文章目录
- 前言
- 一、原始计时器
- 1.1 timer定时器
- timer类的介绍
- 异常安全
- 代码概况
- 1.2 progress_timer类
- 如何使用
- 异常安全
- 代码概况
- 1.3 progress_display类
- 如何使用
- 代码概况
- 总结
前言
在现代软件开发中,时间是一种不可逆转的资源。特别是在需要按时执行任务、调度事件或者处理时间敏感的应用程序中,时间管理变得至关重要。在 C++ 编程中,使用合适的工具和库来管理时间是至关重要的。Boost C++ 库提供了一个强大的定时器库,使得时间管理变得简单而灵活。
本文将探索 Boost 定时器库的用法、特性以及它如何帮助 C++ 程序员处理时间相关的任务。我们将深入了解 Boost 定时器库的核心功能,并展示如何使用它来实现各种时间相关的应用程序。
一、原始计时器
1.1 timer定时器
timer类的介绍
这个计时器就像是一个简易的砂漏,用来测量经过的时间。它适合用于一些小型的计时任务。但是,它的实现依赖于C标准库中的clock()函数,这就像是在未知的沙漏中流动的沙子一样,我们不清楚它的准确度和精度。所以,这个计时器能够测量的最长时间可能只有596.5小时(甚至更少)。由于这些限制,这个计时器并不能保证其稳定性,如果稳定性是一个考虑因素,就不应该使用它。
异常安全
构造函数可能会抛出 .没有其他成员 函数引发异常。std::bad_alloc
代码概况
#include <boost/timer.hpp>
namespace boost {
class timer {
public:
timer(); // postcondition: elapsed()==0
// compiler generated copy constructor, copy assignment, and dtor apply
void restart(); // post: elapsed()==0
double elapsed() const; // return elapsed time in seconds
double elapsed_max() const; // return estimated maximum value for elapsed()
// Portability warning: elapsed_max() may return too high a value on systems
// where std::clock_t overflows or resets at surprising values.
double elapsed_min() const; // return minimum value for elapsed()
}; // timer
} // namespace boost

timer(): 默认构造函数,创建一个计时器对象,初始时计时为0。
restart(): 重置计时器,使其重新开始计时,将已经经过的时间置为0。
elapsed() const: 返回自计时器创建或上次重置以来经过的时间,以秒为单位。
elapsed_max() const: 返回估计的计时器能够测量到的最大时间值。需要注意的是,在某些系统上,std::clock_t 的溢出或重置可能会导致该函数返回意外的值。
elapsed_min() const: 返回计时器能够测量到的最小时间值。
1.2 progress_timer类
如何使用
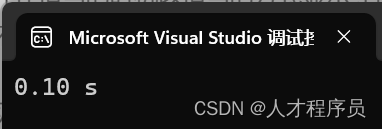
这个“进度计时器”就像是一个神奇的魔法时钟,它会自动测量时间的流逝,并在适当的时机以适当的方式显示经过的时间消息,就像是在合适的地方挂着一面时光之镜一样。它的默认实现是在std::cout上显示字符。
“进度计时器”经常用于计算程序执行的时间。它的使用就像是轻轻一挥,一切都变得简单明了:
#include <boost/progress.hpp>
int main()
{
progress_timer t; // start timing
// do something ...
Sleep(100);
return 0;
}
异常安全
构造函数可能会抛出 .没有其他成员 函数引发异常。std::bad_alloc
代码概况
#include <boost/progress.hpp>
namespace boost {
class progress_timer : public timer, noncopyable {
public:
progress_timer();
progress_timer( std::ostream& os ); // os is hint; implementation may ignore
~progress_timer();
}; // progress_display
} // namespace boost

1.3 progress_display类
如何使用
progress_display 类就像是一个可视化的指南针,它能够在适当的时机以适当的形式展示程序在达到预定目标时的进展情况。它满足了人们对程序是否在顺利进行的需求。
int main()
{
progress_display show_progress(100);
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++)
{
++show_progress;
Sleep(10);
}
return 0;
}

他的参数为进度的count
如果你想使进度条向下进行,你可以使用前置++或者+=来实现
代码概况
#include <boost/progress.hpp>
namespace boost {
class progress_display : noncopyable {
public:
progress_display( unsigned long expected_count );
// Effects: restart(expected_count)
progress_display( unsigned long expected_count,
std::ostream& os, // os is hint; implementation may ignore
const std::string & s1 = "\n", //leading strings
const std::string & s2 = "",
const std::string & s3 = "" )
// Effects: save copy of leading strings, restart(expected_count)
void restart( unsigned long expected_count );
// Effects: display appropriate scale on three lines,
// prefaced by stored copy of s1, s2, s3, respectively, from constructor
// Postconditions: count()==0, expected_count()==expected_count
unsigned long operator+=( unsigned long increment )
// Effects: Display appropriate progress tic if needed.
// Postconditions: count()== original count() + increment
// Returns: count().
unsigned long operator++()
// Returns: operator+=( 1 ).
unsigned long count() const
// Returns: The internal count.
unsigned long expected_count() const
// Returns: The expected_count from the constructor.
}; // progress_display
} // namespace boost

总结
Boost 定时器库为 C++ 开发者提供了一种强大而灵活的方式来处理时间相关的任务。通过使用 Boost 定时器库,开发者可以轻松创建、调度和管理定时任务,而无需过多的编码工作。本文介绍了 Boost 定时器库的重要性,并提供了一个简要的概述,希望读者能够进一步探索并利用 Boost 定时器库来加速他们的 C++ 开发工作。