目录
买卖股票的最佳时机
买卖股票的最佳时机III
买卖股票的最佳时机 IV
买卖股票的最佳时机 II
买卖股票的最佳时机含手续费
买卖股票的最佳时机含冷冻期
买卖股票的最佳时机
121. 买卖股票的最佳时机

buy:手上有股票的最大收益
sell:手上没有股票的最大收益
i:到第 i 天时候的最大收益
j:完成了第 j 次交易时候的最大收益

解释:图中的 -∞ 是 INT_MIN >> 1
buy[i] = max(昨天的持有时最大收益,昨天空手时最大收益)
sell[i] = max(昨天空手时最大收益,昨天持有时最大收益 + 当天可以出售获得的价格)
理解:对 i j 的理解最重要,完成0 比交易,那么buy只能买一次,后序一定是前面的某次价格最便宜的,sell 0 比交易 那就都是0 ;
对于buy完成一笔交易的第一天和第二天来说一定是 取不到的(那就初始化成-INT_MAX,右移一位,此题在buy[1][1]时候越界)因为你第一天买的要到第二天才可以卖,第三天才能重新买入
对于sell完成一笔交易也就是第二天才能有值
重点:如果对sell和buy都初始化为0,不然会在第一次交易出现问题,导致后序不对,在buy[1][1] 0元就可以手上持有股票,对应于sell来说直接就可以当天卖掉
参考代码
class Solution {
public:
int maxProfit(vector<int>& prices) {
int n = prices.size();
vector<vector<int>> buy(n, vector<int>(2, INT_MIN >> 1)), sell(n, vector<int>(2, INT_MIN >> 1));
buy[0][0] = -prices[0];
sell[0][0] = 0;
for(int i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < 2; j++)
{
buy[i][j] = max(buy[i - 1][j], sell[i - 1][j] - prices[i]);
sell[i][j] = sell[i - 1][j];
if(j == 1)
sell[i][j] = max(sell[i][j], buy[i - 1][j - 1] + prices[i]);
}
}
return max(sell[n - 1][0], sell[n - 1][1]);
}
};买卖股票的最佳时机III
123. 买卖股票的最佳时机 III


和上题一样buy[4][2] 第5天才有值,前面4天,两买两卖
参考代码
class Solution {
public:
int maxProfit(vector<int>& prices) {
int n = prices.size();
// vector<vector<int>> buy(n, vector<int>(3)), sell(n, vector<int>(3));
vector<vector<int>> buy(n, vector<int>(3, INT_MIN >> 1));
auto sell = buy;
buy[0][0] = -prices[0], sell[0][0] = 0;
for(int i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < 3; j++)
{
buy[i][j] = max(buy[i - 1][j], sell[i - 1][j] - prices[i]);
// sell[i][j] = max(sell[i - 1][j], buy[i - 1][j - 1] + prices[i]);
sell[i][j] = sell[i - 1][j];
if(j > 0)
sell[i][j] = max(sell[i][j], buy[i - 1][j - 1] + prices[i]);
}
}
return max(sell[n - 1][0], max(sell[n - 1][1], sell[n - 1][2]));
}
};买卖股票的最佳时机 IV
188. 买卖股票的最佳时机 IV

参考代码
class Solution {
public:
int maxProfit(int k, vector<int>& prices) {
int n = prices.size();
// vector<vector<int>> buy(n, vector<int>(3)), sell(n, vector<int>(3));
vector<vector<int>> buy(n, vector<int>(k + 1, INT_MIN >> 1));
auto sell = buy;
buy[0][0] = -prices[0], sell[0][0] = 0;
for(int i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j <= k; j++)
{
buy[i][j] = max(buy[i - 1][j], sell[i - 1][j] - prices[i]);
// sell[i][j] = max(sell[i - 1][j], buy[i - 1][j - 1] + prices[i]);
sell[i][j] = sell[i - 1][j];
if(j > 0)
sell[i][j] = max(sell[i][j], buy[i - 1][j - 1] + prices[i]);
}
}
int ret = 0;
for(int i = 0; i <= k; i++)
ret = max(ret, sell[n - 1][i]);
return ret;
}
};买卖股票的最佳时机 II
122. 买卖股票的最佳时机 II

区别于上三题,就是无限次数,对于无限次数的体现就是sell[i - 1] - prices[i]和buy[i - 1] + prices[i]
只能手持一个股票的体现:buy[0] = -prices[0]和buy[i - 1]

参考代码
class Solution {
public:
int maxProfit(vector<int>& prices) {
int n = prices.size();
vector<int> buy(n), sell(n);
buy[0] = - prices[0];
for(int i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
buy[i] = max(buy[i - 1], sell[i - 1] - prices[i]);
sell[i] = max(sell[i - 1], buy[i - 1] + prices[i]);
}
return sell[n - 1];
}
};买卖股票的最佳时机含手续费
714. 买卖股票的最佳时机含手续费
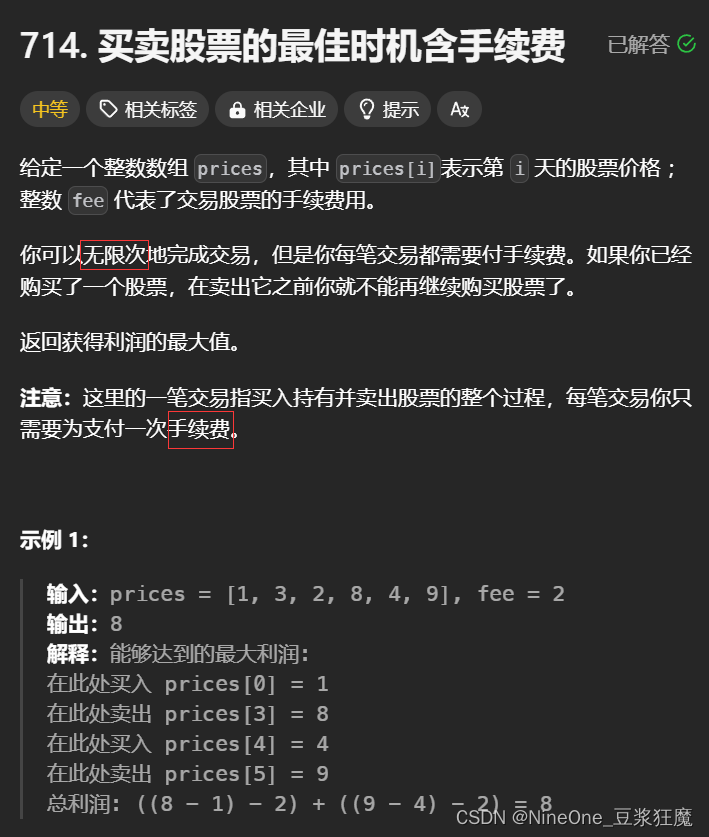
重点:对于fee的位置
①fee一定不能在buy[i - 1] 或 sell[i - 1]后面,因为这两个表示的是一个状态,不是购买或者卖出的一个点
②在购买时减掉fee:sell[i - 1] - prices[i] - 2,刚开始我只改了这里,很奇怪为什么过不了?通过样例发现结果就多了一个fee,
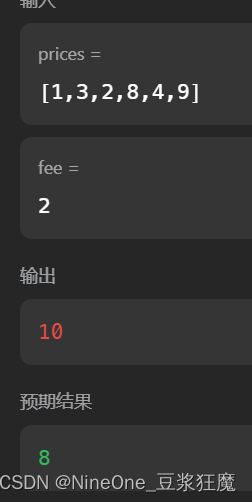
那我想着在返回的时候减掉就行,但是这时候又会返回负数
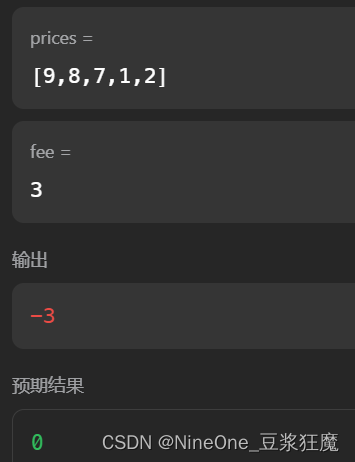
那么再改返回值:sell[n - 1] - fee >= 0 ? sell[n - 1] - fee : 0;
结果出现了不用多减fee???
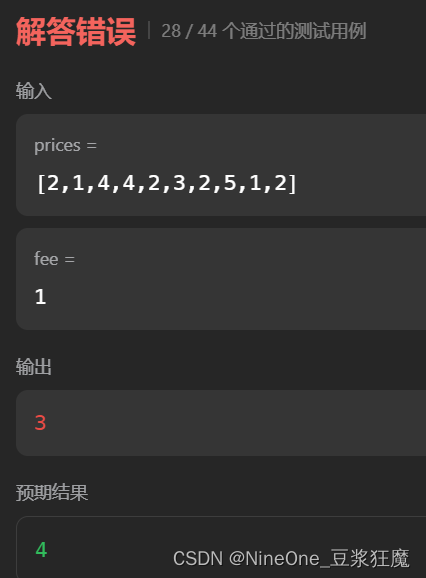
之后我终于发现了是因为buy[0]的原因,在买入的时候就要减掉fee第一次并没有减,
难点:能过的样例是因为没有用到prices[0],相同的prices不同的fee也会导致结果异常,下面的代码,发现取不到1,是比较的(-2 ,-3)了实际应该是比较(-4, -3) 这就是问题所在
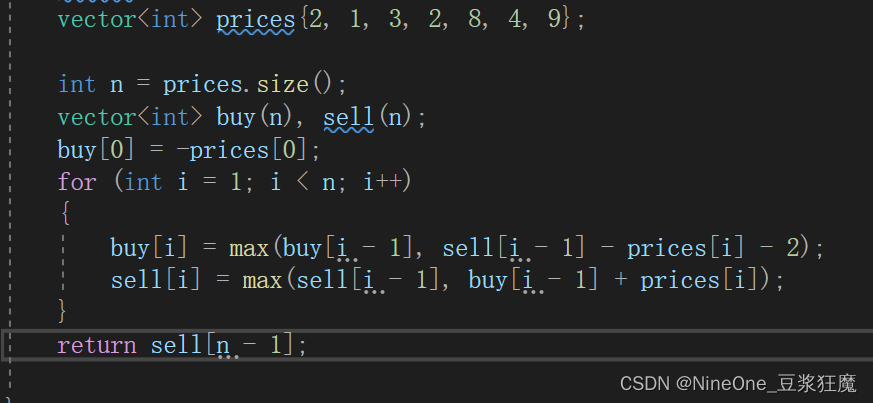
参考代码1
class Solution {
public:
int maxProfit(vector<int>& prices, int fee) {
int n = prices.size();
vector<int> buy(n), sell(n);
buy[0] = -prices[0];
for(int i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
buy[i] = max(buy[i - 1], sell[i - 1] - prices[i]);
sell[i] = max(sell[i - 1], buy[i - 1] + prices[i] - fee);
}
return sell[n - 1];
}
};参考代码2
class Solution {
public:
int maxProfit(vector<int>& prices, int fee) {
int n = prices.size();
vector<int> buy(n), sell(n);
buy[0] = -prices[0] - fee;
for(int i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
buy[i] = max(buy[i - 1], sell[i - 1] - prices[i] - fee);
sell[i] = max(sell[i - 1], buy[i - 1] + prices[i]);
}
return sell[n - 1];
}
};买卖股票的最佳时机含冷冻期
309. 买卖股票的最佳时机含冷冻期
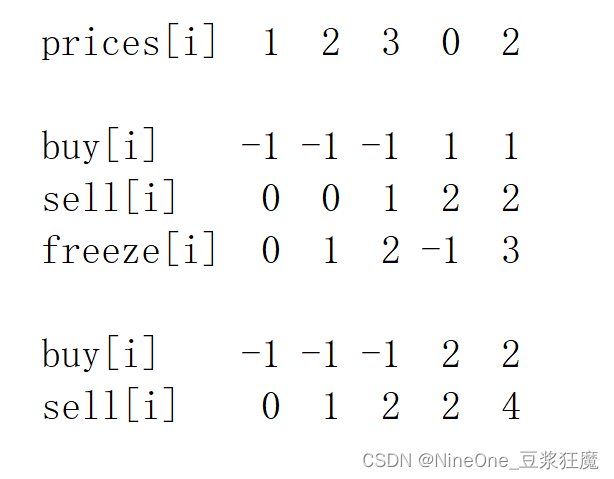
通过freeze[i - 1]来隔一天冷冻期为 1 天
参考代码
class Solution {
public:
int maxProfit(vector<int>& prices) {
int n = prices.size();
vector<int> buy(n), sell(n), freeze(n);
buy[0] = -prices[0];
for(int i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
buy[i] = max(buy[i - 1], sell[i - 1] - prices[i]);
sell[i] = max(sell[i - 1], freeze[i - 1]);
freeze[i] = buy[i - 1] + prices[i];
}
return max(sell[n - 1], freeze[n - 1]);
}
};