本文介绍MD5源码(C语言描述)。
MD5(Message-Digest Algorithm 5),即消息摘要算法5,是一种被广泛使用的消息散列算法。散列算法的基础原理是:将数据(如一段文字)经过运算转换为一段固定长度(16/32)的值。主要用于数据防篡改。
1.源码
1)头文件
头文件(MD5.h)主要包括MD5外部函数声明。头文件定义如下。
#ifndef MD5_H
#define MD5_H
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdint.h>
extern void MD5_String(char *input, uint8_t *result);
extern void MD5_Data(uint8_t *input, uint32_t length, uint8_t *result);
extern void MD5_File(FILE *file, uint8_t *result);
#endif
其中,
a)MD5_String():用于计算字符串的MD5值。
b)MD5_Data():用于计算数据的MD5值。
c)MD5_File():用于计算文件的MD5值。
d)result的结果是1个16字节长度(按16进制表示则为32位长度)的数组。
2)源文件
源文件(MD5. c)主要包括MD5相关外部函数定义。源文件定义如下。
#include "MD5.h"
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
/*
* Constants defined by the MD5 algorithm
*/
#define A (0x67452301)
#define B (0xefcdab89)
#define C (0x98badcfe)
#define D (0x10325476)
/*
* Bit-manipulation functions defined by the MD5 algorithm
*/
#define F(X, Y, Z) ((X & Y) | (~X & Z))
#define G(X, Y, Z) ((X & Z) | (Y & ~Z))
#define H(X, Y, Z) (X ^ Y ^ Z)
#define I(X, Y, Z) (Y ^ (X | ~Z))
typedef struct _MD5_CONTEXT
{
uint64_t size; // Size of input in bytes
uint32_t buffer[4]; // Current accumulation of hash
uint8_t input[64]; // Input to be used in the next step
uint8_t digest[16]; // Result of algorithm
}MD5_CONTEXT;
static const uint32_t S[] =
{
7, 12, 17, 22, 7, 12, 17, 22, 7, 12, 17, 22, 7, 12, 17, 22,
5, 9, 14, 20, 5, 9, 14, 20, 5, 9, 14, 20, 5, 9, 14, 20,
4, 11, 16, 23, 4, 11, 16, 23, 4, 11, 16, 23, 4, 11, 16, 23,
6, 10, 15, 21, 6, 10, 15, 21, 6, 10, 15, 21, 6, 10, 15, 21
};
static const uint32_t K[] =
{
0xd76aa478, 0xe8c7b756, 0x242070db, 0xc1bdceee,
0xf57c0faf, 0x4787c62a, 0xa8304613, 0xfd469501,
0x698098d8, 0x8b44f7af, 0xffff5bb1, 0x895cd7be,
0x6b901122, 0xfd987193, 0xa679438e, 0x49b40821,
0xf61e2562, 0xc040b340, 0x265e5a51, 0xe9b6c7aa,
0xd62f105d, 0x02441453, 0xd8a1e681, 0xe7d3fbc8,
0x21e1cde6, 0xc33707d6, 0xf4d50d87, 0x455a14ed,
0xa9e3e905, 0xfcefa3f8, 0x676f02d9, 0x8d2a4c8a,
0xfffa3942, 0x8771f681, 0x6d9d6122, 0xfde5380c,
0xa4beea44, 0x4bdecfa9, 0xf6bb4b60, 0xbebfbc70,
0x289b7ec6, 0xeaa127fa, 0xd4ef3085, 0x04881d05,
0xd9d4d039, 0xe6db99e5, 0x1fa27cf8, 0xc4ac5665,
0xf4292244, 0x432aff97, 0xab9423a7, 0xfc93a039,
0x655b59c3, 0x8f0ccc92, 0xffeff47d, 0x85845dd1,
0x6fa87e4f, 0xfe2ce6e0, 0xa3014314, 0x4e0811a1,
0xf7537e82, 0xbd3af235, 0x2ad7d2bb, 0xeb86d391
};
/*
* Padding used to make the size (in bits) of the input congruent to 448 mod 512
*/
static const uint8_t PADDING[] =
{
0x80, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00,
0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00,
0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00,
0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00,
0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00,
0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00,
0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00,
0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00
};
static uint32_t RotateLeft(uint32_t x, uint32_t n);
static void MD5_Init(MD5_CONTEXT *ctx);
static void MD5_Update(MD5_CONTEXT *ctx, uint8_t *input, size_t input_len);
static void MD5_Final(MD5_CONTEXT *ctx);
static void MD5_Step(uint32_t *buffer, uint32_t *input);
/*
* Rotates a 32-bit word left by n bits
*/
static uint32_t RotateLeft(uint32_t x, uint32_t n)
{
return (x << n) | (x >> (32 - n));
}
/*
* Initialize a context
*/
static void MD5_Init(MD5_CONTEXT *ctx)
{
ctx->size = (uint64_t)0;
ctx->buffer[0] = (uint32_t)A;
ctx->buffer[1] = (uint32_t)B;
ctx->buffer[2] = (uint32_t)C;
ctx->buffer[3] = (uint32_t)D;
}
/*
* Add some amount of input to the context
*
* If the input fills out a block of 512 bits, apply the algorithm (md5Step)
* and save the result in the buffer. Also updates the overall size.
*/
static void MD5_Update(MD5_CONTEXT *ctx, uint8_t *input_buffer, size_t input_len)
{
uint32_t input[16] = {0};
uint32_t offset = ctx->size % 64;
ctx->size += (uint64_t)input_len;
uint32_t i = 0;
uint32_t j = 0;
// Copy each byte in input_buffer into the next space in our context input
for (i = 0; i < input_len; i++)
{
ctx->input[offset++] = (uint8_t)(*(input_buffer + i));
// If we've filled our context input, copy it into our local array input
// then reset the offset to 0 and fill in a new buffer.
// Every time we fill out a chunk, we run it through the algorithm
// to enable some back and forth between cpu and i/o
if (offset % 64 == 0)
{
for (j = 0; j < 16; j++)
{
// Convert to little-endian
// The local variable `input` our 512-bit chunk separated into 32-bit words
// we can use in calculations
input[j] = (uint32_t)(ctx->input[(j * 4) + 3]) << 24 |
(uint32_t)(ctx->input[(j * 4) + 2]) << 16 |
(uint32_t)(ctx->input[(j * 4) + 1]) << 8 |
(uint32_t)(ctx->input[(j * 4)]);
}
MD5_Step(ctx->buffer, input);
offset = 0;
}
}
}
/*
* Pad the current input to get to 448 bytes, append the size in bits to the very end,
* and save the result of the final iteration into digest.
*/
static void MD5_Final(MD5_CONTEXT *ctx)
{
uint32_t input[16] = {0};
uint32_t offset = ctx->size % 64;
uint32_t padding_length = (offset < 56) ? (56 - offset) : ((56 + 64) - offset);
uint32_t i = 0;
uint32_t j = 0;
// Fill in the padding and undo the changes to size that resulted from the update
MD5_Update(ctx, PADDING, padding_length);
ctx->size -= (uint64_t)padding_length;
// Do a final update (internal to this function)
// Last two 32-bit words are the two halves of the size (converted from bytes to bits)
for (j = 0; j < 14; j++)
{
input[j] = (uint32_t)(ctx->input[(j * 4) + 3]) << 24 |
(uint32_t)(ctx->input[(j * 4) + 2]) << 16 |
(uint32_t)(ctx->input[(j * 4) + 1]) << 8 |
(uint32_t)(ctx->input[(j * 4)]);
}
input[14] = (uint32_t)(ctx->size * 8);
input[15] = (uint32_t)((ctx->size * 8) >> 32);
MD5_Step(ctx->buffer, input);
// Move the result into digest (convert from little-endian)
for (i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
ctx->digest[(i * 4) + 0] = (uint8_t)((ctx->buffer[i] & 0x000000FF));
ctx->digest[(i * 4) + 1] = (uint8_t)((ctx->buffer[i] & 0x0000FF00) >> 8);
ctx->digest[(i * 4) + 2] = (uint8_t)((ctx->buffer[i] & 0x00FF0000) >> 16);
ctx->digest[(i * 4) + 3] = (uint8_t)((ctx->buffer[i] & 0xFF000000) >> 24);
}
}
/*
* Step on 512 bits of input with the main MD5 algorithm.
*/
static void MD5_Step(uint32_t *buffer, uint32_t *input)
{
uint32_t AA = buffer[0];
uint32_t BB = buffer[1];
uint32_t CC = buffer[2];
uint32_t DD = buffer[3];
uint32_t E = 0;
uint32_t temp = 0;
uint32_t i = 0;
uint32_t j = 0;
for(i = 0; i < 64; i++)
{
switch (i / 16)
{
case (0):
{
E = F(BB, CC, DD);
j = i;
break;
}
case (1):
{
E = G(BB, CC, DD);
j = ((i * 5) + 1) % 16;
break;
}
case (2):
{
E = H(BB, CC, DD);
j = ((i * 3) + 5) % 16;
break;
}
default:
{
E = I(BB, CC, DD);
j = (i * 7) % 16;
break;
}
}
temp = DD;
DD = CC;
CC = BB;
BB = BB + RotateLeft(AA + E + K[i] + input[j], S[i]);
AA = temp;
}
buffer[0] += AA;
buffer[1] += BB;
buffer[2] += CC;
buffer[3] += DD;
}
/*
* Functions that run the algorithm on the provided input and put the digest into result.
* result should be able to store 16 bytes.
*/
void MD5_String(char *input, uint8_t *result)
{
MD5_CONTEXT ctx;
if ((input == NULL) || (result == NULL))
{
return ;
}
MD5_Init(&ctx);
MD5_Update(&ctx, (uint8_t *)input, strlen(input));
MD5_Final(&ctx);
memcpy(result, ctx.digest, 16);
}
void MD5_Data(uint8_t *input, uint32_t length, uint8_t *result)
{
MD5_CONTEXT ctx;
if ((input == NULL) || (result == NULL) || (length == 0))
{
return ;
}
MD5_Init(&ctx);
MD5_Update(&ctx, (uint8_t *)input, length);
MD5_Final(&ctx);
memcpy(result, ctx.digest, 16);
}
void MD5_File(FILE *file, uint8_t *result)
{
char *input_buffer = NULL;
size_t input_size = 0;
MD5_CONTEXT ctx;
if ((file == NULL) || (result == NULL))
{
return ;
}
input_buffer = malloc(1024);
MD5_Init(&ctx);
while ((input_size = fread(input_buffer, 1, 1024, file)) > 0)
{
MD5_Update(&ctx, (uint8_t *)input_buffer, input_size);
}
MD5_Final(&ctx);
free(input_buffer);
memcpy(result, ctx.digest, 16);
}
2.测试
这里以计算字符串为例。
#include <stdio.h>
#include "MD5.h"
int main()
{
uint8_t md5[16] = {0};
uint32_t i = 0;
MD5_String("Hello,World", md5);
for (i = 0; i < 16; i++)
{
printf("%x", md5[i]);
}
printf("\r\n");
return 0;
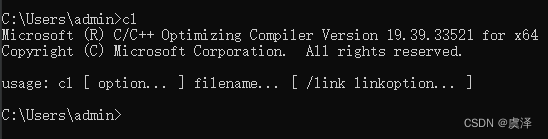
}计算结果如下:
注意:
MD5散列后的位数有两种类型:16位与32位(按16进制表示),默认使用32位。16位实际上是从32位字符串中取中间的第9位到第24位的部分。
总结,本文介绍了MD5源码(C语言描述)。