Sigmoid()
def init_weights(self):
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out')
if m.bias is not None:
init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):
init.constant_(m.weight, 1)
init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
elif isinstance(m, nn.Linear):
init.normal_(m.weight, std=0.001)
if m.bias is not None:
init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
@staticmethod
def channel_shuffle(x, groups):
b, c, h, w = x.shape
x = x.reshape(b, groups, -1, h, w)
x = x.permute(0, 2, 1, 3, 4)
# flatten
x = x.reshape(b, -1, h, w)
return x
def forward(self, x):
b, c, h, w = x.size()
# group into subfeatures
x = x.view(b * self.G, -1, h, w) # bs*G,c//G,h,w
# channel_split
x_0, x_1 = x.chunk(2, dim=1) # bs*G,c//(2*G),h,w
# channel attention
x_channel = self.avg_pool(x_0) # bs*G,c//(2*G),1,1
x_channel = self.cweight * x_channel + self.cbias # bs*G,c//(2*G),1,1
x_channel = x_0 * self.sigmoid(x_channel)
# spatial attention
x_spatial = self.gn(x_1) # bs*G,c//(2*G),h,w
x_spatial = self.sweight * x_spatial + self.sbias # bs*G,c//(2*G),h,w
x_spatial = x_1 * self.sigmoid(x_spatial) # bs*G,c//(2*G),h,w
# concatenate along channel axis
out = torch.cat([x_channel, x_spatial], dim=1) # bs*G,c//G,h,w
out = out.contiguous().view(b, -1, h, w)
# channel shuffle
out = self.channel_shuffle(out, 2)
return outyaml文件实现
# Ultralytics YOLO , GPL-3.0 license
# YOLOv8 object detection model with P3-P5 outputs. For Usage examples see https://docs.ultralytics.com/tasks/detect
# Parameters
nc: 6 # number of classes
scales: # model compound scaling constants, i.e. 'model=yolov8n.yaml' will call yolov8.yaml with scale 'n'
# [depth, width, max_channels]
n: [0.33, 0.25, 1024] # YOLOv8n summary: 225 layers, 3157200 parameters, 3157184 gradients, 8.9 GFLOPs
s: [0.33, 0.50, 1024] # YOLOv8s summary: 225 layers, 11166560 parameters, 11166544 gradients, 28.8 GFLOPs
m: [0.67, 0.75, 768] # YOLOv8m summary: 295 layers, 25902640 parameters, 25902624 gradients, 79.3 GFLOPs
l: [1.00, 1.00, 512] # YOLOv8l summary: 365 layers, 43691520 parameters, 43691504 gradients, 165.7 GFLOPs
x: [1.00, 1.25, 512] # YOLOv8x summary: 365 layers, 68229648 parameters, 68229632 gradients, 258.5 GFLOPs
# YOLOv8.0n backbone
backbone:
# [from, repeats, module, args]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [64, 3, 2]] # 0-P1/2
- [-1, 1, Conv, [128, 3, 2]] # 1-P2/4
- [-1, 3, C2f, [128, True]]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]] # 3-P3/8
- [-1, 6, C2f, [256, True]]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]] # 5-P4/16
- [-1, 6, C2f, [512, True]]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [1024, 3, 2]] # 7-P5/32
- [-1, 3, C2f, [1024, True]]
- [-1, 1, SPPF, [1024, 5]] # 9
# YOLOv8.0n head
head:
- [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']]
- [[-1, 6], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P4
- [-1, 3, C2f, [512]] # 12
- [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']]
- [[-1, 4], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P3
- [-1, 3, C2f, [256]] # 15 (P3/8-small)
- [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]]
- [[-1, 12], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P4
- [-1, 3, C2f, [512]] # 18 (P4/16-medium)
- [-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]]
- [[-1, 9], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P5
- [-1, 3, C2f, [1024]] # 21 (P5/32-large)
- [-1, 3, ShuffleAttention, [1024]]
- [[15, 18, 22], 1, Detect, [nc]] # Detect(P3, P4, P5)完整代码分享
链接: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1NPb6C6svuNGqyZIYUVgsVw?pwd=yjnw 提取码: yjnw
启动命令
yolo detect train model=/path/yolov8_ShuffleAttention.yaml data=/path/coco128.com注意事项
如果报错,查看这篇文章
YOLOv8 | 添加注意力机制报错KeyError:已解决,详细步骤_yolov8 keyerroe-CSDN博客



![服务器中了.[hpssupfast@mailfence.com].Elbie勒索病毒,数据还能恢复吗?](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/afd2ec524ef24d0a9294e773734f93cf.png)