目录
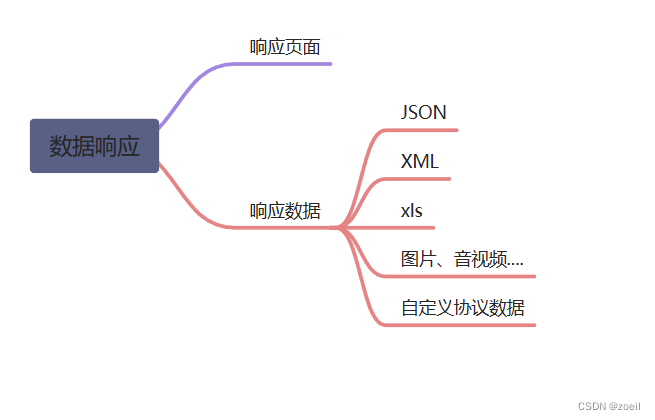
数据响应与内容协商
1、响应JSON
1.1、jackson.jar+@ResponseBody
1.2、SpringMVC到底支持哪些返回值
2、内容协商
1、引入xml依赖
2、postman分别测试返回json和xml
3、开启浏览器参数方式内容协商功能
数据响应与内容协商
1、响应JSON
1.1、jackson.jar+@ResponseBody
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
web场景自动引入了json场景

给前端自动返回json数据;
1、返回值解析器

try {
this.returnValueHandlers.handleReturnValue(
returnValue, getReturnValueType(returnValue), mavContainer, webRequest);
}
=======================================================================
@Override
public void handleReturnValue(@Nullable Object returnValue, MethodParameter returnType,
ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer, NativeWebRequest webRequest) throws Exception {
HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler handler = selectHandler(returnValue, returnType);
if (handler == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unknown return value type: " + returnType.getParameterType().getName());
}
handler.handleReturnValue(returnValue, returnType, mavContainer, webRequest);
}
========================================================================
RequestResponseBodyMethodProcessor
@Override
public void handleReturnValue(@Nullable Object returnValue, MethodParameter returnType,
ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer, NativeWebRequest webRequest)
throws IOException, HttpMediaTypeNotAcceptableException, HttpMessageNotWritableException {
mavContainer.setRequestHandled(true);
ServletServerHttpRequest inputMessage = createInputMessage(webRequest);
ServletServerHttpResponse outputMessage = createOutputMessage(webRequest);
// Try even with null return value. ResponseBodyAdvice could get involved.
// 使用消息转换器进行写出操作
writeWithMessageConverters(returnValue, returnType, inputMessage, outputMessage);
}2、返回值解析器原理

- 1、返回值处理器判断是否支持这种类型返回值 supportsReturnType
- 2、返回值处理器调用 handleReturnValue 进行处理
- 3、RequestResponseBodyMethodProcessor 可以处理返回值标了@ResponseBody 注解的。
- 1. 利用 MessageConverters 进行处理 将数据写为json
- 1、内容协商(浏览器默认会以请求头的方式告诉服务器他能接受什么样的内容类型)
- 2、服务器最终根据自己自身的能力,决定服务器能生产出什么样内容类型的数据,
- 3、SpringMVC会挨个遍历所有容器底层的 HttpMessageConverter ,看谁能处理
- 1、得到MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter可以将对象写为json
- 2、利用MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter将对象转为json再写出去。
- 1. 利用 MessageConverters 进行处理 将数据写为json
1.2、SpringMVC到底支持哪些返回值
ModelAndView
Model
View
ResponseEntity
ResponseBodyEmitter
StreamingResponseBody
HttpEntity
HttpHeaders
Callable
DeferredResult
ListenableFuture
CompletionStage
WebAsyncTask
有 @ModelAttribute 且为对象类型的
@ResponseBody 注解 ---> RequestResponseBodyMethodProcessor;
1.3、HTTPMessageConverter原理
1、MessageConverter规范

HttpMessageConverter: 看是否支持将 此 Class类型的对象,转为MediaType类型的数据。
例子:Person对象转为JSON。或者 JSON转为Person
2、默认的MessageConverter
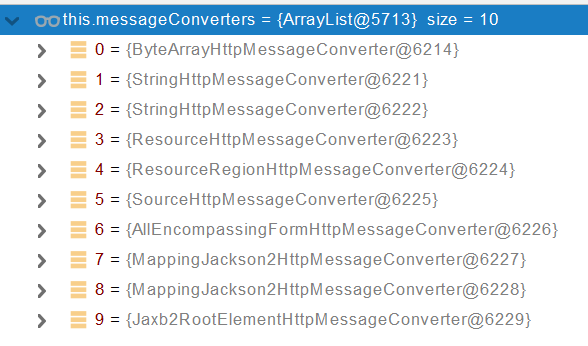
0 - 只支持Byte类型的
1 - String
2 - String
3 - Resource
4 - ResourceRegion
5 - DOMSource.class \ SAXSource.class) \ StAXSource.class \StreamSource.class \Source.class
6 - MultiValueMap
7 - true
8 - true
9 - 支持注解方式xml处理的。
最终 MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter 把对象转为JSON(利用底层的jackson的objectMapper转换的)
2、内容协商
根据客户端接收能力不同,返回不同媒体类型的数据。
1、引入xml依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.dataformat</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-dataformat-xml</artifactId>
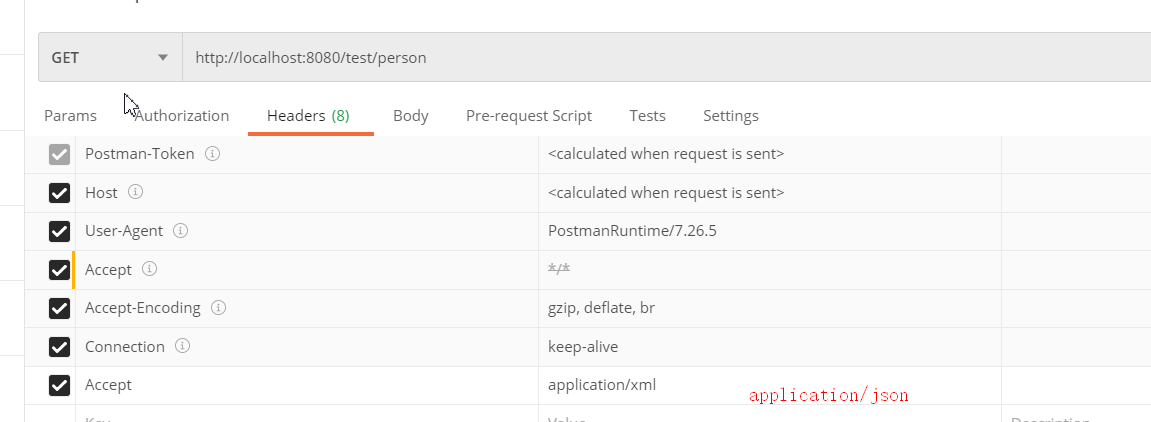
</dependency>2、postman分别测试返回json和xml
只需要改变请求头中Accept字段。Http协议中规定的,告诉服务器本客户端可以接收的数据类型。
3、开启浏览器参数方式内容协商功能
为了方便内容协商,开启基于请求参数的内容协商功能,即浏览器携带format参数指明能够接收的媒体类型。
spring:
contentnegotiation:
favor-parameter: true #开启请求参数内容协商模式例子:http://localhost:8080/test/person?format=json
http://localhost:8080/test/person?format=xml

确定客户端接收什么样的内容类型;
1、Parameter策略优先确定是要返回json数据(获取请求头中的format的值)

2、最终进行内容协商返回给客户端json即可。
4、内容协商原理
●1、判断当前响应头中是否已经有确定的媒体类型。MediaType
●2、获取客户端(PostMan、浏览器)支持接收的内容类型。(获取客户端Accept请求头字段)【application/xml】
○contentNegotiationManager 内容协商管理器 默认使用基于请求头的策略
○
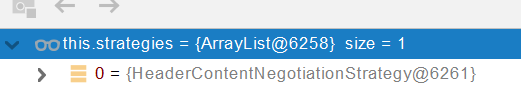
○HeaderContentNegotiationStrategy 确定客户端可以接收的内容类型
○
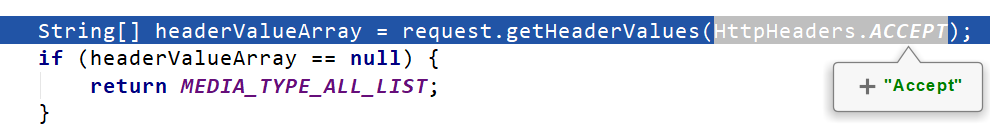
●3、遍历循环所有当前系统的 MessageConverter,看谁支持操作这个对象(Person)
●4、找到支持操作Person的converter,把converter支持的媒体类型统计出来。
●5、客户端需要【application/xml】。服务端能力【10种、json、xml】
●
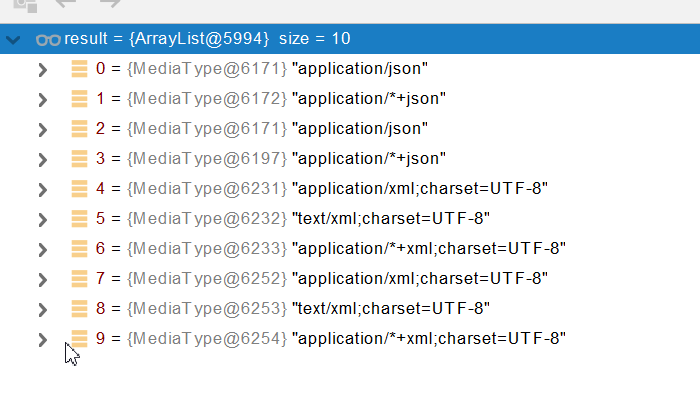
●6、进行内容协商的最佳匹配媒体类型
●7、用 支持 将对象转为 最佳匹配媒体类型 的converter。调用它进行转化 。
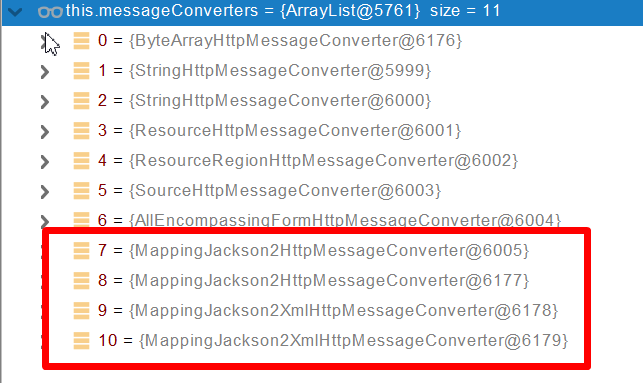
导入了jackson处理xml的包,xml的converter就会自动进来
WebMvcConfigurationSupport
jackson2XmlPresent = ClassUtils.isPresent("com.fasterxml.jackson.dataformat.xml.XmlMapper", classLoader);
if (jackson2XmlPresent) {
Jackson2ObjectMapperBuilder builder = Jackson2ObjectMapperBuilder.xml();
if (this.applicationContext != null) {
builder.applicationContext(this.applicationContext);
}
messageConverters.add(new MappingJackson2XmlHttpMessageConverter(builder.build()));
}

![[JavaEE]synchronized 与 死锁](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/b41fb650558246dc9cb065605700e4d2.png)