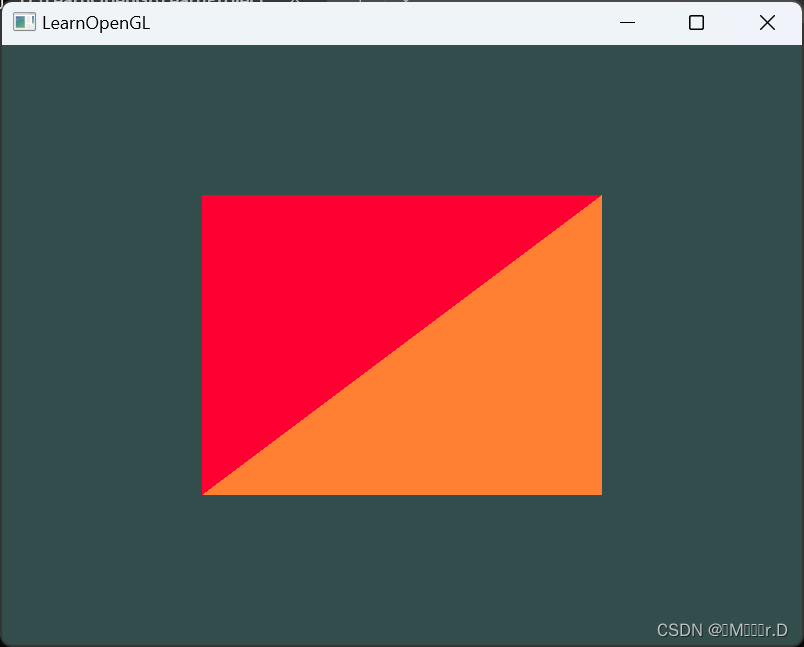
E.多重映射

解题思路
- 对集合进行整体操作,集合大小只增不减,问最后集合标号
- 维护集合,考虑并查集
- 但直接用并差集维护会有以下问题:
- 当前集合变标号,可能会和之前标号相同,则进行并查集
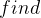 操作时,会接上之前的变换
操作时,会接上之前的变换 - 为消除其影响,考虑加入时间戳,后面新产生的标号与之前的不同
- 进行操作时,若
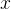 没有则跳过
没有则跳过 - 若
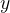 没有,则产生新的
没有,则产生新的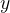 集合,
集合,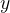 对应的时间戳
对应的时间戳
- 若有,则合并集合,时间戳不变
![fa[Node(x,tim_x)]=Node(y,tim_y)](https://latex.csdn.net/eq?fa%5BNode%28x%2Ctim_x%29%5D%3DNode%28y%2Ctim_y%29)
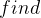 时,带上时间戳
时,带上时间戳
import java.io.*;
import java.math.BigInteger;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Objects;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
import java.util.Stack;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
//implements Runnable
public class Main{
static long md=(long)998244353;
static long Linf=Long.MAX_VALUE/2;
static int inf=Integer.MAX_VALUE/2;
static int N=2000000;
static int n=0;
static int m=0;
static
class Node{
int x;
int y;
public Node(int u,int v) {
x=u;
y=v;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Node may = (Node) o;
return x == may.x && y==may.y;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(x, y);
}
}
static HashMap<Node, Node> fa=new HashMap<Node, Node>();
static Node find(Node x) {//跟正常并查集一样
if(x.x==fa.get(x).x&&x.y==fa.get(x).y)return x;
else {
Node f=fa.get(x);
Node ff=find(f);
fa.put(f, ff);
return ff;
}
}
static int[] a=new int[N+1];
static int[] x=new int[N+1];
static int[] y=new int[N+1];
static boolean[] hs=new boolean[N+1];
static int[] t=new int[N+1];
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
AReader input=new AReader();
PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
int T=input.nextInt();
while(T>0) {
n=input.nextInt();
m=input.nextInt();
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i) {
a[i]=input.nextInt();
Node ro=new Node(a[i], 0);
fa.put(ro, ro);//初始化,重复添无影响
hs[a[i]]=true;
}
for(int i=1;i<=m;++i) {
x[i]=input.nextInt();
y[i]=input.nextInt();
Node lo=new Node(x[i], 0);
Node ro=new Node(y[i], 0);
fa.put(lo, lo);
fa.put(ro, ro);//初始化,重复添无影响
}
// out.print(fa.get(new Node(1, 0)));
for(int i=1;i<=m;++i) {
int l=x[i];
int r=y[i];
if(!hs[l])continue;
if(!hs[r]) {//与之前区别
t[r]++;
}
hs[l]=false;
hs[r]=true;
Node lo=new Node(l, t[l]);
Node ro=new Node(r, t[r]);
fa.put(lo, ro);
// out.print(fa.get(ro));
fa.put(ro, ro);//集合头自己指自己,初始化,重复添无影响
}
// out.print(fa.get(new Node(1, 0)));
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i) {
Node fx=find(new Node(a[i], 0));
out.print(fx.x+" ");
}
out.println();
//清空
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i) {
hs[a[i]]=false;
t[a[i]]=0;
}
for(int i=1;i<=m;++i) {
hs[x[i]]=false;
t[x[i]]=0;
hs[y[i]]=false;
t[y[i]]=0;
}
fa.clear();
T--;
}
out.flush();
out.close();
}
// public static final void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// new Thread(null, new Main(), "线程名字", 1 << 27).start();
// }
// @Override
// public void run() {
// try {
// //原本main函数的内容
// solve();
//
// } catch (Exception e) {
// }
// }
static
class AReader{
BufferedReader bf;
StringTokenizer st;
BufferedWriter bw;
public AReader(){
bf=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
st=new StringTokenizer("");
bw=new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
}
public String nextLine() throws IOException{
return bf.readLine();
}
public String next() throws IOException{
while(!st.hasMoreTokens()){
st=new StringTokenizer(bf.readLine());
}
return st.nextToken();
}
public char nextChar() throws IOException{
//确定下一个token只有一个字符的时候再用
return next().charAt(0);
}
public int nextInt() throws IOException{
return Integer.parseInt(next());
}
public long nextLong() throws IOException{
return Long.parseLong(next());
}
public double nextDouble() throws IOException{
return Double.parseDouble(next());
}
public float nextFloat() throws IOException{
return Float.parseFloat(next());
}
public byte nextByte() throws IOException{
return Byte.parseByte(next());
}
public short nextShort() throws IOException{
return Short.parseShort(next());
}
public BigInteger nextBigInteger() throws IOException{
return new BigInteger(next());
}
public void println() throws IOException {
bw.newLine();
}
public void println(int[] arr) throws IOException{
for (int value : arr) {
bw.write(value + " ");
}
println();
}
public void println(int l, int r, int[] arr) throws IOException{
for (int i = l; i <= r; i ++) {
bw.write(arr[i] + " ");
}
println();
}
public void println(int a) throws IOException{
bw.write(String.valueOf(a));
bw.newLine();
}
public void print(int a) throws IOException{
bw.write(String.valueOf(a));
}
public void println(String a) throws IOException{
bw.write(a);
bw.newLine();
}
public void print(String a) throws IOException{
bw.write(a);
}
public void println(long a) throws IOException{
bw.write(String.valueOf(a));
bw.newLine();
}
public void print(long a) throws IOException{
bw.write(String.valueOf(a));
}
public void println(double a) throws IOException{
bw.write(String.valueOf(a));
bw.newLine();
}
public void print(double a) throws IOException{
bw.write(String.valueOf(a));
}
public void print(char a) throws IOException{
bw.write(String.valueOf(a));
}
public void println(char a) throws IOException{
bw.write(String.valueOf(a));
bw.newLine();
}
}
}

操作时,会接上之前的变换
没有则跳过
没有,则产生新的
集合,
对应的时间戳
时,带上时间戳