wps: option + left 回到上一个视图
Kirsch L, Harrison J, Sohl-Dickstein J, et al. General-purpose in-context learning by meta-learning transformers[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:2212.04458, 2022.
目录
- Kirsch L, Harrison J, Sohl-Dickstein J, et al. General-purpose in-context learning by meta-learning transformers[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:2212.04458, 2022.
- 什么是meta-learning?
- 这篇文章的主要贡献是什么?
- 为了提高发现学习算法的generality:
- 引入inductive bias有一些问题,
- 什么是general-purpose in-context learning with transformers?与其它方法的区别?
- 在meta-learning中有一个问题就是每个任务中的数量是不一致的,一些常见任务的数据量是比较少的(需要task,需要task中有足够的数量)。为了解决这个问题,有一些方法:
- 总结一下,这篇文章的主要贡献是什么?
- 作者分析了3个学习阶段:
- Meta-train中遇到的困难,可以从以下几个方面中进行优化:
- 这篇工作的limitation:
什么是meta-learning?
机器学习需要去显示地定义 losses, architectures, and optimizers,meta-learning(或者是learning to learn)目的是学习这些aspects,然后希望用尽可能少的手工操作来解锁更多的能力。
One particularly ambitious goal of meta-learning is to train general-purpose in-context learning algorithms from scratch, using only black-box models with minimal inductive bias.
这篇文章的主要贡献是什么?
-
In this paper we show that Transformers and other black box models can be meta-trained to act as general-purpose in-context learners.
-
作者做了一下分类:
-
algorithms that generalize,
-
algorithms that memorize,
-
algorithms that fail to meta-train
induced by changes in model size, number of tasks, and meta-optimization.
- They find the capabilities of meta-trained algorithms are bottlenecked by the accessible state size (memory) determining the next prediction, unlike standard models which are thought to be bottlenecked by parameter count.
作者发现,meta-trained算法的能力瓶颈是可访问的内存的大小(用来决定下一次预测),而不是我们传统认为的参数量。
- 做了一些实验用来提高meta-training的meta-generalization of general-purpose learning algorithms.
为了提高发现学习算法的generality:
- 引入inductive bias
- bottlenecking the architecture
- hiding information
- restrict learning rules
- gradients
- symbolic graphs
- Parameter sharing
引入inductive bias有一些问题,
① inductive bisases 成为了设计这些系统的代价,② 潜在地限制了发现学习算法的空间。(①这个我没有太看懂什么意思,不过②说的是对的。inductive biases的设计成为了设计这个系统的代价,也就是设计inductive biases也需要付出一些努力,因为引入了inductive bias所以也就加了一个人为的限制,这就限制了发现学习算法的空间。 引出了这篇文章的目标==>
Instead, we seek to explore general-purpose meta-learning systems with minimal inductive bias.
(supervised)learning algorithm 的目的是找到一个函数满足x到y的mapping,meta-learning对应而言,是通过meta-optimization找到这些函数。

什么是general-purpose in-context learning with transformers?与其它方法的区别?
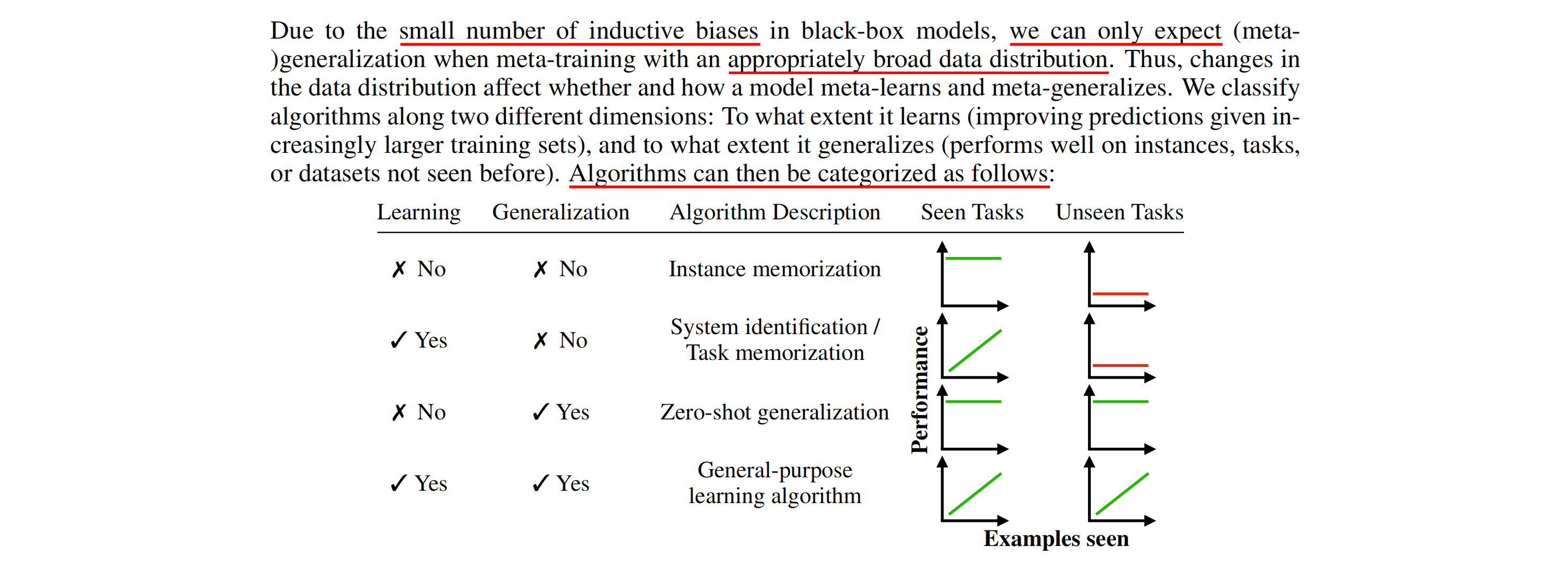
在meta-learning中有一个问题就是每个任务中的数量是不一致的,一些常见任务的数据量是比较少的(需要task,需要task中有足够的数量)。为了解决这个问题,有一些方法:
- by building-in architectural or algorithmic structure into the learning algorithm, in effect drastically reducing the number of tasks required(但是这样的方法要特别对数据集做一些算法上的改进,这与这篇文章中主要研究的问题不相符)
- 生成一些新任务:Unfortunately, it is not easy to generate a wide range of tasks that are both diverse and contain structure as it can be found in the real world.
最终,这篇文章中选择的方法是:take an intermediate step by augmenting existing datasets。
具体上,这篇文章的做法是:generate a large number of tasks by taking existing supervised learning datasets, randomly projecting their inputs and permuting their classification labels. (随机投影在全连接网络中是没有问题的 https://arxiv.org/abs/2008.07545)
🤡 这种随机投影的技术是不是也可以用在很多数量分布不均匀的数据上呢?
好像是不行的,这种随机投影的技术好像只是可以用来扩充任务范围。
总结一下,这篇文章的主要贡献是什么?
We believe our findings open up new possibilities of data-driven general-purpose meta-learning with minimal inductive bias.
开启了一个使用最小minimal inductive进行meta-learning的新局面。
作者分析了3个学习阶段:
-
instance memorization
-
system identifification
-
general learning
Meta-train中遇到的困难,可以从以下几个方面中进行优化:
我们确定了元优化方面的困难,并提出了在优化器、超参数和有偏见的数据分布方面的干预措施
-
优化器
Adam优化器,Using smaller results in more than halving the plateau length。
-
超参数
batchsize
-
有偏见的数据分布
Instead of sampling label permutations uniformly at random, we bias towards a specifific permutation by using a fifixed permutation for a fraction of each batch.
这篇工作的limitation:
- 不能处理任意长度的输入输出
- 在黑盒模型中,transformer的参数量的增长也同样是一个问题。