一、原理分析
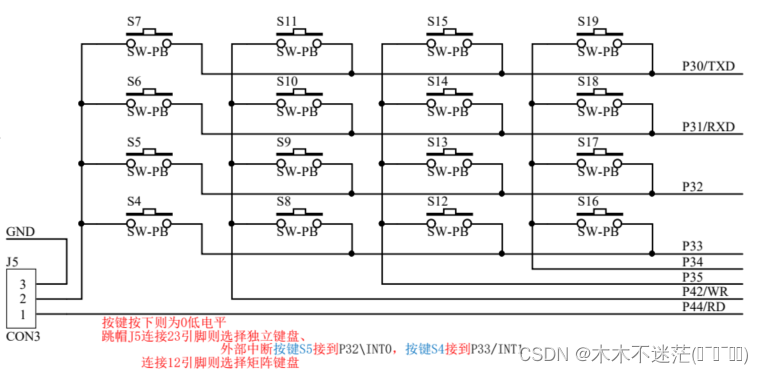
二、示例框架
-
定义了四个位控制变量,用于控制键盘扫描时的行列信号。
-
在
Scan_Keys()函数中,首先设置行列信号,将其中一个行信号置为0,另一个行信号置为1,同时将列信号置为1,用于扫描键盘按键。 -
通过逐个检测每个按键的按下情况,采取延时和松手检测的方式来判断按键是否被按下。
-
当检测到某个按键被按下后,进入相应的处理流程,可能包括等待按键松手和执行特定操作。
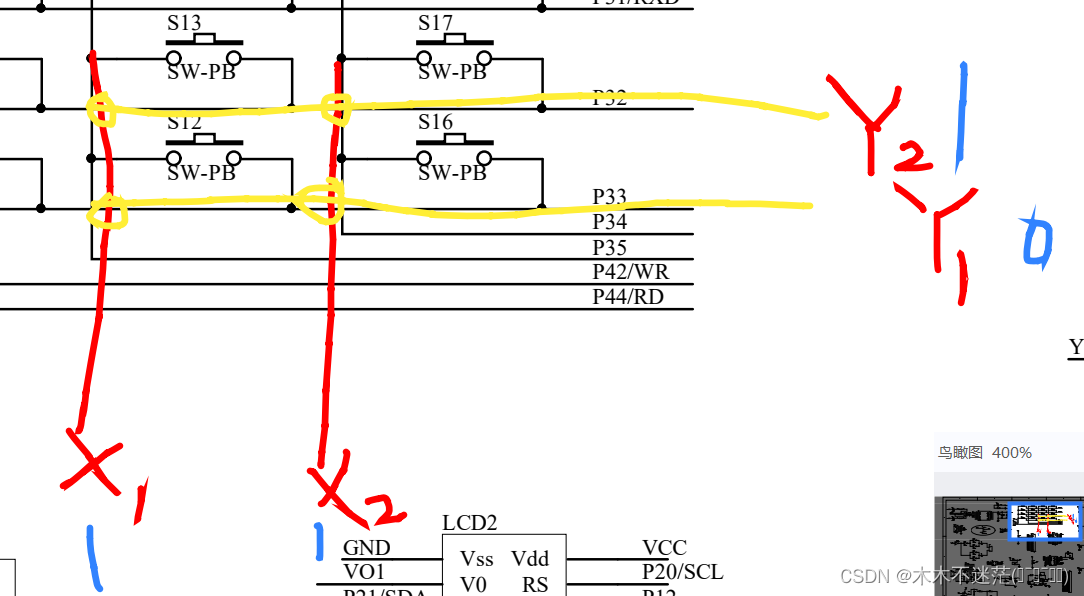
#include "key.h"
#include "delay.h"
#include "reg52.h"
sbit X1 = P3^5;
sbit X2 = P3^4;
sbit Y1 = P3^3;
sbit Y2 = P3^2;
void Scan_Keys() //扫描键盘
{
X1 = 1;
X2 = 1;
Y1 = 0;
Y2 = 1;
//扫描S12
if(X1 == 0)
{
Delay_Key(500);
if(X1 == 0)
{
while(X1 == 0) //松手检测
{
}
}
}
//扫描S16
if(X2 == 0)
{
Delay_Key(500);
if(X2 == 0)
{
while(X2 == 0) //松手检测
{
}
}
}
Y1 = 1;
Y2 = 0;
//扫描S13
if(X1 == 0)
{
Delay_Key(500);
if(X1 == 0)
{
while(X1 == 0) //松手检测
{
}
}
}
//扫描S17
if(X2 == 0)
{
Delay_Key(500);
if(X2 == 0)
{
while(X2 == 0) //松手检测
{
}
}
}
}