String类实现
- 概述
- 示例
- 开发环境
- 代码
- 运行结果
- 注意
概述
本文主要记录自己实现一个String类中的部分功能。
示例
开发环境
Windows下Visual Studio 2019。
代码
MyString.h
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
class MyString{
public:
MyString();
MyString(char *p);
MyString(const char *p);
MyString(const MyString& s);
MyString(MyString&& s);
MyString& operator=(const MyString& s);
MyString& operator=(MyString&& s);
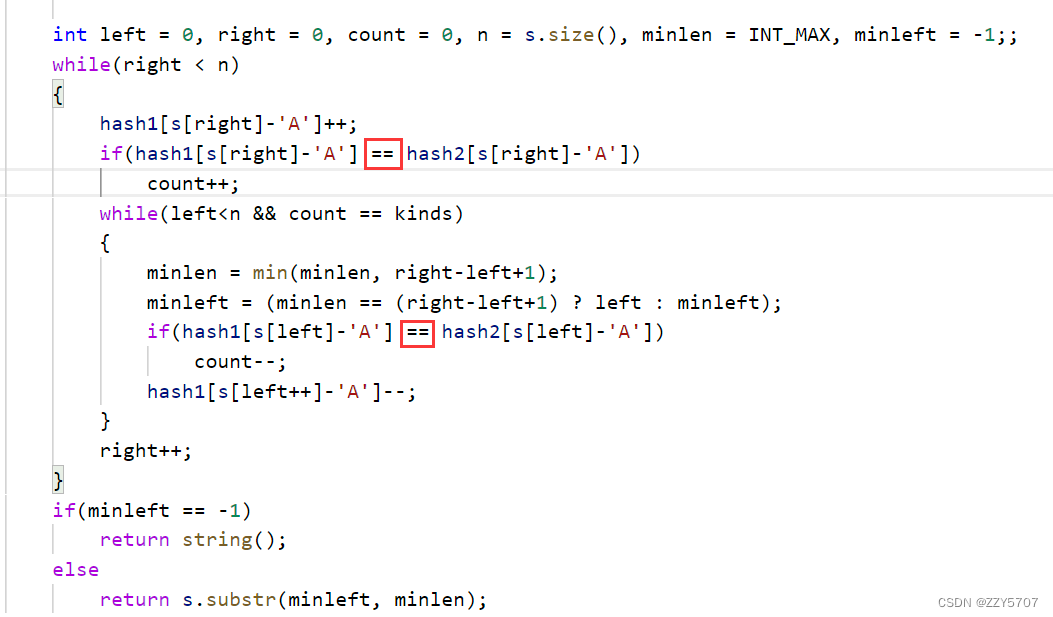
bool operator<(const MyString &s);
bool operator==(const MyString& s);
MyString& operator+=(const MyString& s);
int getLeng()const;
char getIndexCharacter(const int& index);
friend std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream & o,const MyString& s);//友元函数不是类成员函数,可访问私有成员
friend std::istream& operator>>(std::istream& i,MyString &s);
private:
char* m_pStr;
int m_len;
};
MyString.cpp
#include "MyString.h"
#include <string>
MyString::MyString():m_pStr(nullptr),m_len(0)
{
m_pStr = new char[1];
m_pStr[0] = '\0';
m_len = 1;
}
MyString::MyString(char* p)
{
if (p) {
int nLen = strlen(p);
m_pStr = new char[nLen + 1];
memset(m_pStr, 0, nLen + 1);
strcpy_s(m_pStr, nLen + 1, p);//目标缓存区的大小
m_len = nLen;
}
else {
MyString();
}
}
MyString::MyString(const char* p)
{
if(p){
int nLen = strlen(p);
m_pStr = new char[nLen +1];
memset(m_pStr,0,nLen+1);
strcpy_s(m_pStr,nLen+1,p);//目标缓存区的大小
m_len = nLen;
}
else {
MyString();
}
}
MyString::MyString(const MyString& s)
{
m_len = s.m_len;
m_pStr = new char[m_len+1];
memset(m_pStr, 0, m_len + 1);
strcpy_s(m_pStr,m_len+1 ,s.m_pStr);
m_pStr[m_len] = '\0';
}
MyString::MyString(MyString&& s)
{
m_len = s.m_len;
m_pStr = s.m_pStr;
s.m_pStr = nullptr;
s.m_len = 0;
}
MyString& MyString::operator=(const MyString& s)
{
// TODO: 在此处插入 return 语句
if (this != &s) {
m_len = s.m_len;
m_pStr = new char[m_len +1];
memset(m_pStr,0,m_len+1);
strcpy_s(m_pStr,m_len+1,s.m_pStr);
m_pStr[m_len] = '\0';
}
return *this;
}
MyString& MyString::operator=(MyString&& s)
{
// TODO: 在此处插入 return 语句
if (this != &s) {
m_len = s.m_len;
m_pStr = s.m_pStr;
s.m_len = 0;
s.m_pStr = nullptr;
}
return *this;
}
bool MyString::operator<(const MyString& s)
{
if (strcmp(m_pStr,s.m_pStr) < 0) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
bool MyString::operator==(const MyString& s)
{
if (strcmp(m_pStr,s.m_pStr) == 0) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
MyString& MyString::operator+=(const MyString& s)
{
// TODO: 在此处插入 return 语句
m_len += s.m_len;
char* pTemp = m_pStr;
m_pStr = new char[m_len+1];
memset(m_pStr,0,m_len+1);
strcpy_s(m_pStr,m_len+1,pTemp);
strcat_s(m_pStr, m_len + 1, s.m_pStr);
m_pStr[m_len] = '\0';
return *this;
}
int MyString::getLeng() const
{
return m_len;
}
char MyString::getIndexCharacter(const int& index)
{
if (index >=0 && index < m_len) {
return m_pStr[index];
}
return -1;
}
std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& o,const MyString& s)
{
// TODO: 在此处插入 return 语句
o << "字符串的长度:" << s.m_len << ",字符串:" << s.m_pStr;
return o;
}
std::istream& operator>>(std::istream& i,MyString &s)
{
// TODO: 在此处插入 return 语句
i >> s.m_len >> s.m_pStr;
return i;
}
main.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "MyString.h"
using namespace std;
int main(int argc,char *argv[]) {
MyString s;
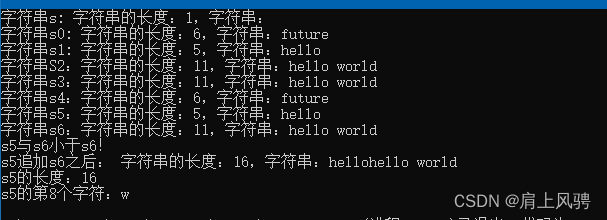
cout <<"字符串s: "<< s << endl;
const char* p = "future";
MyString s0(p);
cout << "字符串s0: " << s0 << endl;
MyString s1("hello");
cout << "字符串s1: " << s1 << endl;
char c[15] = "hello world";
MyString s2(c);
cout << "字符串S2:" << s2 << endl;
MyString s3(s2);
cout << "字符串s3:" << s3 << endl;
MyString s4(move(s0));
cout << "字符串s4:" << s4 << endl;
MyString s5 = s1;
cout << "字符串s5:" << s5 << endl;
MyString s6 = move(s2);
cout << "字符串s6:" << s6 << endl;
if (s5 == s6) {
cout << "s5与s6相等!" << endl;
}
else if(s5 <s6){
cout << "s5与s6小于s6!" << endl;
}
else {
cout << "s5与s6大于s6!" << endl;
}
s5 += s6;
cout << "s5追加s6之后: " << s5 << endl;
cout << "s5的长度:" <<s5.getLeng()<< endl;
cout << "s5的第8个字符:" << s5.getIndexCharacter(11) << endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果
注意
- 上面的示例在实现时,输入输出运算符的重载时作为友元函数来声明的,需要访问类对象的成员变量,故而含有两个参数。
一般输出、输出运算符重载都作为类的友元函数。
friend std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream & o,const MyString& s);//友元函数不是类成员函数,可访问私有成员
friend std::istream& operator>>(std::istream& i,MyString &s);
- 其中构造函数:
MyString(MyString&& s);
为移动拷贝构造函数。
- 下面的赋值运算符重载:
MyString& operator=(MyString&& s);
为移动赋值运算符重载。
参数右值引用传参的时候,使用move()。 可看上述示例调用处。
- 声明为移动构造函数和移动赋值运算符重载的好处 :
避免了深拷贝,只转移所有权,移动之后(即转移所有权之后),原来的对象中的数据被清空,但对象依旧存在。