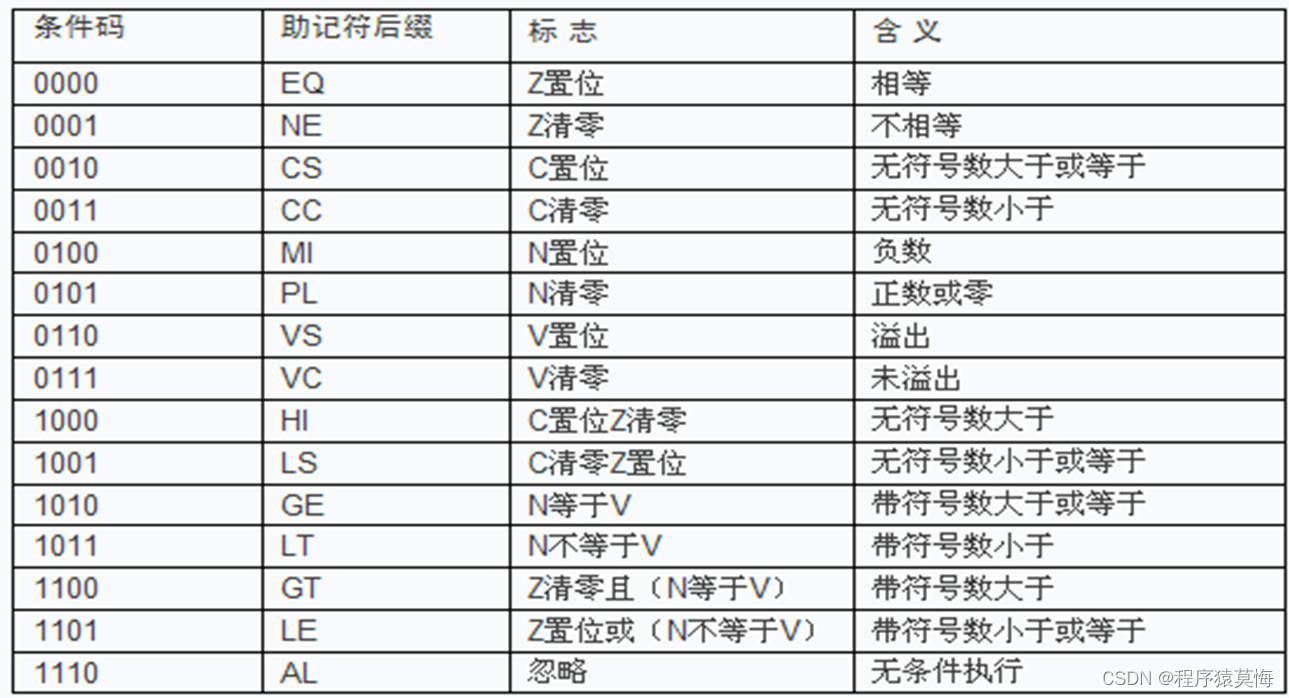
一、顺序表的概念和结构
1.1 线性表
线性表( linearlist )是n个具有相同特性的数据元素的有限序列。线性表是⼀种在实际中⼴泛使⽤的数据结构,常⻅的线性表:顺序表、链表、栈、队列、字符串...
线性表在逻辑上是线性结构,也就说是连续的⼀条直线。但是在物理结构上并不⼀定是连续的,
线性表在物理上存储时,通常以数组和链式结构的形式存储。
案例:蔬菜分为绿叶类、⽠类、菌菇类。线性表指的是具有部分相同特性的⼀类数据结构的集合
二、顺序表分类
顺序表和数组的区别
◦ 顺序表的底层结构是数组,对数组的封装,实现了常⽤的增删改查等接⼝
顺序表分类
◦ 静态顺序表
概念:使⽤定⻓数组存储元素
typedef int SLDataType
#define N 7
typedef struct SeqList{
SLDataType a[N]; //定长数组
int size; //有效数据个数
}静态顺序表缺陷:空间给少了不够⽤,给多了造成空间浪费
◦ 动态顺序表(可增容)
typedef struct SeqList{
SLDataType* a;
int size; //有效数据个数
int capacity; //空间容量
}三、动态顺序表的实现
//SeqList.h
#define INIT_CAPACITY 4
typedef int SLDataType;
// 动态顺序表 -- 按需申请
typedef struct SeqList
{
SLDataType* a;
int size; // 有效数据个数
int capacity; // 空间容量
}SL;
//初始化和销毁
void SLInit(SL* ps);
void SLDestroy(SL* ps);
void SLPrint(SL* ps);
//扩容
void SLCheckCapacity(SL* ps);
//头部插⼊删除 / 尾部插⼊删除
void SLPushBack(SL* ps, SLDataType x);
void SLPopBack(SL* ps);
void SLPushFront(SL* ps, SLDataType x);
void SLPopFront(SL* ps);
//指定位置之前插⼊/删除数据
void SLInsert(SL* ps, int pos, SLDataType x);
void SLErase(SL* ps, int pos);
int SLFind(SL* ps, SLDataType x);//SeqList.c
#include"SeqList.h"
//初始化和销毁
void SLInit(SL* ps) {
ps->arr = NULL; //不是int 而是Info类型
ps->size = ps->capacity = 0;
}
void SLCheckCapacity(SL* ps) {
if (ps->size == ps->capacity) {
int newCapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : 2 * ps->capacity;
SLDataType* tmp = (SLDataType*)realloc(ps->arr, newCapacity * sizeof(SLDataType));
if (tmp == NULL) {
perror("realloc fail!");
exit(1);
}
//扩容成功
ps->arr = tmp;
ps->capacity = newCapacity;
}
}
//顺序表的头部/尾部插入
void SLPushBack(SL* ps, SLDataType x) {
//断言--粗暴的解决方式
//assert(ps != NULL);
assert(ps);
//if判断--温柔的解决方式
//if (ps == NULL) {
// return;
//}
//空间不够,扩容
SLCheckCapacity(ps);
//空间足够,直接插入
ps->arr[ps->size++] = x;
//ps->size++;
}
void SLPushFront(SL* ps, SLDataType x) {
assert(ps);
//判断是否扩容
SLCheckCapacity(ps);
//旧数据往后挪动一位
for (int i = ps->size; i > 0; i--) //i = 1
{
ps->arr[i] = ps->arr[i - 1]; //ps->arr[1] = ps->arr[0]
}
ps->arr[0] = x;
ps->size++;
}
//顺序表的头部/尾部删除
void SLPopBack(SL* ps) {
assert(ps);
assert(ps->size);
//顺序表不为空
//ps->arr[ps->size - 1] = -1;
ps->size--;
}
void SLPopFront(SL* ps) {
assert(ps);
assert(ps->size);
//不为空执行挪动操作
for (int i = 0; i < ps->size - 1; i++)
{
ps->arr[i] = ps->arr[i + 1];
}
ps->size--;
}
//指定位置之前插入数据
void SLInsert(SL* ps, int pos, SLDataType x) {
assert(ps);
assert(pos >= 0 && pos <= ps->size);
SLCheckCapacity(ps);
//pos及之后的数据往后挪动一位,pos空出来
for (int i = ps->size; i > pos; i--)
{
ps->arr[i] = ps->arr[i - 1]; //ps->arr[pos+1] = ps->arr[pos]
}
ps->arr[pos] = x;
ps->size++;
}
//删除指定位置数据
void SLErase(SL* ps, int pos) {
assert(ps);
assert(pos >= 0 && pos < ps->size);
//pos以后的数据往前挪动一位
for (int i = pos; i < ps->size - 1; i++)
{
ps->arr[i] = ps->arr[i + 1];//ps->arr[i-2] = ps->arr[i-1];
}
ps->size--;
}
//在顺序表中查找X
//int SLFind(SL* ps, SLDataType x) {
// //加上断言对代码的健壮性更好
// assert(ps);
// for (int i = 0; i < ps->size; i++)
// {
// if (ps->arr[i] == x) {
// return i;
// }
// }
// return -1;
//}
void SLDestroy(SL* ps) {
assert(ps);
if (ps->arr) {
free(ps->arr);
}
ps->arr = NULL;
ps->size = ps->capacity = 0;
}
void SLPrint(SL* ps) {
for (int i = 0; i < ps->size; i++)
{
printf("%d ", ps->arr[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}//Contach.h
#pragma once
#define NAME_MAX 100
#define GENDER_MAX 10
#define TEL_MAX 12
#define ADDR_MAX 100
//通讯录数据类型
typedef struct personInfo {
char name[NAME_MAX];
int age;
char gender[GENDER_MAX];
char tel[TEL_MAX];
char addr[ADDR_MAX];
}Info;
//使用顺序表的前置声明
struct SeqList;
typedef struct SeqList Contact;
//通讯录的初始化和销毁
void ContactInit(Contact* pcon);//实际初始化的还是顺序表
void ContactDesTroy(Contact* pcon);
//增加、删除、修改、查找、查看通讯录
void ContactAdd(Contact* pcon);
void ContactDel(Contact* pcon);
void ContactModify(Contact* pcon);
void ContactFind(Contact* pcon);
void ContactShow(Contact* pcon);//Contact.c
#include "Contact.h"
#include "SeqList.h"
void ContactInit(Contact* pcon) {
SLInit(pcon);
}
void ContactDesTroy(Contact* pcon) {
SLDestroy(pcon);
}
//增加 删除 修改、查找、查看通讯录
void ContactAdd(Contact* pcon) {
Info info;
printf("请输入联系人的姓名:\n");
scanf("%s", info.name);
printf("请输入联系人的年龄:\n");
scanf("%d", &info.age);
printf("请输入联系人的性别:\n");
scanf("%s", info.gender);
printf("请输入联系人的电话:\n");
scanf("%s", info.tel);
printf("请输入联系人的住址:\n");
scanf("%s", info.addr);
//保存数据到通讯录
SLPushBack(pcon, info);
}
int FindByName(Contact* pcon, char name[]) {
for (int i = 0; i < pcon->size; i++) {
if (strcmp(pcon->arr[i].name, name) == 0) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
void ContactDel(Contact* pcon) {
printf("请输入你要删除的联系人姓名:\n");
char name[NAME_MAX];
scanf("%s", name);
int findIndex = FindByName(pcon, name);
if (findIndex < 0) {
printf("要删除的联系人不存在!\n");
return;
}
SLErase(pcon, findIndex);
printf("删除联系人成功!\n");
}
void ContactModify(Contact* pcon) {
printf("请输入你要修改的联系人姓名:\n");
char name[NAME_MAX];
scanf("%s", name);
int findIndex = FindByName(pcon, name);
if (findIndex < 0) {
printf("要修改的联系人不存在!\n");
return;
}
printf("请输入联系人的姓名:\n");
scanf("%s", pcon->arr[findIndex].name);
printf("请输入联系人的年龄:\n");
scanf("%d", &pcon->arr[findIndex].age);
printf("请输入联系人的性别:\n");
scanf("%s", pcon->arr[findIndex].gender);
printf("请输入联系人的电话:\n");
scanf("%s", pcon->arr[findIndex].tel);
printf("请输入联系人的住址:\n");
scanf("%s", pcon->arr[findIndex].addr);
printf("联系人修改成功!\n");
}
void ContactShow(Contact* pcon) {
printf("%s %s %s %s %s \n", "姓名", "性别", "年龄", "电话", "住址");
for (int i = 0; i < pcon->size; i++) {
printf("%s %s %d %s %s\n",
pcon->arr[i].name,
pcon->arr[i].gender,
pcon->arr[i].age,
pcon->arr[i].tel,
pcon->arr[i].addr
);
}
}
void ContactFind(Contact* pcon) {
printf("请输入你要查找的联系人姓名:\n");
char name[NAME_MAX];
scanf("%s", name);
int findIndex = FindByName(pcon, name);
if (findIndex < 0) {
printf("要查找的联系人不存在!\n");
return;
}
printf("%s %s %s %s %s \n", "姓名", "性别", "年龄", "电话", "住址");
for (int i = 0; i < pcon->size; i++) {
printf("%s %s %d %s %s\n",
pcon->arr[i].name,
pcon->arr[i].gender,
pcon->arr[i].age,
pcon->arr[i].tel,
pcon->arr[i].addr
);
}
}//test.c
#include "SeqList.h"
void menu() {
printf("************ 通讯录*******************\n");
printf("******1.添加联系人 2.删除联系人*******\n");
printf("******3.修改联系人 4.查找联系人*******\n");
printf("******5.查看通讯录 0.退出通讯录*******\n");
printf("**************************************\n");
}
int main() {
int op = -1;
Contact con;
ContactInit(&con);
do {
menu();
printf("请选择你的操作:\n");
scanf("%d", &op);
switch (op) {
case 1:
ContactAdd(&con);
break;
case 2:
ContactDel(&con);
break;
case 3:
ContactModify(&con);
break;
case 4:
ContactFind(&con);
break;
case 5:
ContactShow(&con);
break;
case 0:
printf("退出通讯录中.....\n");
default:
break;
}
} while (op);
ContactDesTroy(&con);
return 0;
}四、顺序表经典算法题
经典算法OJ题1:移除元素 27. 移除元素 - 力扣(LeetCode)![]() https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-element/
https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-element/

定义一个数组,确定两个整型变量,遍历整个数组,如果该数字等于val就看下一个数字,如果不等于就进入另一个数组中,src++ 看下一个数字 dst++找到该数组的下一个下标。
int removeElement(int* nums, int numsSize, int val) {
int dst=0,src=0;
while(src<numsSize){
if(nums[src]==val){
src++;
}
else{
nums[dst]=nums[src];
src++;
dst++;
}
}
return dst
}经典算法OJ题2:合并两个有序数组 . - 力扣(LeetCode). - 备战技术面试?力扣提供海量技术面试资源,帮助你高效提升编程技能,轻松拿下世界 IT 名企 Dream Offer。![]() https://leetcode.cn/problems/merge-sorted-array/
https://leetcode.cn/problems/merge-sorted-array/
遍历两个数组,从后向前遍历,将大的插入到数组尾部,再--,&&前面加则全为假,判断一下l2是否大于等于0,再将剩余数据导入数组中。
void merge(int* nums1, int nums1Size, int m, int* nums2, int nums2Size, int n) {
int l1=m-1;
int l2=n-1;
int l3=m+n-1;
while(l1>=0 &&l2>=0){
if(nums1[l1]>nums2[l2]){
nums1[l3]=nums1[l1];
l3--;
l1--;
}
else{
nums1[l3]=nums1[l2];
l3--;
l2--;
}
}
while(l2>=0){
nums1[l3--]=nums1[l2--];
}
}五、顺序表的问题及思考
1.中间/头部的插⼊删除,时间复杂度为O(N)
2.增容需要申请新空间,拷⻉数据,释放旧空间。会有不⼩的消耗。
3.增容⼀般是呈2倍的增⻓,势必会有⼀定的空间浪费。例如当前容量为100,满了以后增容到
200,我们再继续插⼊了5个数据,后⾯没有数据插⼊了,那么就浪费了95个数据空间。
思考:如何解决以上问题呢?
可以使用链表来实现顺序表即可解决这个问题,下集继续,请听下回将解!!!