一、组合模式
概述
组合模式(Composite Pattern),又叫部分整体模式,是用于把一组相似的对象当作一个单一的对象。组合模式依据树形结构来组合对象,用来表示部分以及整体层次。这种类型的设计模式属于结构型模式,它创建了对象组的树形结构
这种模式创建了一个包含自己对象组的类。该类提供了修改相同对象组的方式
主要解决:它在我们树型结构的问题中,模糊了简单元素和复杂元素的概念,客户程序可以像处理简单元素一样来处理复杂元素,从而使得客户程序与复杂元素的内部结构解耦
何时使用:1、想表示对象的部分-整体层次结构(树形结构) 2、希望用户忽略组合对象与单个对象的不同,用户将统一地使用组合结构中的所有对象
优缺点
优点:
- 组合模式通过递归的形式遍历组合对象,使得对象可以无限层次地嵌套。这样可以更加灵活地表示复杂的结构,并能够方便地对整个结构进行操作
- 通过组合模式,以统一的方式处理整体和部分,不需要关心当前操作的对象是叶节点还是组合节点,可以统一地进行操作
缺点:
- 在使用组合模式时,其叶子和树枝的声明都是实现类,而不是接口,违反了依赖倒置原则
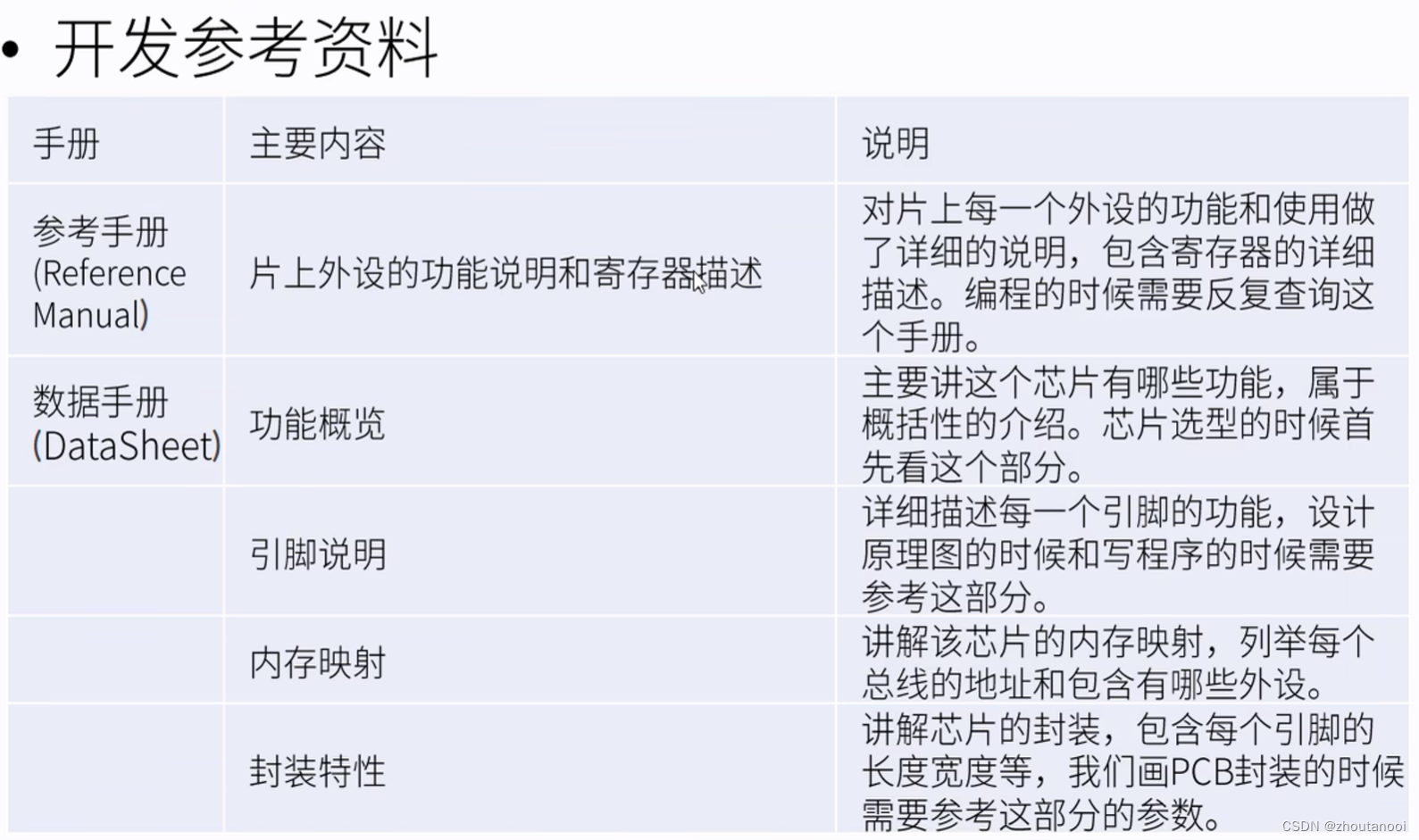
1. 各个角色介绍
1.1 组件(Component)
- 定义了组合中所有对象的通用接口,可以是抽象类或接口。它声明了用于访问和管理子组件的方法,包括添加、删除、获取子组件等
1.2 叶子节点(Leaf)
- 表示组合中的叶子节点对象,叶子节点没有子节点。它实现了组件接口的方法,但通常不包含子组件
1.3 复合节点(Composite)
- 表示组合中的复合对象,复合节点可以包含子节点,可以是叶子节点,也可以是其他复合节点。它实现了组件接口的方法,包括管理子组件的方法
2. UML图
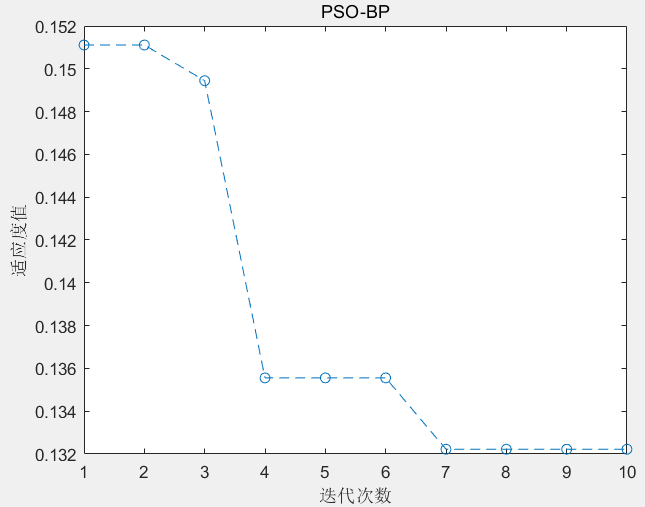
我们有一个类 Component 对象作为所有对象的通用接口,然后 Leaf、Composite 分别实现该接口,并通过 Composite 构建非叶子节点和叶子节点,形成树状图,并以中序遍历的形式输出

3. 具体例子和代码
角色分配
- Component:抽象组件
- Leaf:叶子节点(叶子节点下,无组件,继承Component)
- Composite:组合节点(继承Component)
3.1 抽象组件
- Component
package com.vinjcent.prototype.composite;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiModelProperty;
/**
* @author vinjcent
* @description 抽象组件
* @since 2024/3/11 22:16
*/
public abstract class Component {
@ApiModelProperty("组件名称")
protected String name;
public Component(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
/**
* 组件操作
*/
public abstract void operation();
/**
* 为当前组件添加组件
*
* @param component 需要添加的组件
*/
public abstract void add(Component component);
/**
* 移除某一组件
*
* @param component 需要移除的组件
*/
public abstract void remove(Component component);
/**
* 根据下标获取子组件
*
* @param index 下标
* @return 下标对应组件
*/
public abstract Component getChild(int index);
}
3.2 叶子节点
- Leaf
package com.vinjcent.prototype.composite;
/**
* @author vinjcent
* @description 叶子节点(叶子节点下,无组件)
* @since 2024/3/11 22:20
*/
public class Leaf extends Component {
public Leaf(String name) {
super(name);
}
public void operation() {
System.out.println("Leaf " + name + " is performing operation.");
}
public void add(Component component) {
// 在叶节点中无法添加子节点,可以选择抛出异常或忽略该操作
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Unsupported operation: add");
}
public void remove(Component component) {
// 在叶节点中无法移除子节点,可以选择抛出异常或忽略该操作
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Unsupported operation: remove");
}
public Component getChild(int index) {
// 叶节点没有子节点,返回null或抛出异常
return null;
}
}
3.3 组合节点
- Composite
package com.vinjcent.prototype.composite;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiModelProperty;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author vinjcent
* @description 组合节点
* @since 2024/3/11 22:44
*/
public class Composite extends Component {
@ApiModelProperty("子节点")
private List<Component> children;
public Composite(String name) {
super(name);
children = new ArrayList<>();
}
@Override
public void operation() {
System.out.println("Composite " + name + " is performing operation.");
for (Component child : children) {
child.operation();
}
}
@Override
public void add(Component component) {
children.add(component);
}
@Override
public void remove(Component component) {
children.remove(component);
}
@Override
public Component getChild(int index) {
return children.get(index);
}
}
3.4 测试主函数
package com.vinjcent.prototype.composite;
/**
* @author vinjcent
* @description 组合模式
* @since 2024/3/11 22:51:07
*/
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 根节点
Component root = new Composite("Root");
// 叶子节点1、2
Component leaf1 = new Leaf("L. one");
Component leaf2 = new Leaf("L. two");
// 子节点1
Component node1 = new Composite("N. one");
Component leaf3 = new Leaf("L. three");
// 子节点2
Component node2 = new Composite("N. two");
Component leaf4 = new Leaf("L. four");
// 为子节点添加叶子节点
node1.add(leaf3);
node2.add(leaf4);
// 为根节点添加子节点、叶子节点
root.add(leaf1);
root.add(leaf2);
root.add(node1);
root.add(node2);
// 输出结果,相当于中序遍历
root.operation();
}
}
- 测试结果

4. 使用场景
- 部分、整体场景,如树形菜单,文件、文件夹的管理