增加其他功能
一、增加变量显示
1、目的:在TensorBoard当中观察模型的参数、损失值等变量值的变化
2、收集变量
不同的变量要用不同的方式收集
(1)tf.summary.scalar(name='', tensor)
收集对于损失函数和准确率等单值变量,name为变量的名字,tensor为值
(2)tf.summary.histogram(name='', tensor)
收集高维度的变量参数
(3)tf.summary.image(name='', tensor)
收集输入的图片张量,能显示图片
3、合并变量写入事件文件
(1)merged = tf.summary.merge_all()
4、修改代码
import os
os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL']='2'
import tensorflow as tf
def tensorflow_demo():
"""
TensorFlow的基本结构
"""
# TensorFlow实现加减法运算
a_t = tf.constant(2)
b_t = tf.constant(3)
c_t = a_t + b_t
print("TensorFlow加法运算结果:\n", c_t)
print(c_t.numpy())
# 2.0版本不需要开启会话,已经没有会话模块了
return None
def graph_demo():
"""
图的演示
"""
# TensorFlow实现加减法运算
a_t = tf.constant(2)
b_t = tf.constant(3)
c_t = a_t + b_t
print("TensorFlow加法运算结果:\n", c_t)
print(c_t.numpy())
# 查看默认图
# 方法1:调用方法
default_g = tf.compat.v1.get_default_graph()
print("default_g:\n", default_g)
# 方法2:查看属性
# print("a_t的图属性:\n", a_t.graph)
# print("c_t的图属性:\n", c_t.graph)
# 自定义图
new_g = tf.Graph()
# 在自己的图中定义数据和操作
with new_g.as_default():
a_new = tf.constant(20)
b_new = tf.constant(30)
c_new = a_new + b_new
print("c_new:\n", c_new)
print("a_new的图属性:\n", a_new.graph)
print("b_new的图属性:\n", b_new.graph)
# 开启new_g的会话
with tf.compat.v1.Session(graph=new_g) as sess:
c_new_value = sess.run(c_new)
print("c_new_value:\n", c_new_value)
print("我们自己创建的图为:\n", sess.graph)
# 可视化自定义图
# 1)创建一个writer
writer = tf.summary.create_file_writer("./tmp/summary")
# 2)将图写入
with writer.as_default():
tf.summary.graph(new_g)
return None
def session_run_demo():
"""
feed操作
"""
tf.compat.v1.disable_eager_execution()
# 定义占位符
a = tf.compat.v1.placeholder(tf.float32)
b = tf.compat.v1.placeholder(tf.float32)
sum_ab = tf.add(a, b)
print("a:\n", a)
print("b:\n", b)
print("sum_ab:\n", sum_ab)
# 开启会话
with tf.compat.v1.Session() as sess:
print("占位符的结果:\n", sess.run(sum_ab, feed_dict={a: 1.1, b: 2.2}))
return None
def tensor_demo():
"""
张量的演示
"""
tensor1 = tf.constant(4.0)
tensor2 = tf.constant([1, 2, 3, 4])
linear_squares = tf.constant([[4], [9], [16], [25]], dtype=tf.int32)
print("tensor1:\n", tensor1)
print("tensor2:\n", tensor2)
print("linear_squares:\n", linear_squares)
# 张量类型的修改
l_cast = tf.cast(linear_squares, dtype=tf.float32)
print("before:\n", linear_squares)
print("l_cast:\n", l_cast)
return None
def variable_demo():
"""
变量的演示
"""
a = tf.Variable(initial_value=50)
b = tf.Variable(initial_value=40)
c = tf.add(a, b)
print("a:\n", a)
print("b:\n", b)
print("c:\n", c)
with tf.compat.v1.variable_scope("my_scope"):
d = tf.Variable(initial_value=30)
e = tf.Variable(initial_value=20)
f = tf.add(d, e)
print("d:\n", d)
print("e:\n", e)
print("f:\n", f)
return None
def linear_regression():
"""
自实现一个线性回归
"""
# 1、准备数据
x = tf.random.normal(shape=[100,1])
y_true = tf.matmul(x, [[0.8]]) + 0.7
# 2、构造模型
# 定义模型参数,用变量
weights = tf.Variable(initial_value=tf.random.normal(shape=[1, 1]))
bias = tf.Variable(initial_value=tf.random.normal(shape=[1, 1]))
y_predict = tf.matmul(x, weights) + bias
# 3、构造损失函数
error = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(y_predict - y_true))
# 4、优化器
#optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate=0.01).minimize(error)
optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.SGD(learning_rate=0.01)
# 创建事件文件
file_writer = tf.summary.create_file_writer("./tmp/summary")
# 收集变量
with file_writer.as_default():
tf.summary.experimental.set_step(0)
# 记录标量变量
tf.summary.scalar("error", error)
# 记录变量的直方图
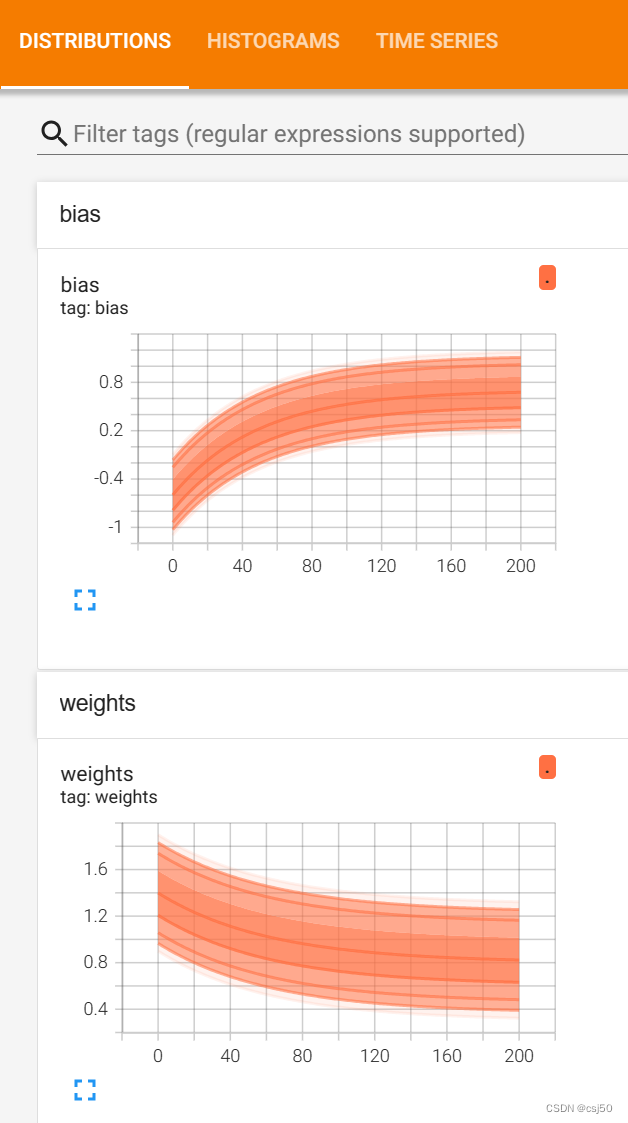
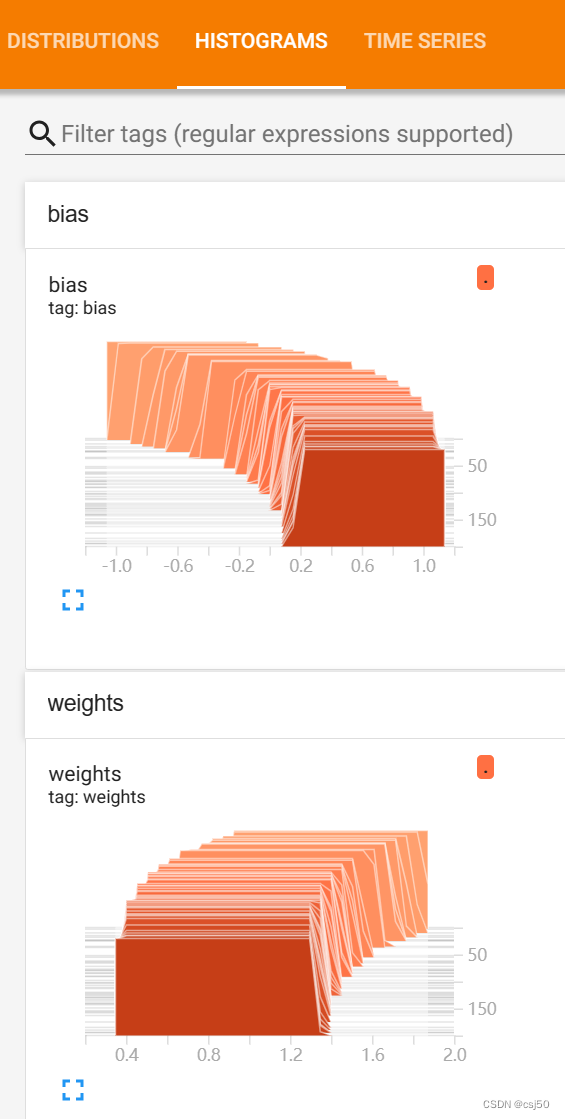
tf.summary.histogram("weights", weights)
tf.summary.histogram("bias", bias)
# 5、查看初始化模型参数之后的值
print("训练前模型参数为:权重%f,偏置%f,损失%f" % (weights, bias, error))
# 6、开始训练
num_epoch = 200 # 定义迭代次数
for e in range(num_epoch): # 迭代多次
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
y_predict = tf.matmul(x, weights) + bias
error = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(y_predict - y_true))
#error = loss_function(y_predict, y_true)
grads = tape.gradient(error, [weights, bias]) # 求损失关于参数weights、bias的梯度
optimizer.apply_gradients(grads_and_vars=zip(grads, [weights, bias])) # 自动根据梯度更新参数,即利用梯度信息修改weights与bias,使得损失减小
# 每个步骤记录变量
with file_writer.as_default():
tf.summary.experimental.set_step(e + 1)
# 记录标量变量
tf.summary.scalar("error", error)
# 记录变量的直方图
tf.summary.histogram("weights", weights)
tf.summary.histogram("bias", bias)
file_writer.close()
print("训练后模型参数为:权重%f,偏置%f,损失%f" % (weights, bias, error))
return None
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 代码1:TensorFlow的基本结构
# tensorflow_demo()
# 代码2:图的演示
#graph_demo()
# feed操作
#session_run_demo()
# 代码4:张量的演示
#tensor_demo()
# 代码5:变量的演示
#variable_demo()
# 代码6:自实现一个线性回归
linear_regression()运行结果:
训练前模型参数为:权重1.398883,偏置-0.596879,损失1.965775
训练后模型参数为:权重0.823115,偏置0.676830,损失0.0010035、查看TensorBoard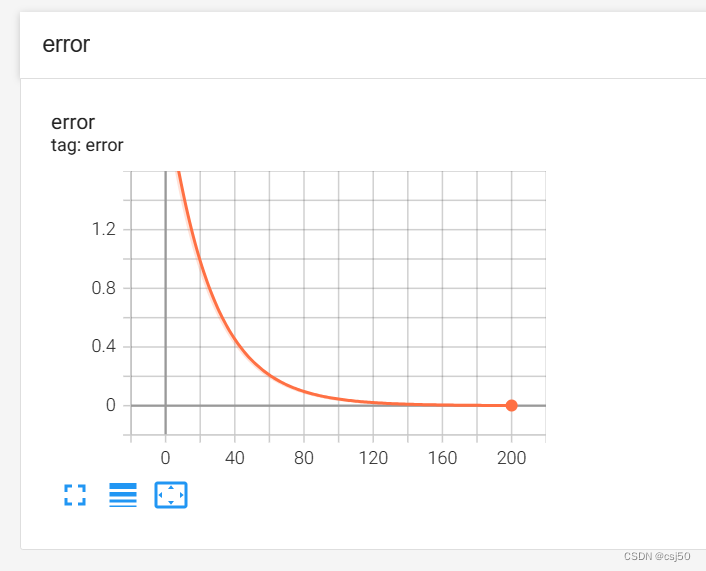
二、TensorFlow2.0如何显示静态图
1、在TensorFlow1.0时代,采用的是静态计算图,需要先使用TensorFlow的各种算子创建计算图,然后再开启一个会话Session,显式执行计算图
2、而在TensorFlow2.0时代,采用的是动态计算图,即每使用一个算子后,该算子会被动态加入到隐含的默认计算图中立即执行得到结果,而无需开启Session
3、如果需要在TensorFlow2.0中使用静态图,可以使用@tf.function装饰器将普通Python函数转换成对应的TensorFlow计算图构建代码。运行该函数就相当于在TensorFlow1.0中用Session执行代码。使用tf.function构建静态图的方式叫做Autograph
4、计算图简介
计算图由节点(nodes)和线(edges)组成
节点表示操作符Operator,或者称之为算子,线表示计算间的依赖
实线表示有数据传递依赖,传递的数据即张量
虚线通常可以表示控制依赖,即执行先后顺序
5、因为代码里用到了变量,没法用tf.function把静态图弄出来