1 基础概念
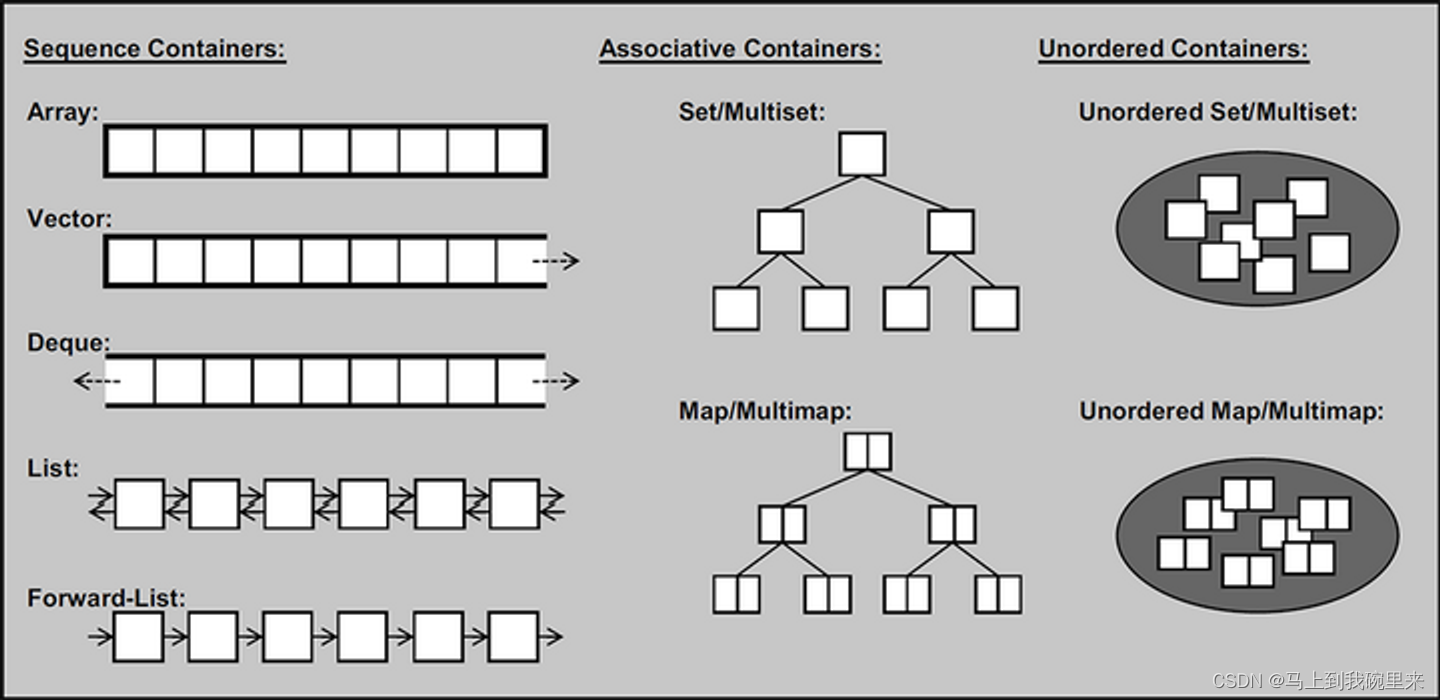
所有元素都会在插入时自动被排序
本质:
set/multiset属于关联式容器,底层结构是用二叉树实现。
set和multiset区别:
set不允许容器中有重复的元素;
multiset允许容器中有重复的元素 。
2 代码示例
Talk is cheap, show me the code.
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<set>
void printSet(const set<int>& ss)
{
for (set<int>::const_iterator it = ss.begin(); it != ss.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void printMultiset(const multiset<int>& ss)
{
for (multiset<int>::const_iterator it = ss.begin(); it != ss.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
/*
构造:
set<T> st; //默认构造函数:
set(const set &st); //拷贝构造函数
赋值:
set& operator=(const set &st); //重载等号操作符
*/
void test01()
{
set<int> s1;
s1.insert(10);
s1.insert(20);
s1.insert(30);
s1.insert(40);
printSet(s1);
set<int> s2(s1);
printSet(s2);
set<int> s3;
s3 = s2;
printSet(s3);
}
/*
大小和交换函数原型:
size(); //返回容器中元素的数目
empty(); //判断容器是否为空
swap(st); //交换两个集合容器
*/
void test02()
{
set<int> s1;
s1.insert(10);
s1.insert(20);
s1.insert(30);
s1.insert(40);
printSet(s1);
if (s1.empty())
{
cout << "Empty" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "Size: " << s1.size() << endl;
}
set<int> s2;
s2.insert(100);
cout << "交换前:" << endl;
printSet(s1);
printSet(s2);
s1.swap(s2);
cout << "交换后" << endl;
printSet(s1);
printSet(s2);
}
/*
插入和删除函数原型:
insert(elem); //在容器中插入元素。
clear(); //清除所有元素
erase(pos); //删除pos迭代器所指的元素,返回下一个元素的迭代器。
erase(beg, end); //删除区间[beg,end)的所有元素 ,返回下一个元素的迭代器。
erase(elem); //删除容器中值为elem的元素。
*/
void test03()
{
multiset<int> s1;
s1.insert(10);
s1.insert(20);
s1.insert(30);
s1.insert(40);
s1.insert(40);
s1.insert(40);
s1.insert(40);
printMultiset(s1);
s1.erase(s1.begin());
printMultiset(s1);
s1.erase(40);
printMultiset(s1);
s1.erase(s1.begin(), s1.end());
printMultiset(s1);
}
/*
查找和统计函数原型:
find(key); //查找key是否存在,若存在,返回该键的元素的迭代器;若不存在,返回set.end();
count(key); //统计key的元素个数
*/
void test04()
{
multiset<int> s1;
s1.insert(10);
s1.insert(20);
s1.insert(30);
s1.insert(40);
s1.insert(40);
s1.insert(40);
s1.insert(40);
printMultiset(s1);
multiset<int>::iterator pp = s1.find(20);
if (pp != s1.end())
{
cout << "Find It: " << *pp << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "No this element" << endl;
}
cout << s1.count(40) << endl;
}
/*
set和multiset区别:
set不可以插入重复数据,而multiset可以
set插入数据的同时会返回插入结果,表示插入是否成功
multiset不会检测数据,因此可以插入重复数据
*/
void test05()
{
set<int> s1;
pair<set<int>::iterator, bool> ret = s1.insert(10);
if (ret.second)
{
cout << "Insert OK" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "Failed!" << endl;
}
ret = s1.insert(10);
if (ret.second)
{
cout << "Insert OK" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "Failed!" << endl;
}
}
/*
pair对组创建
功能描述:
成对出现的数据,利用对组可以返回两个数据
两种创建方式:
pair<type, type> p ( value1, value2 );
pair<type, type> p = make_pair( value1, value2 );
*/
void test06()
{
pair<string, int> pp1("zhangsan", 20);
pair<string, int> pp2 = make_pair("lisi", 23);
cout << pp1.first << " " << pp1.second << endl;
cout << pp2.first << " " << pp2.second << endl;
}
/*
set容器排序:
set容器默认排序规则为从小到大,掌握如何改变排序规则
主要技术点:
利用仿函数,可以改变排序规则
*/
class Person
{
public:
Person(string name, int age)
{
this->name = name;
this->age = age;
}
string name;
int age;
};
class compareP
{
public:
bool operator()(const Person& p1, const Person& p2)const //VS2019需要在这个后面加一个const
{
return p1.age > p2.age;
}
};
void test07()
{
set<Person, compareP> s;
Person p1("刘备", 23);
Person p2("关羽", 27);
Person p3("张飞", 25);
Person p4("赵云", 21);
s.insert(p1);
s.insert(p2);
s.insert(p3);
s.insert(p4);
for (set<Person, compareP>::iterator it = s.begin(); it != s.end(); it++)
{
cout << (*it).name << " " << (*it).age << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
test07();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
3 应用场景
C++的STL(标准模板库)中的set容器是一个有序的集合,其中的元素都是唯一的。它基于红黑树实现,提供了高效的插入、删除和查找操作。在实际项目中,set容器经常用于以下场景:
-
去重操作:
当你需要从一组数据中去除重复元素时,set容器是一个理想的选择。由于set只允许存储唯一的元素,插入重复元素时不会导致集合中存在相同的值。这对于需要保持元素唯一性的情况非常有用。#include <set> #include <iostream> int main() { std::set<int> uniqueNumbers; uniqueNumbers.insert(10); uniqueNumbers.insert(20); uniqueNumbers.insert(10); // 这个插入操作不会改变集合,因为10已经存在 for (const auto& num : uniqueNumbers) { std::cout << num << " "; } return 0; } -
查找操作:
set容器提供了快速的查找操作,因为底层实现是红黑树,保证了对数时间的查找复杂度。这对于需要快速检查元素是否存在于集合中的场景非常有帮助。#include <set> #include <iostream> int main() { std::set<std::string> names = {"Alice", "Bob", "Charlie"}; std::string searchName = "Bob"; if (names.find(searchName) != names.end()) { std::cout << searchName << " found in the set." << std::endl; } else { std::cout << searchName << " not found in the set." << std::endl; } return 0; } -
有序遍历:
由于set是有序的容器,可以很容易地实现按顺序遍历元素的需求。这在需要按照一定顺序处理元素的情况下非常有用。#include <set> #include <iostream> int main() { std::set<int> numbers = {5, 2, 8, 1, 9}; for (const auto& num : numbers) { std::cout << num << " "; } return 0; }
这些是set容器在实际项目中的一些常见应用场景。根据具体需求,set还可以与其他STL容器和算法结合使用,提供更丰富的功能。
4 实际用例
假设你正在开发一个简单的单词计数应用,需要统计一段文本中不同单词的出现次数。在这种情况下,set容器可以很方便地帮助你实现去重操作,确保每个单词只被计数一次。以下是一个使用set的小demo:
#include <iostream>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <string>
#include <sstream>
int main() {
// 输入的文本
std::string text = "This is a sample text with some repeated words. This is just a demo.";
// 使用set进行去重操作
std::set<std::string> uniqueWords;
// 使用map来记录单词出现的次数
std::map<std::string, int> wordCount;
// 通过istringstream分割文本并处理单词
std::istringstream iss(text);
std::string word;
while (iss >> word) {
// 将单词插入set,确保唯一性
uniqueWords.insert(word);
// 更新单词计数
wordCount[word]++;
}
// 打印去重后的单词
std::cout << "Unique words in the text:" << std::endl;
for (const auto& uniqueWord : uniqueWords) {
std::cout << uniqueWord << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
// 打印每个单词的出现次数
std::cout << "Word count:" << std::endl;
for (const auto& pair : wordCount) {
std::cout << pair.first << ": " << pair.second << " times." << std::endl;
}
return 0;
}
在这个例子中,set容器确保了每个单词的唯一性,而map用于记录每个单词的出现次数。通过使用set,我们可以方便地获取文本中的唯一单词列表,而不必担心重复计数。这展示了set在项目中用于处理数据唯一性的优势。