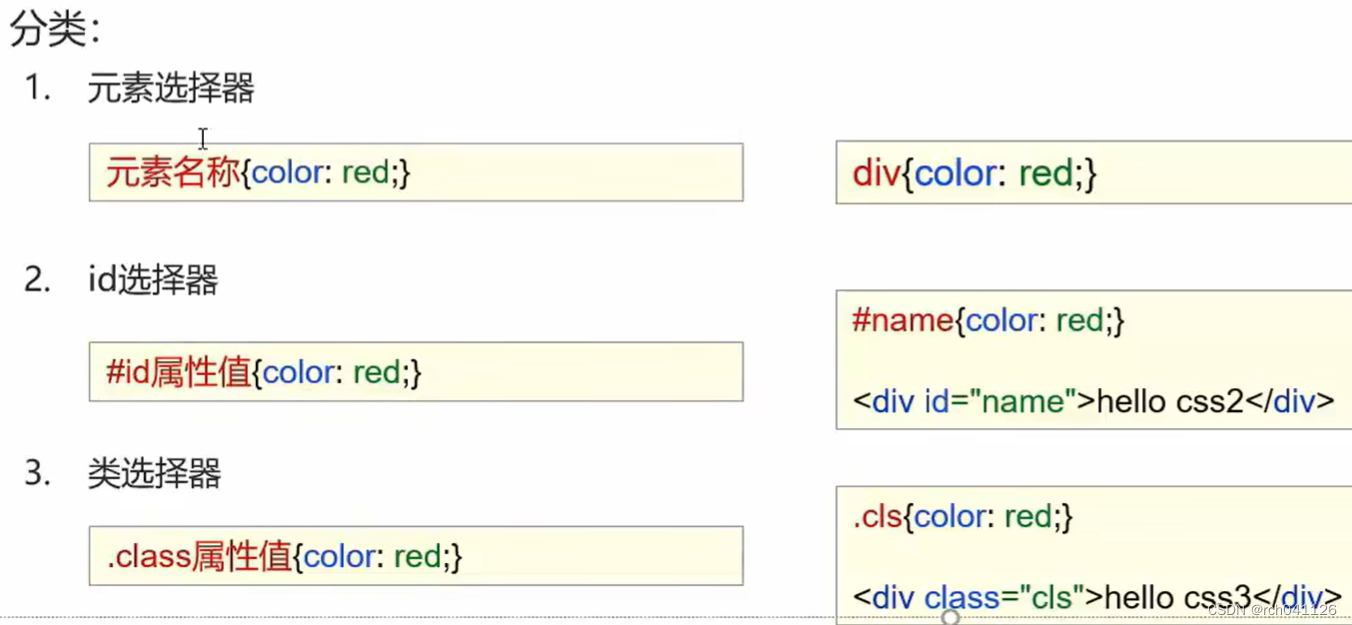
文章目录
- 二叉搜索树
- 查找
- 插入
- 删除
- 实现
- 应用
- 性能分析
二叉搜索树
二叉搜索树(BST,Binary Search Tree)又称为二叉排序树,空树也算
二叉搜索树有如下性质
- 若左子树不为空,则左子树上所有节点值小于根节点
- 若右子树不为空,则右子树上所有节点值大于根节点
- 左子树和右子树也都是二叉搜索树
例如
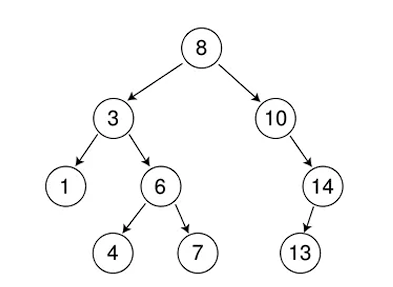
当然如果左大右小也可以
二叉搜索树的一个性质是中序遍历有序
查找
从根节点开始查找比较,比根大向右查找,比根小向左查找
最多查找高度次,如果没找到就代表值不存在
插入
如果为空,新增节点
如果不为空,按照性质插入节点
删除
首先需要确定值是否在二叉树中
要删除就右四种情况
- 无子节点——直接删除即可,可以合并到只有一个节点的情况
- 只有左节点——删除,令该节点的父节点指向左节点
- 只有右节点——删除,令该节点的父节点指向右节点
- 有两个子节点——在左子树寻找关键之最大的节点或右子树的最小节点,以最小节点为例,找到最小节点后与删除节点替换,再处理替换后的节点删除问题
实现
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
template<class K>
struct BSTreeNode // 二叉树节点,K表示关键字
{
BSTreeNode<K>* _left;
BSTreeNode<K>* _right;
K _key;
BSTreeNode(cosnt K& key)
:_left(nullptr)
,_right(nullptr)
,_key(key)
{}
};
template<class K>
class BSTree
{
typedef BSTreeNode<K> Node;
public:
// C++11
BSTree() = default; // 强制生成默认构造
~BSTree()
{
Destroy(_root);
}
BSTree(const BSTreeNode<K>& t)
{
_root = Copy(t._root);
}
BSTree<K>& operator=(BSTree<k> t)
{
swap(_root, t._root);
return *this;
}
bool Insert(const K& key) // 建树,插入
{
if (_root == nullptr) // 空树
{
_root = new Node(key);
return tree;
}
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur) // 找位置
{
parent = cur;
if (cur->_key < key)
cur = cur->_left; // 插入值比当前值小,进左树
else if (cur->_key > key)
cur = cur->_right; // 插入值比当前值大,进右树
else
return false; // 不允许出现重复值
}
cur = new Node(key);
if (parent->_key < key) // 连接父节点
parent->_right = cur;
else
parent->_left = cur;
}
bool Find(const K& key)
{
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key < key)
cur = cur->_right;
else if (cur->_key > key)
cur = cur->_left;
else
return true;
}
return false;
}
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key < key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (cur->_key > key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else // 找到了,准备删除
{
if (cur->_left == nullptr) // 左子树为空
{
// 当删除节点为根节点时,直接让根节点变为右子树即可
if (cur == _root)
{
_root = cur->_right;
}
// 当删除节点不是根节点时,需要连接父节点和右子树
else
{
// 判断当前节点是父节点的左孩子还是右孩子,确保正确连接
if (cur == parent->_left)
// 这里为什么不用防止parent是空指针呢
// 因为只有根节点没有父节点,而前面一个判断已经把根节点单独处理过了
parent->_left = cur->_right;
else
parent->_right = cur->_right;
}
delete cur;
}
else if (cur->_right == nullptr) // 右子树为空,与左子树为空类似
{
if (cur == _root)
{
_root = cur->_left;
}
else
{
if (cur == parent->_left)
parent->_left = cur->_left;
else
parent->_right = cur->_left;
}
delete cur;
}
else // 左右都不为空
{
// 找到右子树的最小节点,替换后删除
parent = cur; // 因为后面需要替换,防止出现解引用空指针
Node* SubLeft = cur->_right;
// 表示右子树最小值,他一定在右子树的最高的最左边的那个节点上
while (SubLeft->_left) // 找到该节点
{
parent = SubLeft;
SubLeft = SubLeft->_left;
}
swap(cur->_key, SubLeft->_key); // 交换节点值
// 最左节点一定是左子树为空,因此只需要父节点连接最左节点的右子树
if (SubLeft == parent->_left) // 判断该节点是父节点的左节点还是右节点,再连接
parent->_left = SubLeft->_right;
else
parent->_right = SubLeft->_right;
delete SubLeft;
}
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
void InOrder() // 中序遍历打印
{
// 中序遍历需要根节点,又不希望类外得到根节点
// 这里可以只实现一个接口,内容是private即可
// 后面的同理
_InOrder(_root);
cout << endl;
}
bool FindR(const K& key) // 递归查找
{
return _FindR(_root, key);
}
bool InsertR(const K& key)
{
return _InsertR(_root, K);
}
bool EraseR(const K& key)
{
return _EraseR(_root, key);
}
private:
Node* Copy(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return nullptr;
Node* newRoot = new Node(root->_key);
newRoot->_left = Copy(root->_left);
newRoot->_right = Copy(root->_right);
return newRoot;
}
void Destroy(Node*& root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return;
Destroy(root->_left);
Destroy(root->_right);
delete root;
root = nullptr;
}
void _InOrder(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return;
_InOrder(root->_left);
cout << root->_key << ' ';
_InOrder(root->_right);
}
bool _FindR(Node* root, const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return false;
if (root->_key < key)
return _FindR(root->_right, key);
else if (root->_key > key)
return _FindR(root->_left, key);
else
return true;
}
bool _InsertR(Node*& root, const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
// 这里的根节点是父节点左子树或者右子树的引用
// 因此直接赋值就能连接
root = new Node(key);
return true;
}
if (root->_key < key)
return _InsertR(root->_right, key);
else if (root->_key > key)
return _InsertR(root->_left, key);
else
return false;
}
bool _EraseR(Node*& root, const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return false;
if (root->_key < key)
return _EraseR(root->_right, key);
else if (root->_key > key)
return _EraseR(root->_left, key);
else
{
if (root->_left == nullptr)
{
Node* del = root;
root = root->_right; // root也是父节点左右子树的别名,因此直接赋值
delete del;
return true;
}
else if (root->_right == nullptr)
{
Node* del = root;
root = root->_left;
delete del;
return true;
}
else
{
Node* SubLeft = root->_right;
while (SubLeft->_left)
SubLeft = SubLeft->_left;
swap(root->_key, SubLeft->_key);
// 替换之后,转换成在右子树递归删除即可
return _EraseR(root->_right, key);
}
}
}
Node* _root = nullptr;
};
应用
二叉搜索树一般有两个应用
第一类是K模型,结构中只需要存储Key即可,关键之就是所需要的值,一般用于检测某个值是否存在
第二类是KV模型,结构中是<Key,Value>键值对,类似于字典
性能分析
插入和删除都必须先查找
插入的次序不同,会影响到二叉树的结构
最优情况下,二叉树为完全二叉树,其平均比较次数为 log 2 N \log_2N log2N
最差情况下,二叉树为单支树,其平均比较次数为 N 2 \frac{N}{2} 2N
因此当二叉树为单支树,我们应当如何改进,使其性能都达到最优,就需要引入AVL树和红黑树,这些我们在后面也会陆续讲解和实现



![[HackMyVM]靶场 Zeug](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/83bb609f90624bcc83f7fc7d65258617.png)