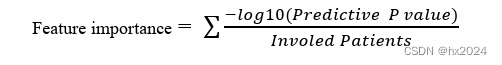《LeetCode热题100》笔记&题解&思路&技巧&优化_Part_3
- 😍😍😍 相知
- 🙌🙌🙌 相识
- 😢😢😢 开始刷题
- 链表
- 🟢1. 相交链表
- 🟢2. 反转链表
- 🟡3. 回文链表
- 🟢4. 环形链表
- 🟡5. 环形链表II
- 🟢6. 并两个有序链表
- 🟡7. 两数相加
- 🟡8. 删除链表的倒数第N个结点
- 🟡9. 两两交换链表中的节点
- 🔴10. K个一组翻转链表
- 🟡11. 随机链表的复制
- 🟡12. 排序链表
- 🔴13. 合并K个升序链表
- 🟡14. LRU缓存

😍😍😍 相知
刷题不要一上来就直接干,先看题,明白题说的什么意思,然后想一下用什么现成的算法和数据结构可以快速解决,如果还是无从下手,建议先去看视频,不要直接翻评论或官方代码实现,看完视频,自己在idea中模拟敲几遍代码,如果跑通了,先别急着上leetcode黏贴,而是再回顾一下要点,然后确定自己完全懂了后,在leetcode中手敲,注意是手敲下来!!! 目前我就是采用的这种方法,虽然慢,但是可以维持一周忘不掉它,如果要想长期不忘,只能隔段时间就review一下了,就算是大牛,知道方法,长时间不碰,也不可能保证一次到位把代码敲完一遍过!!!
🙌🙌🙌 相识
刷LeetCode热题100的想法有几个原因:
-
流行度高:LeetCode是一个广受欢迎的在线刷题平台,拥有大量用户和活跃的讨论社区。因此,热门题目通常代表了大多数人认为重要的题目或者面试中常见的题目。
-
面试备战:LeetCode上的题目往往和面试题目有很大的重合度。刷LeetCode热题100可以帮助你熟悉常见的面试题型和解题思路,提高应对面试的能力。
-
广泛的覆盖:热题100覆盖了各种难度级别的题目,包括简单、中等和困难。通过解答这些题目,可以提高自己的算法和编程能力,并扩展自己的知识面。
-
反馈和讨论:由于热题100是根据用户的反馈和讨论度排名的,因此这些题目往往有大量的解题思路和讨论可以参考。你可以从其他人的解题过程中学习到很多知识和技巧。
😢😢😢 开始刷题
链表
🟢1. 相交链表
题目链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/intersection-of-two-linked-lists/?envType=study-plan-v2&envId=top-100-liked

我们需要做的事情是,让两个链表从同距离末尾同等距离的位置开始遍历。这个位置只能是较短链表的头结点位置。
为此,我们必须消除两个链表的长度差
- 指针 pA 指向 A 链表,指针 pB 指向 B 链表,依次往后遍历
- 如果 pA 到了末尾,则 pA = headB 继续遍历
- 如果 pB 到了末尾,则 pB = headA 继续遍历
- 比较长的链表指针指向较短链表head时,长度差就消除了
- 如此,只需要将最短链表遍历两次即可找到位置

public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
if(headA==null||headB==null)return null;
ListNode tempA = headA;
ListNode tempB = headB;
while(tempA!=tempB){
tempA = tempA==null?headB:tempA.next;
tempB = tempB==null?headA:tempB.next;
}
return tempA;
}
}
🟢2. 反转链表
题目链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/reverse-linked-list/?envType=study-plan-v2&envId=top-100-liked
头插法!

/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
if(head==null||head.next == null) return head;
ListNode result = new ListNode(0);
result.next = null;
while(head!=null){
ListNode tempafter = result.next;
ListNode headtemp = head;
head = head.next;
headtemp.next = tempafter;
result.next = headtemp;
}
return result.next;
}
}
🟡3. 回文链表
题目链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/palindrome-linked-list/?envType=study-plan-v2&envId=top-100-liked
利用栈的反转功能
遍历两次,填充1次,对比一次即可
class Solution {
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
Stack<Integer> stack=new Stack<Integer>();
ListNode cur=head;
while(cur!=null){
stack.push(cur.val);
cur=cur.next;
}
while(head!=null){
if(stack.pop()!=head.val)
return false;
head=head.next;
}
return true;
}
}
🟢4. 环形链表
题目链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/linked-list-cycle/description/?envType=study-plan-v2&envId=top-100-liked
利用快慢指针
如果有环总有一天会遇到!
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
if(head==null)return false;
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
while(slow!=null)
{
if(fast.next==null) return false;
if(fast.next.next==null) return false;
if(slow.next == null) return false;
fast =fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
if(fast==slow)
{
return true;
}
}
return true;
}
}
🟡5. 环形链表II
题目链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/linked-list-cycle-ii/description/?envType=study-plan-v2&envId=top-100-liked
双指针的第一次相遇:
设两指针 fast,slow 指向链表头部 head 。
令 fast 每轮走 2 步,slow 每轮走 1 步。
执行以上两步后,可能出现两种结果:
- 第一种结果: fast 指针走过链表末端,说明链表无环,此时直接返回 null。
如果链表存在环,则双指针一定会相遇。因为每走 1 轮,fast 与 slow 的间距 +1,fast 一定会追上 slow 。
第二种结果: 当fast == slow时, 两指针在环中第一次相遇。下面分析此时 fast 与 slow 走过的步数关系:
设链表共有 a+b 个节点,其中 链表头部到链表入口 有 aaa 个节点(不计链表入口节点), 链表环 有 b 个节点(这里需要注意,aaa 和 bbb 是未知数,例如图解上链表 a=4 , b=5);设两指针分别走了 fff,sss 步,则有:
fast 走的步数是 slow 步数的 2 倍,即 f = 2s;(解析: fast 每轮走 2 步)
fast 比 slow 多走了 nnn 个环的长度,即 f = s + nb;( 解析: 双指针都走过 a 步,然后在环内绕圈直到重合,重合时 fast 比 slow 多走 环的长度整数倍 )。
将以上两式相减得到f = 2nb,s = nb,即 fast 和 slow 指针分别走了 2n,n 个环的周长。
接下来该怎么做呢?
如果让指针从链表头部一直向前走并统计步数k,那么所有 走到链表入口节点时的步数 是:k=a+nb ,即先走 aaa 步到入口节点,之后每绕 1 圈环( b 步)都会再次到入口节点。而目前 slow 指针走了 nb 步。因此,我们只要想办法让 slow 再走 a 步停下来,就可以到环的入口。
但是我们不知道 a 的值,该怎么办?依然是使用双指针法。考虑构建一个指针,此指针需要有以下性质:此指针和 slow 一起向前走 a 步后,两者在入口节点重合。那么从哪里走到入口节点需要 a 步?答案是链表头节点head。
双指针第二次相遇:
令 fast 重新指向链表头部节点。此时 f=0,s=nb 。
slow 和 fast 同时每轮向前走 1 步。
当 fast 指针走到 f=a 步时,slow 指针走到 s=a+nb 步。此时两指针重合,并同时指向链表环入口,返回 slow 指向的节点即可。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode fast = head,slow = head;
while (true) {
if (fast == null || fast.next == null) return null;
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
if (fast == slow) break;
}
fast = head;
while (slow != fast) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
}
return fast;
}
}
🟢6. 并两个有序链表
题目链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/merge-two-sorted-lists/description/?envType=study-plan-v2&envId=top-100-liked
递归法
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
if(list1==null)return list2;
if(list2==null)return list1;
if(list1.val<list2.val){
list1.next = mergeTwoLists(list1.next,list2);
return list1;
}
else{
list2.next = mergeTwoLists(list1,list2.next);
return list2;
}
}
}
🟡7. 两数相加
题目链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/add-two-numbers/?envType=study-plan-v2&envId=top-100-liked
利用进位节点。逐层相加,更新进位 而且要考虑进位不为零,2个链表不一样长等情况
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
int jinwei = 0;
ListNode temp = new ListNode(0);
ListNode temp1 = l1;
ListNode temp2 = l2;
ListNode result = temp;
while(temp1!=null|temp2!=null||jinwei!=0){
int a = temp1==null?0:temp1.val;
int b = temp2==null?0:temp2.val;
ListNode arr = new ListNode((a+b+jinwei)%10);
temp.next= arr;
temp = temp.next;
jinwei = (a+b+jinwei)/10;
temp1 = temp1==null?temp1:temp1.next;
temp2 = temp2==null?temp2:temp2.next;
}
return result.next;
}
}
🟡8. 删除链表的倒数第N个结点
题目链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-nth-node-from-end-of-list/description/?envType=study-plan-v2&envId=top-100-liked
双指针
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
ListNode result = head;
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
for(int i =0;i<n;i++){
fast = fast.next;
}
if(fast==null){
return head.next;
}
while(fast.next!=null){
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
slow.next = slow.next.next;
return head;
}
}
🟡9. 两两交换链表中的节点
题目链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/swap-nodes-in-pairs/?envType=study-plan-v2&envId=top-100-liked
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
if(head==null||head.next==null)return head;
ListNode result= new ListNode(0);
ListNode temp = result;
ListNode slow = head;
while(slow!=null&&slow.next!=null){
temp.next = slow.next;
slow.next = slow.next.next;
temp.next.next = slow;
temp = temp.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return result.next;
}
}
🔴10. K个一组翻转链表
题目链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/reverse-nodes-in-k-group/description/?envType=study-plan-v2&envId=top-100-liked
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseKGroup(ListNode head, int k) {
ListNode post = head;
for(int i = 0;i<k;i++){
if(post==null)return head;
post = post.next;
}
ListNode pre = null;
ListNode cur = head;
while(cur!=post){
ListNode temp = cur.next;
cur.next= pre;
pre = cur;
cur = temp;
}
head.next = reverseKGroup(cur,k);
return pre;
}
}
🟡11. 随机链表的复制
题目链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/copy-list-with-random-pointer/?envType=study-plan-v2&envId=top-100-liked
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
int val;
Node next;
Node random;
public Node(int val) {
this.val = val;
this.next = null;
this.random = null;
}
}
*/
class Solution {
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
Node temp = head;
HashMap <Node,Node> hashmap = new HashMap<>();
while(temp!=null){
hashmap.put(temp,new Node(temp.val));
temp = temp.next;
}
temp = head;
while(temp!=null){
hashmap.get(temp).next = hashmap.get(temp.next);
hashmap.get(temp).random = hashmap.get(temp.random);
temp = temp.next;
}
return hashmap.get(head);
}
}
🟡12. 排序链表
题目链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/sort-list/description/?envType=study-plan-v2&envId=top-100-liked
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) {
return head==null?head:mergesort(head);
}
public ListNode mergesort(ListNode head){
if(head==null||head.next == null) return head;
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode pre = null;
while(fast!=null&&fast.next!=null){
pre = slow;
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
pre.next = null;
ListNode l = mergesort(head);
ListNode r = mergesort(slow);
return mergeTwoLists(l, r);
}
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
if(list1==null)return list2;
if(list2==null)return list1;
if(list1.val<list2.val){
list1.next = mergeTwoLists(list1.next,list2);
return list1;
}
else{
list2.next = mergeTwoLists(list1,list2.next);
return list2;
}
}
}
🔴13. 合并K个升序链表
题目链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/merge-k-sorted-lists/?envType=study-plan-v2&envId=top-100-liked
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {
if(lists.length==0||(lists.length==1&&lists[0]==null))return null;
ListNode result = lists[0];
for(int i= 1;i<lists.length;i++){
result = mergeTwoLists(result,lists[i]);
}
return result;
}
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
if(list1==null)return list2;
if(list2==null)return list1;
if(list1.val<list2.val){
list1.next = mergeTwoLists(list1.next,list2);
return list1;
}
else{
list2.next = mergeTwoLists(list1,list2.next);
return list2;
}
}
}
🟡14. LRU缓存
题目链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/lru-cache/description/?envType=study-plan-v2&envId=top-100-liked
class LRUCache {
private int cap;
private Map<Integer, Integer> map = new LinkedHashMap<>();
public LRUCache(int capacity) {
this.cap = capacity;
}
public int get(int key) {
if (map.containsKey(key)) {
int val = map.get(key);
map.remove(key);
map.put(key,val);
return val;
}
return -1;
}
public void put(int key, int value) {
if (map.containsKey(key)) {
map.remove(key);
}else if (map.size() == cap){
Iterator<Map.Entry<Integer, Integer>> iterator = map.entrySet().iterator();
iterator.next();
iterator.remove();
}
map.put(key,value);
}
}
/**
* Your LRUCache object will be instantiated and called as such:
* LRUCache obj = new LRUCache(capacity);
* int param_1 = obj.get(key);
* obj.put(key,value);
*/