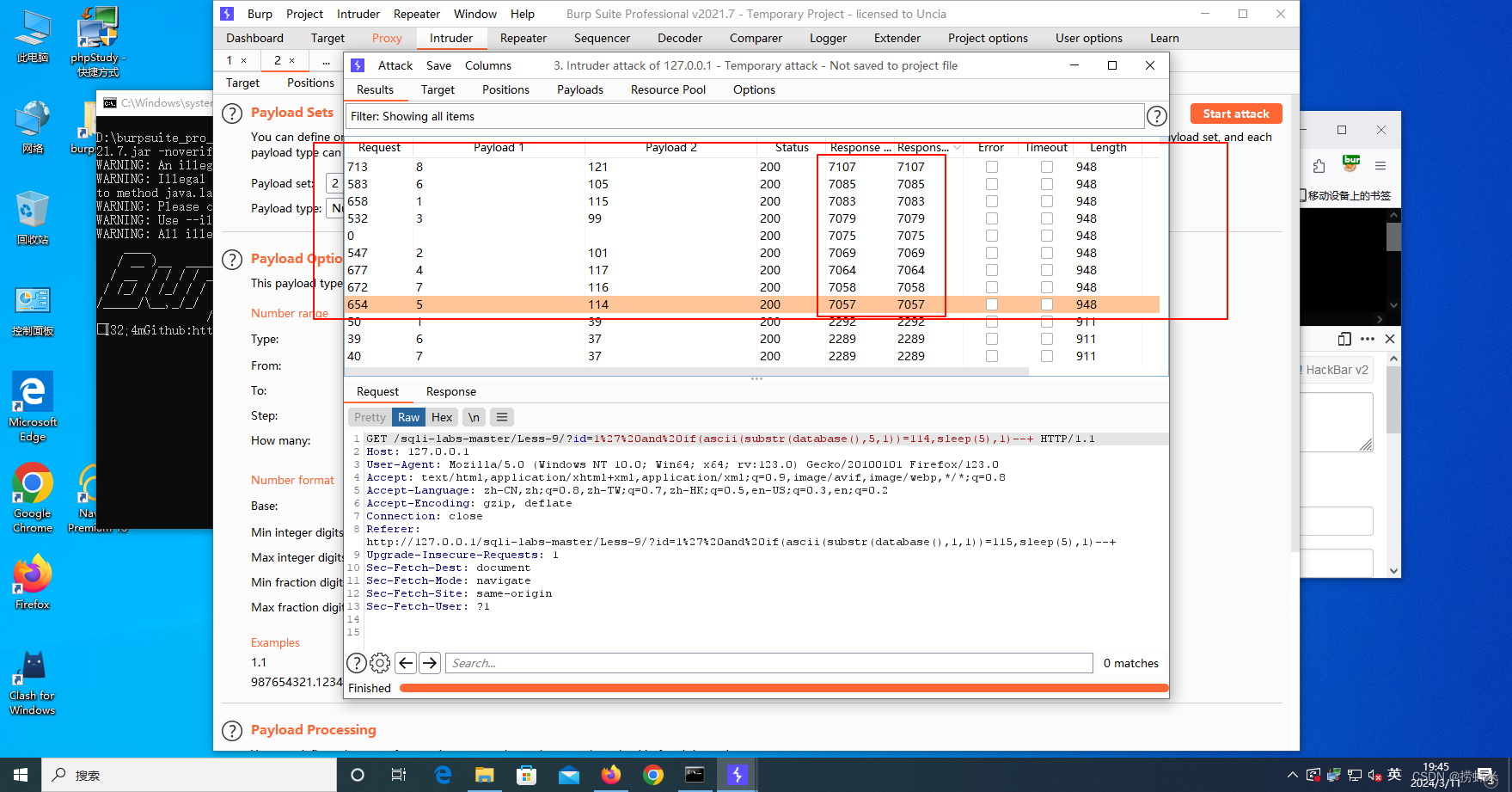
目录
汉诺塔游戏
完整游戏
后期展望
汉诺塔游戏
汉诺塔(Tower of Hanoi),是一个源于印度古老传说的益智玩具。这个传说讲述了大梵天创造世界的时候,他做了三根金刚石柱子,并在其中一根柱子上从下往上按照大小顺序摞着64片黄金圆盘。大梵天命令婆罗门将这些圆盘从下面开始按大小顺序重新摆放在另一根柱子上,并规定在小圆盘上不能放大圆盘,同时在三根柱子之间一次只能移动一个圆盘。当盘子的数量增加时,移动步骤的数量会呈指数级增长,圆盘数为n时,总步骤数steps为2^n - 1。
n = 64, steps = 2^64 - 1 = 18446744073709551616 ≈ 1.845 x 10^19
汉诺塔问题是一个递归问题,也可以使用非递归法来解决,例如使用栈来模拟递归过程。这个问题不仅是一个数学和逻辑问题,也是一个很好的教学工具,可以用来教授递归、算法和逻辑思考等概念。同时,汉诺塔游戏也具有一定的娱乐性,人们可以通过解决不同规模的汉诺塔问题来挑战自己的智力和耐心。
本篇接着上期讲下去,前2篇的链接地址:
Python 一步一步教你用pyglet制作汉诺塔游戏(续)-CSDN博客
Python 一步一步教你用pyglet制作汉诺塔游戏-CSDN博客
完整游戏
前2期代码的基础上,添加了完整的提示功能,一个汉诺塔游戏作品终于完工了,效果如下:
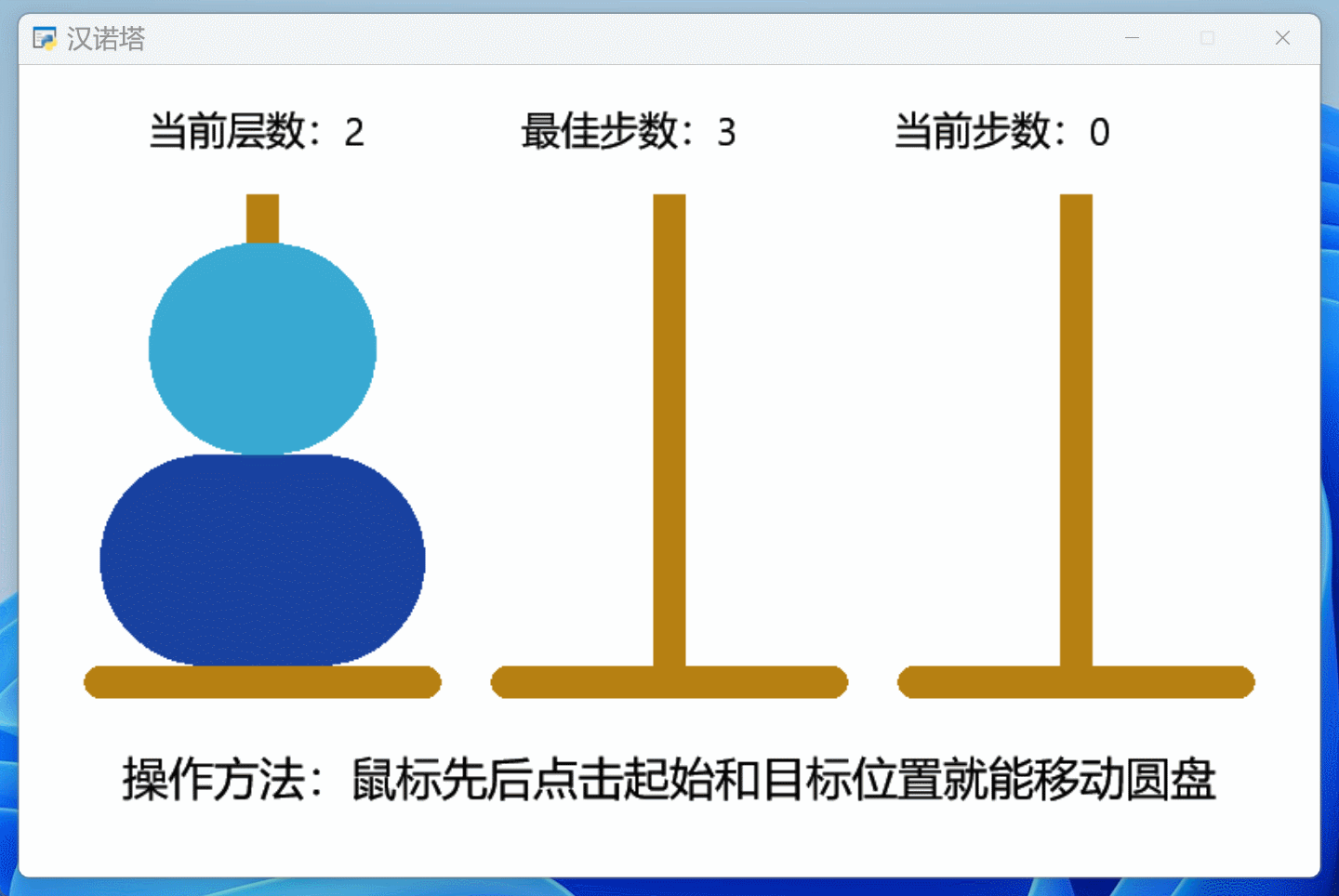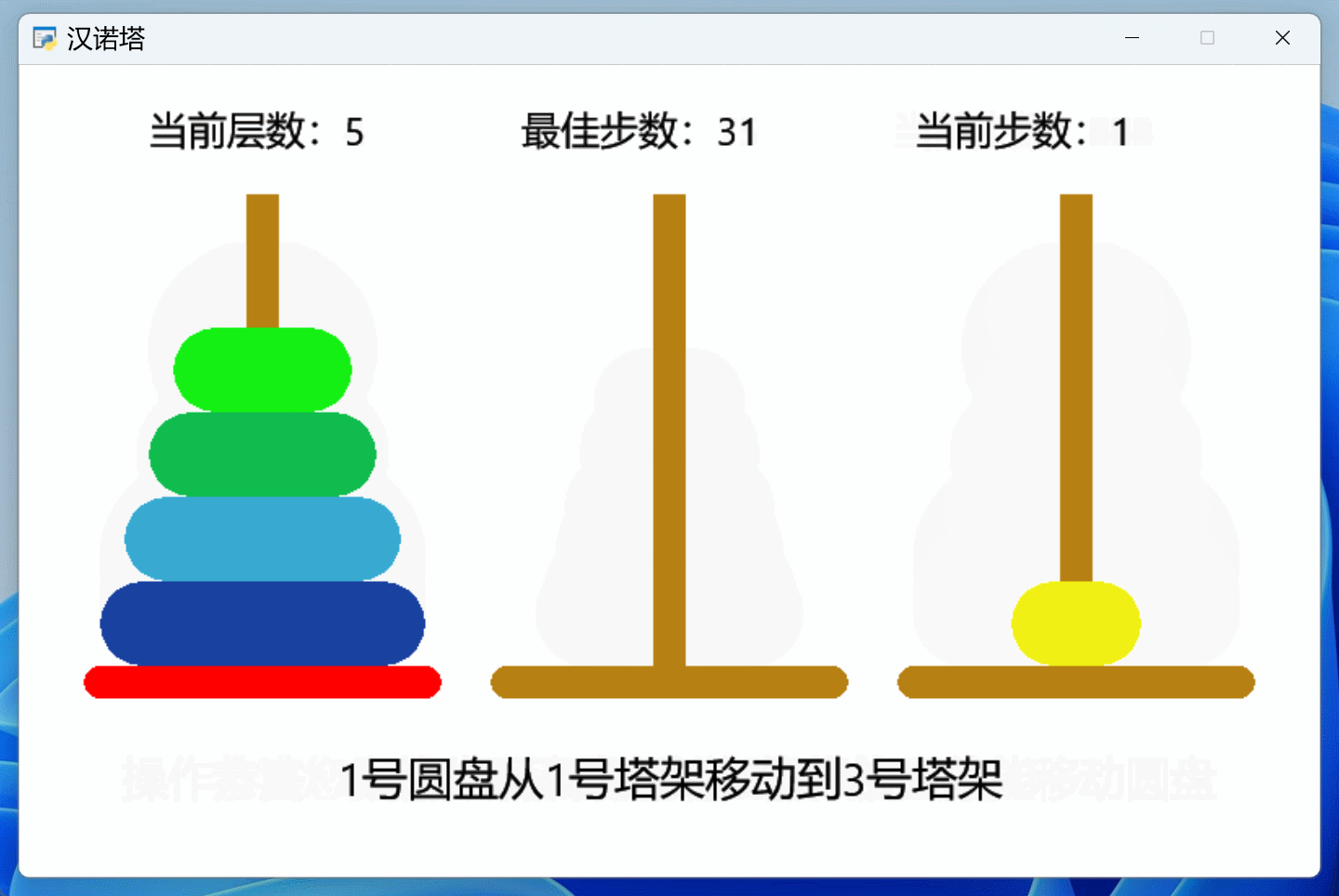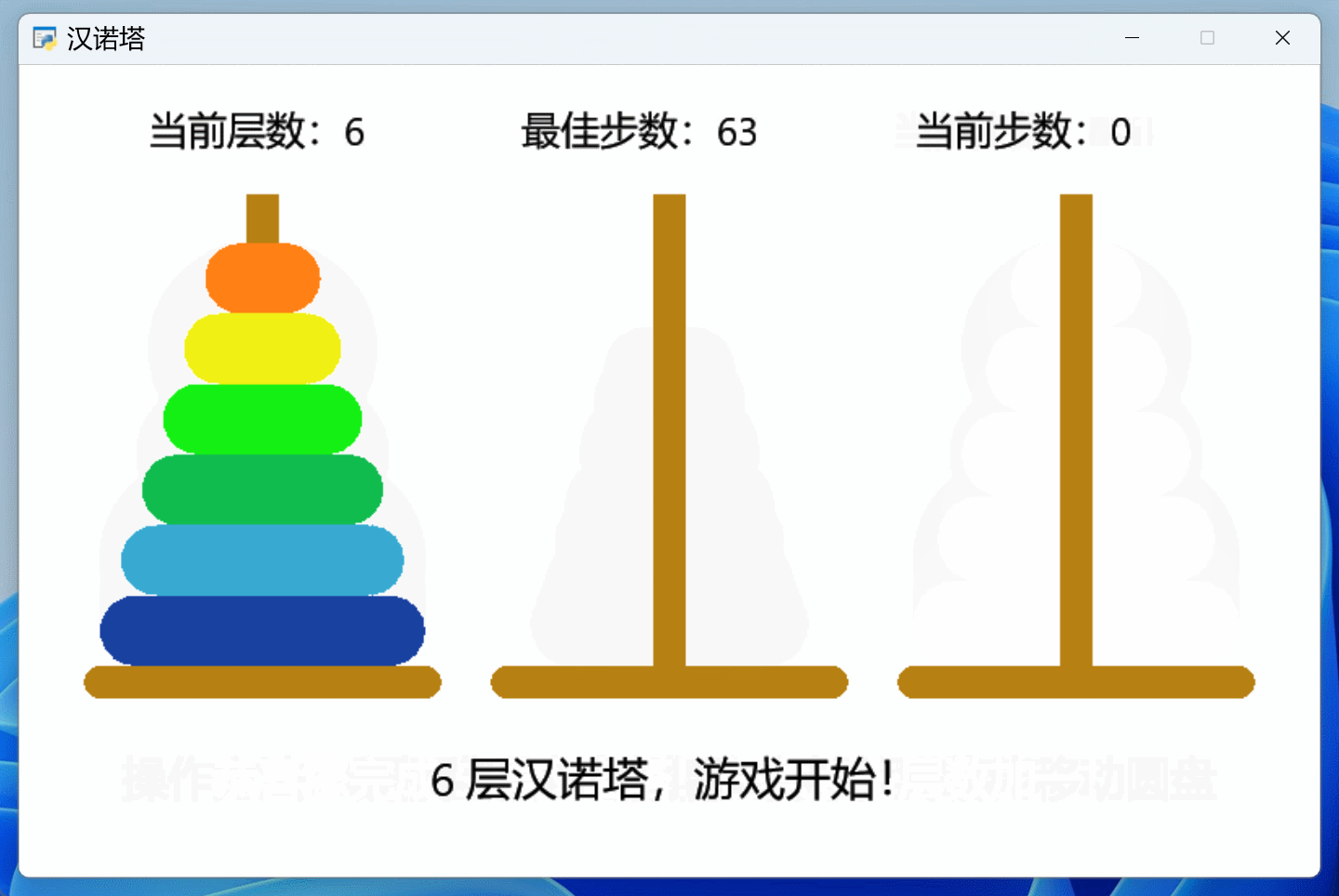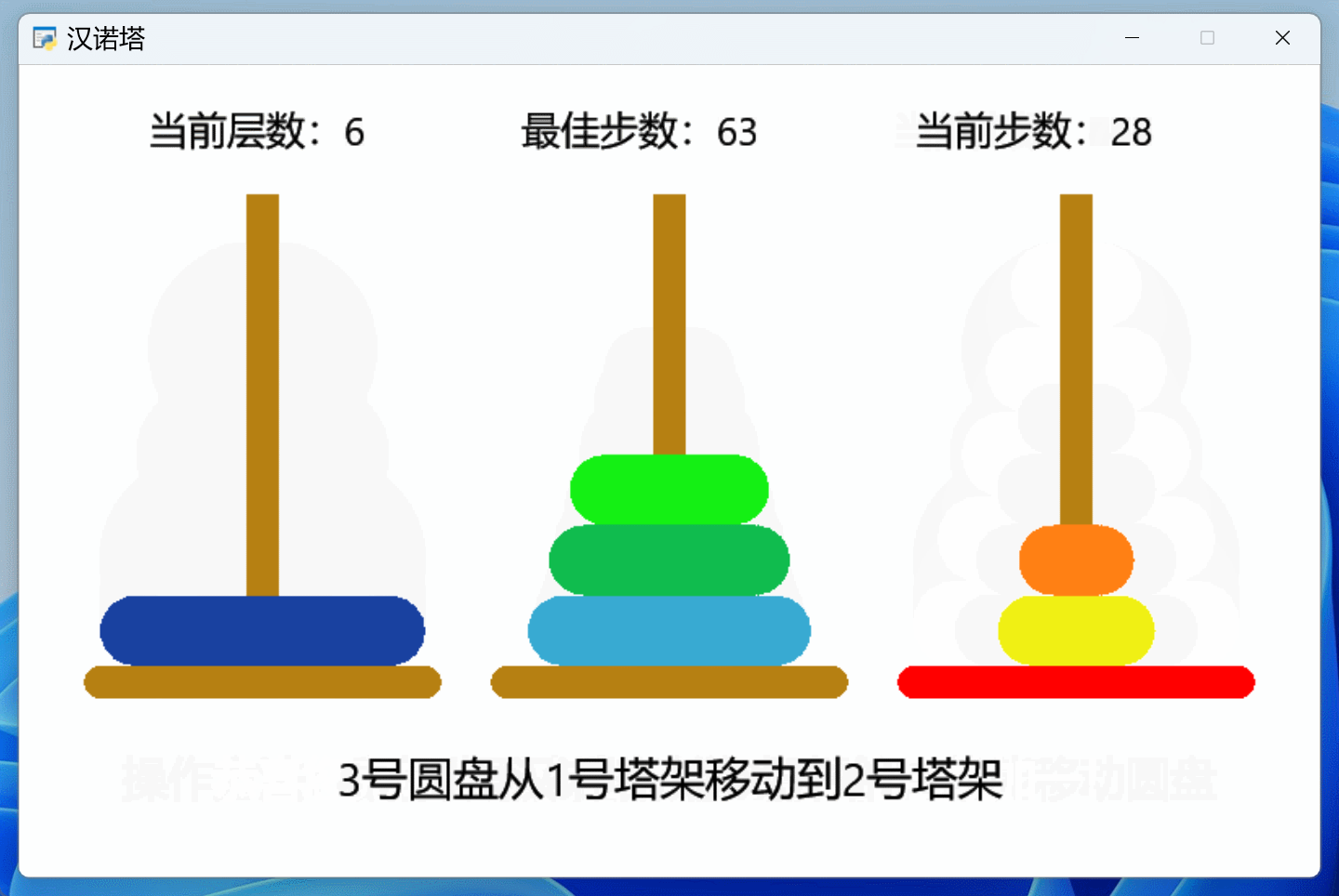
信息提示功能都放在了鼠标事件中:
@window.event
def on_mouse_press(x, y, dx, dy):
global xy, hanns, gamecompleted
if not hanns.success():
pole = hanns.on_mouse_over(x, y)
if pole is not None:
xy.append(pole)
if len(xy)==1:
hanns.setdiskcolor(xy[0], (255,0,0))
if not hanns.array[pole]:
hanns.setdiskcolor(xy[0])
xy.pop()
return
if len(xy)==2:
if xy[0]!=xy[1]:
info = hanns.move(*xy)
hanns.setdiskcolor(xy[0])
if info is False:
info1.text = '起始圆盘大于目标位置的圆盘'
elif info is None:
info1.text = '所选起始位置的塔架不能为空'
else:
info1.text = f'{hanns.order-hanns.array[xy[1]][-1]}号圆盘从{xy[0]+1}号塔架移动到{xy[1]+1}号塔架'
hanns.setdiskcolor(xy[0])
xy.clear()
info2.text = f'当前层数:{hanns.order}\t最佳步数:{2**hanns.order-1}\t当前步数:{hanns.steps}'
if hanns.success():
if hanns.order<24:
info1.text = f'恭喜您完成 {hanns.order} 层汉诺塔!任意点击层数加一!'
else:
info1.text = f'太棒了!您已完成 {hanns.order} 层汉诺塔,游戏结束!'
gamecompleted = True
return
elif not gamecompleted:
hanns = Hann(window.width/2, 120, hanns.order+1)
info1.text = f' {hanns.order} 层汉诺塔,游戏开始!'
info2.text = f'当前层数:{hanns.order}\t最佳步数:{2**hanns.order-1}\t当前步数:{hanns.steps}'
Hann 类中增加一个改色的方法,用于标注被点击的要移动的源塔架:
def setdiskcolor(self, n, color=Color[0]):
self.disk[n].cir1.color = color
self.disk[n].cir2.color = color
self.disk[n].rect.color = color
完整代码:
import pyglet
window = pyglet.window.Window(800, 500, caption='汉诺塔')
pyglet.gl.glClearColor(1, 1, 1, 1)
batch = pyglet.graphics.Batch()
Color = (182,128,18),(25,65,160),(56,170,210),(16,188,78),(20,240,20),(240,240,20),(255,128,20),(240,20,20),(245,60,138)
class Disk:
def __init__(self, x, y, color=(0,0,0), width=200, height=20):
self.cir1 = pyglet.shapes.Circle(x+width/2-height/2, y, radius=height/2, color=color, batch=batch)
self.cir2 = pyglet.shapes.Circle(x-width/2+height/2, y, radius=height/2, color=color, batch=batch)
self.rect = pyglet.shapes.Rectangle(x-width/2+height/2, y-height/2, width-height, height, color=color, batch=batch)
def move(self, dx, dy):
self.cir1.x += dx; self.cir1.y += dy
self.cir2.x += dx; self.cir2.y += dy
self.rect.x += dx; self.rect.y += dy
class Hann:
def __init__(self, x, y, order=2, space=250, thickness=20, width=200, height=300):
assert(order>1)
self.pole = [pyglet.shapes.Line(x-i*space, y, x-i*space, y+height, width=thickness, color=Color[0], batch=batch) for i in range(-1,2)]
self.disk = [Disk(x+i*space, y, color=Color[0], width=width+thickness, height=thickness) for i in range(-1,2)]
self.x, self.y = x, y
self.order = order
self.space = space
self.thickness = thickness
self.width = width
self.poleheight = height
self.beadheight = (height-thickness*2)/order
self.step = (width-thickness)/(order+1)
self.steps = 0
self.macro = []
coordinates = [(self.x-space, self.y+(i+1)*self.beadheight-(self.beadheight-thickness)/2) for i in range(order)]
self.beads = [Disk(*xy, Color[i%8+1], width=self.width-i*self.step, height=self.beadheight) for i,xy in enumerate(coordinates)]
self.array = [[*range(order)], [], []]
def move(self, pole1, pole2):
if self.array[pole1]:
bead = self.array[pole1].pop()
if self.array[pole2] and bead<self.array[pole2][-1]:
self.array[pole1].append(bead)
return False
else:
return None
self.beads[bead].move((pole2-pole1)*self.space, (len(self.array[pole2])-len(self.array[pole1]))*self.beadheight)
self.array[pole2].append(bead)
self.steps += 1
self.macro.append((pole1, pole2))
return True
def setdiskcolor(self, n, color=Color[0]):
self.disk[n].cir1.color = color
self.disk[n].cir2.color = color
self.disk[n].rect.color = color
def on_mouse_over(self, x, y):
for i in range(-1,2):
if hanns.x-hanns.width/2 < x-i*hanns.space < hanns.x+hanns.width/2 and hanns.y-hanns.thickness/2 < y < hanns.y+hanns.poleheight:
return i+1
def success(self):
return len(self.array[2]) == self.order
@window.event
def on_draw():
window.clear()
batch.draw()
@window.event
def on_mouse_press(x, y, dx, dy):
global xy, hanns, gamecompleted
if not hanns.success():
pole = hanns.on_mouse_over(x, y)
if pole is not None:
xy.append(pole)
if len(xy)==1:
hanns.setdiskcolor(xy[0], (255,0,0))
if not hanns.array[pole]:
hanns.setdiskcolor(xy[0])
xy.pop()
return
if len(xy)==2:
if xy[0]!=xy[1]:
info = hanns.move(*xy)
hanns.setdiskcolor(xy[0])
if info is False:
info1.text = '起始圆盘大于目标位置的圆盘'
elif info is None:
info1.text = '所选起始位置的塔架不能为空'
else:
info1.text = f'{hanns.order-hanns.array[xy[1]][-1]}号圆盘从{xy[0]+1}号塔架移动到{xy[1]+1}号塔架'
hanns.setdiskcolor(xy[0])
xy.clear()
info2.text = f'当前层数:{hanns.order}\t最佳步数:{2**hanns.order-1}\t当前步数:{hanns.steps}'
if hanns.success():
if hanns.order<24:
info1.text = f'恭喜您完成 {hanns.order} 层汉诺塔!任意点击层数加一!'
else:
info1.text = f'太棒了!您已完成 {hanns.order} 层汉诺塔,游戏结束!'
gamecompleted = True
return
elif not gamecompleted:
hanns = Hann(window.width/2, 120, hanns.order+1)
info1.text = f' {hanns.order} 层汉诺塔,游戏开始!'
info2.text = f'当前层数:{hanns.order}\t最佳步数:{2**hanns.order-1}\t当前步数:{hanns.steps}'
xy = []
order = 2
hanns = Hann(window.width/2, 120, order)
info1 = pyglet.text.Label('操作方法:鼠标先后点击起始和目标位置就能移动圆盘', font_size=21, color=(0,0,0,255), x=window.width/2, y=50, anchor_x='center', batch=batch)
info2 = pyglet.text.Label(f'当前层数:{order}\t最佳步数:{2**order-1}\t当前步数:0', font_size=18, color=(0,0,0,255), x=80, y=450, batch=batch)
gamecompleted = False
pyglet.app.run()
后期展望
之后有空再优化一下代码,再添加上音效、回放等功能,游戏效果会理想些。还能把上期的自动演示功能也加进去,就更加完美了。
本文完,以下仅为凑字数,请忽略:
自动演示功能,即把以下递归函数的结果展现出来即可:
def hanoi(n, start, mid, end, moves=None):
if moves is None:
moves = []
if n == 1:
moves.append((start, end))
else:
hanoi(n-1, start, end, mid, moves)
moves.append((start, end))
hanoi(n-1, mid, start, end, moves)
return moves
for order in (4,7,8):
moves = hanoi(order, 0, 1, 2)
print(len(moves)==2**order-1)
print(moves)
运行结果:
True
[(0, 1), (0, 2), (1, 2), (0, 1), (2, 0), (2, 1), (0, 1), (0, 2), (1, 2), (1, 0), (2, 0), (1, 2), (0, 1), (0, 2), (1, 2)]
True
[(0, 2), (0, 1), (2, 1), (0, 2), (1, 0), (1, 2), (0, 2), (0, 1), (2, 1), (2, 0), (1, 0), (2, 1), (0, 2), (0, 1), (2, 1), (0, 2), (1, 0), (1, 2), (0, 2), (1, 0), (2, 1), (2, 0), (1, 0), (1, 2), (0, 2), (0, 1), (2, 1), (0, 2), (1, 0), (1, 2), (0, 2), (0, 1), (2, 1), (2, 0), (1, 0), (2, 1), (0, 2), (0, 1), (2, 1), (2, 0), (1, 0), (1, 2), (0, 2), (1, 0), (2, 1), (2, 0), (1, 0), (2, 1), (0, 2), (0, 1), (2, 1), (0, 2), (1, 0), (1, 2), (0, 2), (0, 1), (2, 1), (2, 0), (1, 0), (2, 1), (0, 2), (0, 1), (2, 1), (0, 2), (1, 0), (1, 2), (0, 2), (1, 0), (2, 1), (2, 0), (1, 0), (1, 2), (0, 2), (0, 1), (2, 1), (0, 2), (1, 0), (1, 2), (0, 2), (1, 0), (2, 1), (2, 0), (1, 0), (2, 1), (0, 2), (0, 1), (2, 1), (2, 0), (1, 0), (1, 2), (0, 2), (1, 0), (2, 1), (2, 0), (1, 0), (1, 2), (0, 2), (0, 1), (2, 1), (0, 2), (1, 0), (1, 2), (0, 2), (0, 1), (2, 1), (2, 0), (1, 0), (2, 1), (0, 2), (0, 1), (2, 1), (0, 2), (1, 0), (1, 2), (0, 2), (1, 0), (2, 1), (2, 0), (1, 0), (1, 2), (0, 2), (0, 1), (2, 1), (0, 2), (1, 0), (1, 2), (0, 2)]
True
[(0, 1), (0, 2), (1, 2), (0, 1), (2, 0), (2, 1), (0, 1), (0, 2), (1, 2), (1, 0), (2, 0), (1, 2), (0, 1), (0, 2), (1, 2), (0, 1), (2, 0), (2, 1), (0, 1), (2, 0), (1, 2), (1, 0), (2, 0), (2, 1), (0, 1), (0, 2), (1, 2), (0, 1), (2, 0), (2, 1), (0, 1), (0, 2), (1, 2), (1, 0), (2, 0), (1, 2), (0, 1), (0, 2), (1, 2), (1, 0), (2, 0), (2, 1), (0, 1), (2, 0), (1, 2), (1, 0), (2, 0), (1, 2), (0, 1), (0, 2), (1, 2), (0, 1), (2, 0), (2, 1), (0, 1), (0, 2), (1, 2), (1, 0), (2, 0), (1, 2), (0, 1), (0, 2), (1, 2), (0, 1), (2, 0), (2, 1), (0, 1), (2, 0), (1, 2), (1, 0), (2, 0), (2, 1), (0, 1), (0, 2), (1, 2), (0, 1), (2, 0), (2, 1), (0, 1), (2, 0), (1, 2), (1, 0), (2, 0), (1, 2), (0, 1), (0, 2), (1, 2), (1, 0), (2, 0), (2, 1), (0, 1), (2, 0), (1, 2), (1, 0), (2, 0), (2, 1), (0, 1), (0, 2), (1, 2), (0, 1), (2, 0), (2, 1), (0, 1), (0, 2), (1, 2), (1, 0), (2, 0), (1, 2), (0, 1), (0, 2), (1, 2), (0, 1), (2, 0), (2, 1), (0, 1), (2, 0), (1, 2), (1, 0), (2, 0), (2, 1), (0, 1), (0, 2), (1, 2), (0, 1), (2, 0), (2, 1), (0, 1), (0, 2), (1, 2), (1, 0), (2, 0), (1, 2), (0, 1), (0, 2), (1, 2), (1, 0), (2, 0), (2, 1), (0, 1), (2, 0), (1, 2), (1, 0), (2, 0), (1, 2), (0, 1), (0, 2), (1, 2), (0, 1), (2, 0), (2, 1), (0, 1), (0, 2), (1, 2), (1, 0), (2, 0), (1, 2), (0, 1), (0, 2), (1, 2), (1, 0), (2, 0), (2, 1), (0, 1), (2, 0), (1, 2), (1, 0), (2, 0), (2, 1), (0, 1), (0, 2), (1, 2), (0, 1), (2, 0), (2, 1), (0, 1), (2, 0), (1, 2), (1, 0), (2, 0), (1, 2), (0, 1), (0, 2), (1, 2), (1, 0), (2, 0), (2, 1), (0, 1), (2, 0), (1, 2), (1, 0), (2, 0), (1, 2), (0, 1), (0, 2), (1, 2), (0, 1), (2, 0), (2, 1), (0, 1), (0, 2), (1, 2), (1, 0), (2, 0), (1, 2), (0, 1), (0, 2), (1, 2), (0, 1), (2, 0), (2, 1), (0, 1), (2, 0), (1, 2), (1, 0), (2, 0), (2, 1), (0, 1), (0, 2), (1, 2), (0, 1), (2, 0), (2, 1), (0, 1), (0, 2), (1, 2), (1, 0), (2, 0), (1, 2), (0, 1), (0, 2), (1, 2), (1, 0), (2, 0), (2, 1), (0, 1), (2, 0), (1, 2), (1, 0), (2, 0), (1, 2), (0, 1), (0, 2), (1, 2), (0, 1), (2, 0), (2, 1), (0, 1), (0, 2), (1, 2), (1, 0), (2, 0), (1, 2), (0, 1), (0, 2), (1, 2)]