ARM开发板实现24位BMP图片缩放
一、linux平台bmp图片缩放
最近想在ARM开发板实现BMP图片的缩放,查看了一些资料,大家部分理论知识可参考:
akynazh博主 ,这位博主程序以window平台为主进行显示,发现在linux平台下编译时有些错误,经过疯狂的修改好,终于能在linux下运行,并实现了缩放。
先放代码吧,代码就看注释了,代码名字:test.c
#include <math.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
// 文件头
struct tagBITMAPFILEHEADER {
unsigned short bfType; //
// 保存图片类型,读取时需要注释掉,文本标识符只能单独进行读写
unsigned int bfSize; // 文件大小
unsigned short bfReserved1; // 保留,设置为0
unsigned short bfReserved2; // 保留,设置为0
unsigned int bfOffBits; // 从文件头到实际的图像数据之间的字节的偏移量(没调色板的话是54)
} __attribute__((packed));
// 信息头
struct tagBITMAPINFOHEADER {
unsigned int biSize; // 此结构体的大小
unsigned int biWidth; // 图像的宽
unsigned int biHeight; // 图像的高
unsigned short biPlanes; // 颜色平面数 恒为1
unsigned short biBitCount; // 一像素所占的位数 Windows系统有8,16,24
unsigned int biCompression; // 说明图象数据压缩的类型,0为不压缩
unsigned int biSizeImage; // 图像大小, 值等于上面文件头结构中bfSize-bfOffBits
int biXPelsPerMeter; // 说明水平分辨率,用像素/米表示 一般为0
int biYPelsPerMeter; // 说明垂直分辨率,用像素/米表示 一般为0
unsigned int biClrUsed; // 说明位图实际使用的彩色表中的颜色索引数(设为0的话,则说明使用所有调色板项)
unsigned int biClrImportant; // 说明对图象显示有重要影响的颜色索引的数目
// 如果是0表示都重要
} __attribute__((packed));
// 调色板
struct tagRGBQUAND {
unsigned char r;
unsigned char g;
unsigned char b;
unsigned char rgbReserved;
} __attribute__((packed));
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
// 打开图片
char *oldPhoto = argv[1], *newPhoto = argv[3];
FILE *fp1 = fopen(oldPhoto, "r+");
double pzoom = atof(argv[2]);
printf("pzoom:%f\n", pzoom);
if (fp1 == NULL ) {
printf("Opening photos failed!\n");
if (fp1 == NULL) fclose(fp1);
return -1;
}
// 单独读取bmp图片文本标识符0x4d42
unsigned short fileType;
fread(&fileType, sizeof(unsigned short), 1, fp1);
if (fileType != 0x4d42) { // 如果不是的话证明不是bmp图片
printf("The photo is not of bmp type!\n");
return -1;
}
fseek(fp1, 0, SEEK_SET);
// 读取原图信息
struct tagBITMAPFILEHEADER fileHeader; // 原图文件头
struct tagBITMAPINFOHEADER infoHeader; // 原图消息头
fread(&fileHeader, sizeof(struct tagBITMAPFILEHEADER), 1, fp1);
fread(&infoHeader, sizeof(struct tagBITMAPINFOHEADER), 1, fp1);
int byte = infoHeader.biBitCount / 8; // 每个像素的字节数
struct tagRGBQUAND *palette = (struct tagRGBQUAND *)malloc((int)pow(2, infoHeader.biBitCount) *
4); // 分配调色板空间
if (infoHeader.biBitCount != 24) // 如果是24位图的没有调色板
fread(palette, sizeof(struct tagRGBQUAND), (int)pow(2, infoHeader.biBitCount),
fp1);
// 得到原图宽高和修改后的宽高
unsigned int oldWidth, oldHeight, newWidth, newHeight;
oldWidth = infoHeader.biWidth;
oldHeight = infoHeader.biHeight;
printf("Oldphoto's height:%d\n", oldHeight);
printf("Oldphoto's width:%d\n", oldWidth);
// 图像显示不出来原因在于图像长或宽不是4的倍数
// 下面这一步可以保证得到的宽高是4的倍数
newHeight = ((int)(oldHeight * pzoom) + 3) / 4 * 4;
newWidth = ((int)(oldWidth * pzoom) + 3) / 4 * 4;
//newHeight = (int)(oldHeight * pzoom);
//newWidth = (int)(oldWidth * pzoom);
printf("Newphoto's height:%d\n", newHeight);
printf("Newphoto's width:%d\n", newWidth);
unsigned int oldsize = oldWidth * oldHeight * byte, //byte = 3
newsize = newWidth * newHeight * byte;
// 获取原图位图数据
unsigned char *sourceData = (unsigned char *)malloc(oldsize);
if (infoHeader.biBitCount == 24)
{ // 无调色板时
fseek(fp1, 54, SEEK_SET); // 文件指针指向文件的第54个字节
fread(sourceData, oldsize, 1, fp1);
} else if (infoHeader.biBitCount ==8)
{ // 有调色板是要加上分配调色板所需要的空间
fseek(fp1, 1078, SEEK_SET); // 文件指针指向文件的第54+2^8*4=1078个字节
fread(sourceData, oldsize, 1, fp1);
}
// 修改两个header的数据并把修改后的header(及调色板信息)写入新图片中
infoHeader.biWidth = newWidth;
infoHeader.biHeight = newHeight;
if (infoHeader.biBitCount == 24) {
fileHeader.bfSize = 54 + newsize;
infoHeader.biSizeImage = newsize;
printf("fileHeader.bfSize:%#x\n", fileHeader.bfSize);
} else if (infoHeader.biBitCount == 8) {
fileHeader.bfSize = 1078 + newsize;
infoHeader.biSizeImage = newsize;
}
FILE *fp2 = fopen(newPhoto, "w+");
fseek(fp2, 0, SEEK_SET);
// fwrite(&fileType, sizeof(unsigned short), 1, fp2);
fwrite(&fileHeader, sizeof(struct tagBITMAPFILEHEADER), 1, fp2);
fwrite(&infoHeader, sizeof(struct tagBITMAPINFOHEADER), 1, fp2);
if (infoHeader.biBitCount != 24)
{
fwrite(palette, sizeof(struct tagRGBQUAND), pow(2, infoHeader.biBitCount), fp2);
printf("error\n");
}
// 使用双线性差值法进行图片缩放
double p, q;
unsigned int x1, y1, x2, y2; // 原图所在像素点的宽高
unsigned int X, Y;
unsigned char *pDestination; // 修改像素的位置(即字节偏移量)
unsigned char a, b, c;
unsigned char *pSource1=&a, *pSource2=&b; // 获取像素的位置(即字节偏移量)
unsigned char *destinationData =
(unsigned char *)malloc(newsize); // 开好新图片的位图数据所需空间
for (Y = 0; Y < newHeight; Y++) {
y1 = Y / pzoom;
y2 = Y / pzoom + 1;
q = Y / pzoom - y1;
pDestination = destinationData + Y * newWidth * byte;
pSource1 = sourceData + y1 * oldWidth * byte;
pSource2 = sourceData + y2 * oldWidth * byte;
for (X = 0; X < newWidth; X++) {
x1 = X / pzoom;
x2 = X / pzoom + 1;
p = X / pzoom - x1;
if (byte == 3) {
*(pDestination + X * byte) =
*(pSource1 + x1 * byte) * (1 - p) * (1 - q) +
*(pSource1 + x2 * byte) * p * (1 - q) +
*(pSource2 + x1 * byte) * (1 - p) * q +
*(pSource2 + x2 * byte) * p * q;
*(pDestination + X * byte + 1) =
*(pSource1 + x1 * byte + 1) * (1 - p) * (1 - q) +
*(pSource1 + x2 * byte + 1) * p * (1 - q) +
*(pSource2 + x1 * byte + 1) * (1 - p) * q +
*(pSource2 + x2 * byte + 1) * p * q;
*(pDestination + X * byte + 2) =
*(pSource1 + x1 * byte + 2) * (1 - p) * (1 - q) +
*(pSource1 + x2 * byte + 2) * p * (1 - q) +
*(pSource2 + x1 * byte + 2) * (1 - p) * q +
*(pSource2 + x2 * byte + 2) * p * q;
} else if (byte == 1) {
*(pDestination + X * byte) =
*(pSource1 + x1 * byte) * (1 - p) * (1 - q) +
*(pSource1 + x2 * byte) * p * (1 - q) +
*(pSource2 + x1 * byte) * (1 - p) * q +
*(pSource2 + x2 * byte) * p * q;
}
}
}
// 将位图数据写入新的图片并进行后续处理
fwrite(destinationData, newsize, 1, fp2);
printf("success!\n");
free(destinationData);
free(sourceData);
free(palette);
fclose(fp1);
fclose(fp2);
return 0;
}
编译时记得加上链接上数学库,编译如下:
gcc test.c -o test -lm
执行
./test aa.bmp 1.5 bb.bmp
aa.bmp:原图
1.5:放大1.5位
bb.生成的新图
原图

放大1.5倍

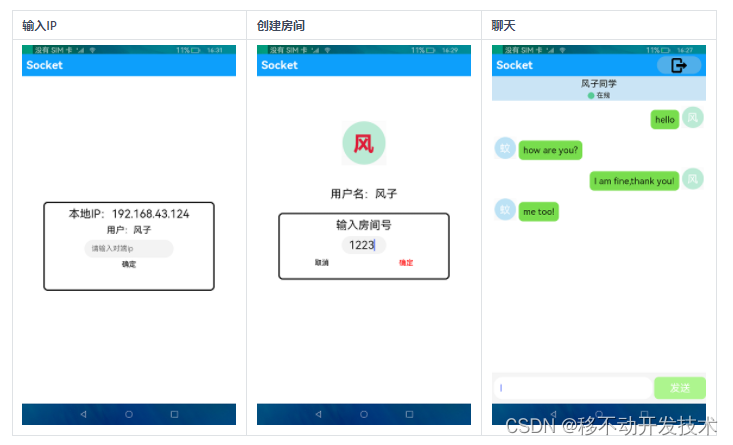
二、ARM开板显示bmp图片缩放
功能实现:通过点击Y轴坐标,实现(0.1~1倍的缩放),想要实现缩放,先了解硬件平台信息
屏幕坐标:800480
触摸屏坐标:1024600
接上来放一张800*480的24位bmp图片。

代码部分加入了触摸屏,事个程序做了较大的改变,代码proiect.c如下
#include <math.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/mman.h>
#include <linux/input.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#define LCD_PATH "/dev/fb0" //屏幕文件
#define TS_PATH "/dev/input/event0" //触摸屏文件
unsigned char *mmap_p;
int lcd_fd;
int ts_fd;
// 文件头
struct tagBITMAPFILEHEADER {
unsigned short bfType; //
// 保存图片类型,读取时需要注释掉,文本标识符只能单独进行读写
unsigned int bfSize; // 文件大小
unsigned short bfReserved1; // 保留,设置为0
unsigned short bfReserved2; // 保留,设置为0
unsigned int bfOffBits; // 从文件头到实际的图像数据之间的字节的偏移量(没调色板的话是54)
} __attribute__((packed));
// 信息头
struct tagBITMAPINFOHEADER {
unsigned int biSize; // 此结构体的大小
unsigned int biWidth; // 图像的宽
unsigned int biHeight; // 图像的高
unsigned short biPlanes; // 颜色平面数 恒为1
unsigned short biBitCount; // 一像素所占的位数 Windows系统有8,16,24
unsigned int biCompression; // 说明图象数据压缩的类型,0为不压缩
unsigned int biSizeImage; // 图像大小, 值等于上面文件头结构中bfSize-bfOffBits
int biXPelsPerMeter; // 说明水平分辨率,用像素/米表示 一般为0
int biYPelsPerMeter; // 说明垂直分辨率,用像素/米表示 一般为0
unsigned int biClrUsed; // 说明位图实际使用的彩色表中的颜色索引数(设为0的话,则说明使用所有调色板项)
unsigned int biClrImportant; // 说明对图象显示有重要影响的颜色索引的数目
// 如果是0表示都重要
} __attribute__((packed));
// 调色板
struct tagRGBQUAND {
unsigned char r;
unsigned char g;
unsigned char b;
unsigned char rgbReserved;
} __attribute__((packed));
void Lcd_Init(void);
void Lcd_Uninit(void);
void TS_Init(void);
void TS_UnInit(void);
void Get_XY(int *X, int *Y);
void Show_bmp(const char *pathname);
void Lcd_Init(void)
{
lcd_fd = open(LCD_PATH, O_RDWR);
if(lcd_fd == -1)
{
printf("open lcd failure\n");
}
//lcd映射
mmap_p = (unsigned char *)mmap(NULL,800*480*4, PROT_READ|PROT_WRITE, MAP_SHARED, lcd_fd, 0);
if(mmap == MAP_FAILED)
{
printf("mmap failure\n");
close(lcd_fd);
return ;
}
}
void Lcd_Uninit(void)
{
//撤消映射
munmap(mmap_p, 800*480*4);
close(lcd_fd);
}
void TS_Init(void)
{
ts_fd = open(TS_PATH, O_RDWR);
if(ts_fd == -1)
{
printf("open ts failure\n");
}
}
void TS_UnInit(void)
{
close(ts_fd);
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
Lcd_Init();
TS_Init();
//24位bmp格式图片。
Show_bmp("aa.bmp");
Lcd_Uninit();
TS_UnInit();
return 0;
}
void Get_XY(int *X, int *Y)
{
int xx, yy;
struct input_event ts;
//松开触摸后,再打印
while (1)
{
read(ts_fd, &ts, sizeof(struct input_event));
//判断类型
if(ts.type == EV_ABS && ts.code == ABS_X)
{
xx = ts.value;
}
if(ts.type == EV_ABS && ts.code == ABS_Y)
{
yy = ts.value;
}
//判断按下
if(ts.type == EV_KEY && ts.code == BTN_TOUCH && ts.value == 1)
{
}
//判断是否松开
if(ts.type == EV_KEY && ts.code == BTN_TOUCH && ts.value == 0)
{
//开发板坐标为800*480, 点击时得到的坐标是:1024*600,所以按比例做了缩放
*X = xx*(800.0/1024.0);
*Y = yy*(480.0/600.0);
break;
}
}
printf("X:%d, Y:%d\n", *X, *Y);
}
void Show_bmp(const char *pathname)
{
int XX, YY; //X与Y轴坐标
// 打开图片
FILE *fp1 = fopen(pathname, "r+");
if (fp1 == NULL ) {
printf("Opening photos failed!\n");
if (fp1 == NULL) fclose(fp1);
return ;
}
// 单独读取bmp图片文本标识符0x4d42
unsigned short fileType;
fread(&fileType, sizeof(unsigned short), 1, fp1);
if (fileType != 0x4d42) { // 如果不是的话证明不是bmp图片
printf("The photo is not of bmp type!\n");
return ;
}
fseek(fp1, 0, SEEK_SET);
// 读取原图信息
struct tagBITMAPFILEHEADER fileHeader; // 原图文件头
struct tagBITMAPINFOHEADER infoHeader; // 原图消息头
fread(&fileHeader, sizeof(struct tagBITMAPFILEHEADER), 1, fp1);
fread(&infoHeader, sizeof(struct tagBITMAPINFOHEADER), 1, fp1);
int byte = infoHeader.biBitCount / 8; // 每个像素的字节数
struct tagRGBQUAND *palette = (struct tagRGBQUAND *)malloc((int)pow(2, infoHeader.biBitCount) *
4); // 分配调色板空间
if (infoHeader.biBitCount != 24) // 如果是24位图的没有调色板
fread(palette, sizeof(struct tagRGBQUAND), (int)pow(2, infoHeader.biBitCount),
fp1);
// 得到原图宽高和修改后的宽高
unsigned int oldWidth, oldHeight, newWidth, newHeight;
oldWidth = infoHeader.biWidth;
oldHeight = infoHeader.biHeight;
printf("Oldphoto's height:%d\n", oldHeight);
printf("Oldphoto's width:%d\n", oldWidth);
unsigned int oldsize = oldWidth * oldHeight * byte, //byte = 3
newsize = newWidth * newHeight * byte;
// 获取原图位图数据
unsigned char *sourceData = (unsigned char *)malloc(oldsize);
if (infoHeader.biBitCount == 24)
{ // 无调色板时
fseek(fp1, 54, SEEK_SET); // 文件指针指向文件的第54个字节
fread(sourceData, oldsize, 1, fp1);
} else if (infoHeader.biBitCount ==8)
{ // 有调色板是要加上分配调色板所需要的空间
fseek(fp1, 1078, SEEK_SET); // 文件指针指向文件的第54+2^8*4=1078个字节
fread(sourceData, oldsize, 1, fp1);
}
//unsigned char *destinationData; // 开好新图片的位图数据所需空间
while(1)
{
//获取坐标
Get_XY(&XX, &YY);
//先黑屏
for(int i=0; i<800*480; i++)
{
mmap_p[4*i+0] = 0x00;
mmap_p[4*i+1] = 0x00;
mmap_p[4*i+2] = 0x00;
}
//点击右上角,退出图片绽放
if(XX > 700 && XX<800 && YY>0 && YY<100)
break;
//计算放大倍数,以YY轴坐标做为倍数,y轴坐标:0~480
//由于暂定设置的图片全屏,所以图片只能设置为缩小显示,编放比例:
double pzoom = YY/480.0;
printf("点击后的Y轴坐标:%d, 放大的倍:%0.1f\n", YY, pzoom);
if(pzoom < 0.1)
pzoom = 0.1; //最低缩小为0.1倍
// 图像显示不出来原因在于图像长或宽不是4的倍数
// 下面这一步可以保证得到的宽高是4的倍数
newHeight = ((int)(oldHeight * pzoom) + 3) / 4 * 4;
newWidth = ((int)(oldWidth * pzoom) + 3) / 4 * 4;
int start_x = (800-newWidth)/2;
int start_y = (480-newHeight)/2;
printf("start_x:%d\n", start_x);
printf("start_y:%d\n", start_y);
//newHeight = (int)(oldHeight * pzoom);
//newWidth = (int)(oldWidth * pzoom);
printf("Newphoto's height:%d\n", newHeight);
printf("Newphoto's width:%d\n", newWidth);
unsigned int oldsize = oldWidth * oldHeight * byte; //byte = 3
newsize = newWidth * newHeight * byte;
// 使用双线性差值法进行图片缩放
double p, q;
unsigned int x1, y1, x2, y2; // 原图所在像素点的宽高
unsigned int X, Y;
unsigned char a, b, c;
unsigned char *pDestination = &a; // 修改像素的位置(即字节偏移量)
unsigned char *pSource1 = &b, *pSource2 = &c; // 获取像素的位置(即字节偏移量)
//destinationData = (unsigned char *)malloc(newsize); // 开好新图片的位图数据所需空间
unsigned char destinationData[newsize];
printf("newsize:%d\n", newsize);
for (Y = 0; Y < newHeight; Y++) {
y1 = Y / pzoom;
y2 = Y / pzoom + 1;
q = Y / pzoom - y1;
pDestination = destinationData + Y * newWidth * byte;
pSource1 = sourceData + y1 * oldWidth * byte;
pSource2 = sourceData + y2 * oldWidth * byte;
for (X = 0; X < newWidth; X++) {
x1 = X / pzoom;
x2 = X / pzoom + 1;
p = X / pzoom - x1;
if (byte == 3) {
*(pDestination + X * byte) =
*(pSource1 + x1 * byte) * (1 - p) * (1 - q) +
*(pSource1 + x2 * byte) * p * (1 - q) +
*(pSource2 + x1 * byte) * (1 - p) * q +
*(pSource2 + x2 * byte) * p * q;
*(pDestination + X * byte + 1) =
*(pSource1 + x1 * byte + 1) * (1 - p) * (1 - q) +
*(pSource1 + x2 * byte + 1) * p * (1 - q) +
*(pSource2 + x1 * byte + 1) * (1 - p) * q +
*(pSource2 + x2 * byte + 1) * p * q;
*(pDestination + X * byte + 2) =
*(pSource1 + x1 * byte + 2) * (1 - p) * (1 - q) +
*(pSource1 + x2 * byte + 2) * p * (1 - q) +
*(pSource2 + x1 * byte + 2) * (1 - p) * q +
*(pSource2 + x2 * byte + 2) * p * q;
} else if (byte == 1) {
*(pDestination + X * byte) =
*(pSource1 + x1 * byte) * (1 - p) * (1 - q) +
*(pSource1 + x2 * byte) * p * (1 - q) +
*(pSource2 + x1 * byte) * (1 - p) * q +
*(pSource2 + x2 * byte) * p * q;
}
}
}
printf("zoom finish\n");
for(int yyy=0; yyy<newHeight; yyy++)
{
for(int xxx=0; xxx<newWidth; xxx++)
{
//mmap_p[(start_y+y)*800+start_x+x] = buff[(high-y)*width+x];
mmap_p[(start_y+yyy)*800*4 + 4*start_x+4*xxx + 0] = destinationData[(newHeight-1-yyy)*newWidth*3+3*xxx+2];
mmap_p[(start_y+yyy)*800*4 + 4*start_x+4*xxx + 1] = destinationData[(newHeight-1-yyy)*newWidth*3+3*xxx+1];
mmap_p[(start_y+yyy)*800*4 + 4*start_x+4*xxx + 2] = destinationData[(newHeight-1-yyy)*newWidth*3+3*xxx+0];
}
}
}
// free(destinationData);
free(sourceData);
free(palette);
fclose(fp1);
}
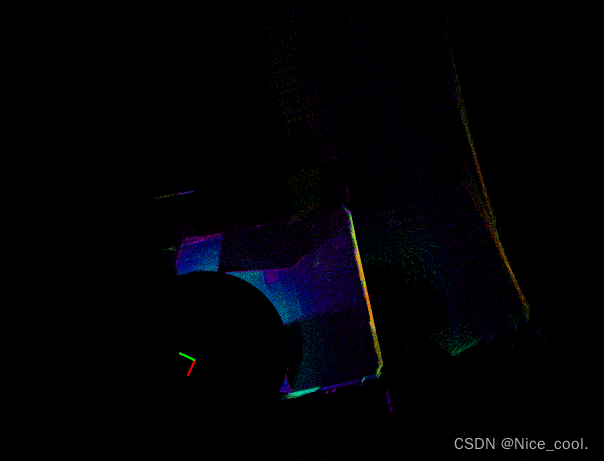
三、验证
0.4倍缩放效果


缩放0.8倍效果


就写到这里吧,程序由于要先刷新黑屏再显示图片,看起来不是很流畅,需要加入帧缓冲与多线程协同处理可解决问题。如果需要的这种写的话,看评论来吧,多了就写下。







![[蓝桥杯 2020 省 AB3] 限高杆](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/2ae712876b444a97a66fb8f9276fdd87.png)