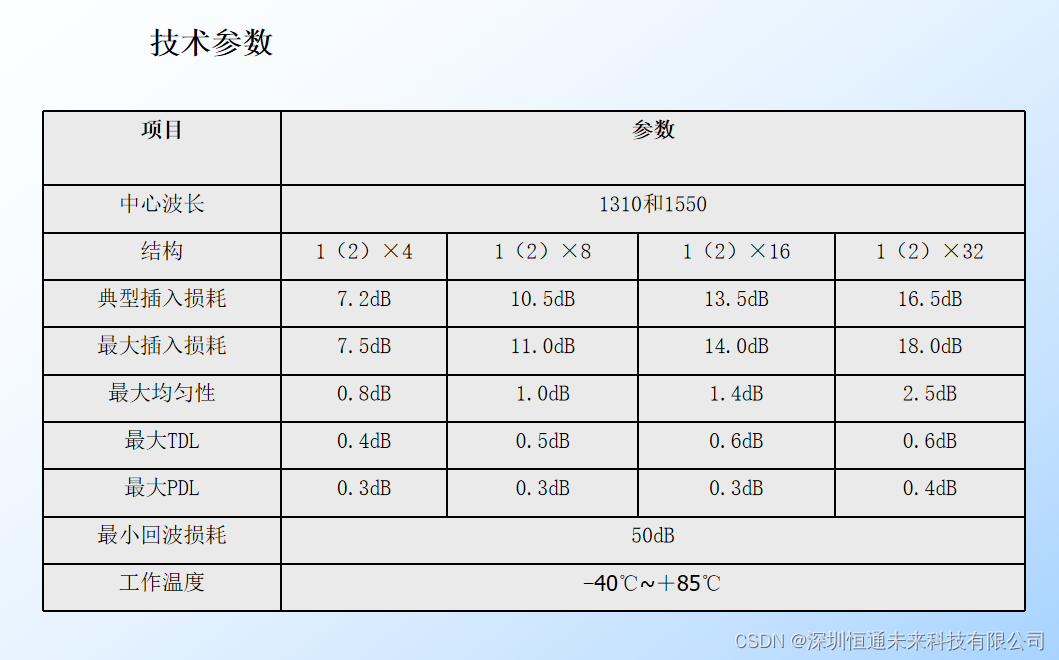
33、排序链表
给你链表的头结点 head ,请将其按 升序 排列并返回 排序后的链表 。
示例 1:
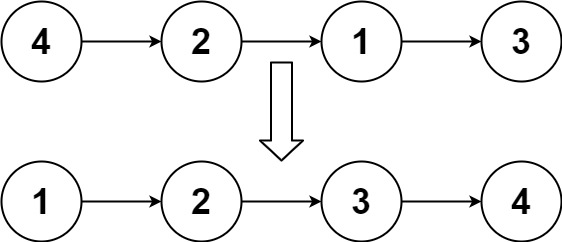
输入:head = [4,2,1,3]
输出:[1,2,3,4]
示例 2:
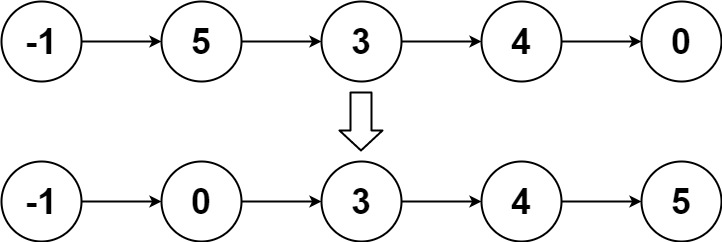
输入:head = [-1,5,3,4,0]
输出:[-1,0,3,4,5]
示例 3:
输入:head = []
输出:[]
提示:
- 链表中节点的数目在范围
[0, 5 * 104]内 -105 <= Node.val <= 105
思路解答:
- 使用快慢指针找到链表的中点,将链表分为两部分。
- 递归地对左右两部分链表进行排序。
- 合并两个已排序的链表。
def sortList(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
if not head or not head.next:
return head
def getMiddle(head):
slow = head
fast = head
while fast.next and fast.next.next:
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next.next
return slow
def merge(left, right):
dummy = ListNode(0)
current = dummy
while left and right:
if left.val < right.val:
current.next = left
left = left.next
else:
current.next = right
right = right.next
current = current.next
current.next = left if left else right
return dummy.next
# 获取链表中点,将链表分为两部分
mid = getMiddle(head)
left = head
right = mid.next
mid.next = None
# 递归地对左右两部分链表进行排序
left_sorted = sortList(left)
right_sorted = sortList(right)
# 合并两个已排序的链表
return merge(left_sorted, right_sorted)
34、合并K个升序链表
给你一个链表数组,每个链表都已经按升序排列。
请你将所有链表合并到一个升序链表中,返回合并后的链表。
示例 1:
输入:lists = [[1,4,5],[1,3,4],[2,6]]
输出:[1,1,2,3,4,4,5,6]
解释:链表数组如下:
[
1->4->5,
1->3->4,
2->6
]
将它们合并到一个有序链表中得到。
1->1->2->3->4->4->5->6
示例 2:
输入:lists = []
输出:[]
示例 3:
输入:lists = [[]]
输出:[]
提示:
k == lists.length0 <= k <= 10^40 <= lists[i].length <= 500-10^4 <= lists[i][j] <= 10^4lists[i]按 升序 排列lists[i].length的总和不超过10^4
思路解答:
- 初始化一个优先队列(heap):首先,创建一个空的优先队列(heap),用于存储链表的头部节点。将每个链表的头部节点(值和节点本身的元组)加入到优先队列中,并根据节点的值进行排序。
- 创建一个虚拟头节点和当前节点:创建一个虚拟头节点
dummy和一个指向当前节点的指针curr,初始时它们都指向虚拟头节点。 - 循环处理优先队列:在一个循环中,不断从优先队列中弹出最小的节点。将该节点接入到合并后的链表中,更新当前节点指针
curr。如果被弹出的节点有下一个节点,则将下一个节点(值和节点本身的元组)重新加入到优先队列中。 - 返回合并后的链表:最终,返回虚拟头节点的下一个节点,即为合并后的链表的头节点。
def mergeKLists(self, lists: list[Optional[ListNode]]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
setattr(ListNode, "__lt__", lambda a, b: a.val < b.val)
heap = []
for l in lists:
if l:
heapq.heappush(heap, (l.val, l)) # 将节点的值和节点本身存入堆中
dummy = ListNode(0)
current = dummy
while heap:
val, node = heapq.heappop(heap) # 从堆中取出节点的值和节点本身
current.next = node
current = current.next
if node.next:
heapq.heappush(heap, (node.next.val, node.next)) # 将下一个节点的值和节点本身存入堆中
return dummy.next
35、LRU缓存
请你设计并实现一个满足 LRU (最近最少使用) 缓存 约束的数据结构。
实现 LRUCache 类:
LRUCache(int capacity)以 正整数 作为容量capacity初始化 LRU 缓存int get(int key)如果关键字key存在于缓存中,则返回关键字的值,否则返回-1。void put(int key, int value)如果关键字key已经存在,则变更其数据值value;如果不存在,则向缓存中插入该组key-value。如果插入操作导致关键字数量超过capacity,则应该 逐出 最久未使用的关键字。
函数 get 和 put 必须以 O(1) 的平均时间复杂度运行。
示例:
输入
["LRUCache", "put", "put", "get", "put", "get", "put", "get", "get", "get"]
[[2], [1, 1], [2, 2], [1], [3, 3], [2], [4, 4], [1], [3], [4]]
输出
[null, null, null, 1, null, -1, null, -1, 3, 4]
解释
LRUCache lRUCache = new LRUCache(2);
lRUCache.put(1, 1); // 缓存是 {1=1}
lRUCache.put(2, 2); // 缓存是 {1=1, 2=2}
lRUCache.get(1); // 返回 1
lRUCache.put(3, 3); // 该操作会使得关键字 2 作废,缓存是 {1=1, 3=3}
lRUCache.get(2); // 返回 -1 (未找到)
lRUCache.put(4, 4); // 该操作会使得关键字 1 作废,缓存是 {4=4, 3=3}
lRUCache.get(1); // 返回 -1 (未找到)
lRUCache.get(3); // 返回 3
lRUCache.get(4); // 返回 4
提示:
1 <= capacity <= 30000 <= key <= 100000 <= value <= 105- 最多调用
2 * 105次get和put
思路解答:
- 使用一个哈希表(dictionary)来存储key和对应的节点。
- 使用一个双向链表来维护节点的访问顺序,链表头部表示最久未使用的节点,链表尾部表示最近访问的节点。
- LRUCache类中包含
get和put方法:get(key)方法:- 如果key存在于缓存中,从哈希表中获取对应的节点,并将该节点移动到链表尾部表示最近访问。
- 如果key不存在于缓存中,返回-1。
put(key, value)方法:- 如果key已存在于缓存中,更新对应节点的值,并将其移动到链表尾部表示最近访问。
- 如果key不存在于缓存中:
- 创建一个新节点,插入到链表尾部表示最近访问。
- 将key和对应节点存入哈希表。
- 如果插入操作导致缓存容量超过限制,移除链表头部节点,同时从哈希表中删除对应的键值对。
class ListNode:
def __init__(self, key=0, val=0):
self.key = key
self.val = val
self.prev = None
self.next = None
class LRUCache:
def __init__(self, capacity):
self.capacity = capacity
self.cache = {}
self.head = ListNode()
self.tail = ListNode()
self.head.next = self.tail
self.tail.prev = self.head
def get(self, key):
if key in self.cache:
node = self.cache[key]
self._remove(node)
self._add(node)
return node.val
return -1
def put(self, key, value):
if key in self.cache:
self._remove(self.cache[key])
node = ListNode(key, value)
self.cache[key] = node
self._add(node)
if len(self.cache) > self.capacity:
node_to_remove = self.head.next
self._remove(node_to_remove)
del self.cache[node_to_remove.key]
def _add(self, node):
prev_node = self.tail.prev
prev_node.next = node
node.prev = prev_node
node.next = self.tail
self.tail.prev = node
def _remove(self, node):
prev_node = node.prev
next_node = node.next
prev_node.next = next_node
next_node.prev = prev_node