默认的路由转换器:
| string | (缺省值) 接受任何不包含斜杠的文本 |
| int | 接受正整数 |
| float | 接受正浮点数 |
| path | 类似 string,但可以包含斜杠 |
| uuid | 接受 UUID 字符串 |
代码示例:
@app.route('/user/<username>')
def show_user_profile(username):
return 'User %s' % escape(username)
@app.route('/post/<int:post_id>')
def show_post(post_id):
return 'Post %d' % post_id
@app.route('/path/<path:subpath>')
def show_subpath(subpath):
return 'Subpath %s' % escape(subpath)自定义路由转换器:
from flask import Flask
# 导入所有转换器的基类BaseConverter
from werkzeug.routing import BaseConverter
# 生成实例对象
app = Flask(__name__)
# 创建自定义转换器 继承转换器的基类BaseConverter
class RegexConverter(BaseConverter):
# 重写构造方法传入url_map,regex
def __init__(self, url_map, regex):
super().__init__(map=url_map)
self.regex = regex
# 将定义的 RegexConverter 添加到 Flask 应用的 URL 转换器字典中,并为其分配了一个键 're'。可以在路由中使用 re:<pattern> 来使用这个转换器。
app.url_map.converters['re'] = RegexConverter
# re中传入正则表达式 校验手机号格式是11位
@app.route("/index1/<re(r'\d{11}'):mobile>")
def index1(mobile):
print(mobile)
return "Index"
if __name__ == "__main__":
app.run()注:通过app.url_map.converters['re'] = RegexConverter注册自定义转换器后,打印出的结果如下:
print(app.url_map.converters)
#结果:
{'default': <class 'werkzeug.routing.converters.UnicodeConverter'>,
'string': <class 'werkzeug.routing.converters.UnicodeConverter'>,
'any': <class 'werkzeug.routing.converters.AnyConverter'>,
'path': <class 'werkzeug.routing.converters.PathConverter'>,
'int': <class 'werkzeug.routing.converters.IntegerConverter'>,
'float': <class 'werkzeug.routing.converters.FloatConverter'>,
'uuid': <class 'werkzeug.routing.converters.UUIDConverter'>,
#自定义转换器,上面为默认转换器
're': <class '__main__.RegexConverter'>}
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
#源代码中的映射关系:
#: the default converter mapping for the map.
DEFAULT_CONVERTERS: t.Mapping[str, type[BaseConverter]] = {
"default": UnicodeConverter,
"string": UnicodeConverter,
"any": AnyConverter,
"path": PathConverter,
"int": IntegerConverter,
"float": FloatConverter,
"uuid": UUIDConverter,
}所有转换器的基类:
class BaseConverter:
# 匹配多个不包含/的字符串
regex = "[^/]+"
# 权重
weight = 100
part_isolating = True
# 类方法 子类被创建的时候会被调用
def __init_subclass__(cls, **kwargs: t.Any) -> None:
super().__init_subclass__(**kwargs)
# __dict__就是用来存储对象属性的一个字典,键是属性名,值是属性的值
# 重写了regex属性并没有重写part_isolating属性
if "regex" in cls.__dict__ and "part_isolating" not in cls.__dict__:
# 设置part_isolating 的值
cls.part_isolating = "/" not in cls.regex
# 构造方法
def __init__(self, map: Map, *args: t.Any, **kwargs: t.Any) -> None:
self.map = map
# 将 URL 中的字符串值转换为 Python 中使用的值
def to_python(self, value: str) -> t.Any:
return value
# 将 Python 中的值转换为 URL 中使用的字符串
def to_url(self, value: t.Any) -> str:
# safe = https://url.spec.whatwg.org/#url-path-segment-string
return quote(str(value), safe="!$&'()*+,/:;=@")基类中的to_python方法,可以在子类中进行重写,并按照需求将url进行处理转换成需要的值:
from flask import Flask
from werkzeug.routing import BaseConverter
app = Flask(__name__)
class RegexConverter(BaseConverter):
# 重写的to_python方法,将 URL 中的字符串值转换为 Python 中使用的值
def to_python(self, value):
# 返回参数通过+ 分割之后的数据
return value.split('+')
app.url_map.converters['re'] = RegexConverter
#http://127.0.0.1:5000/index1/12+56
@app.route("/index1/<re:info>")
def index(info):
print(info)
return "Index"
if __name__ == "__main__":
app.run()执行的结果:
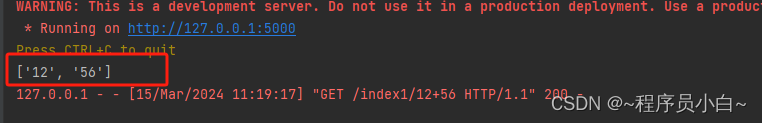

![[Python初阶]2255.统计是给定字符串前缀的字符串数目](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/e4c41b09197d4345864104e8e80af794.png)


![[MySQL]数据库基础](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/64a213090e444564a75adf2f49c4bc68.png)